* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download false norm - K-State Courses
Communication in small groups wikipedia , lookup
Social dilemma wikipedia , lookup
Albert Bandura wikipedia , lookup
Social commerce wikipedia , lookup
Self-categorization theory wikipedia , lookup
Social tuning wikipedia , lookup
False consensus effect wikipedia , lookup
Group dynamics wikipedia , lookup
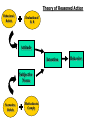
Project Wellness and The Social Norms Method for Health Enhancement and Harm Reduction (and Implications for Physical Activity Promotion) Goals of Project Wellness Correct campus misperceptions that most KState students are heavy drinkers who do not know how to use alcohol safely or responsibly and therefore cause harm to themselves or others. Reduce heavy drinking among K-State students to more moderate and safer levels. And increase use of protective behaviors. Reduce harm experienced as a result of heavy drinking and/or infrequent use of protective behaviors. Theory and Research Behind the Social Norms Method Social Norm An expected standard of behavior and belief established and enforced by a group A pattern or trait taken to be typical in the behavior of a social group People’s perception of social norms are often a good predictor of what they will say and do October 1987: Students Carrying Backpacks March 2003: Students Carrying Backpacks Sociological Theory Norms are fundamental to understanding the social order and variations in human behavior (Campbell, 1964; Durkheim, 1951) Sociological Theory Sociologist Wesley Perkins (2002) notes that “social psychologists have long argued that people tend to adopt group attitudes and act in accordance with group expectations and behaviors based on affiliation needs and social comparison processes (Festinger, 1954), social pressure toward group conformity (Asch, 1951, 1952), and the formation and acquisition of reference group norms (Newcomb, 1943; Newcomb and Wilson, 1966: Sherif, 1936, 1972) Research of W. Perkins and A. Berkowitz, Sociologists Found that college students regularly and grossly overestimated the drinking of their peers, and thus created a false norm of heavy drinking A Premise of Social Norms Method A powerful determinant of college student behavior (particularly related to drinking) is what they perceive or believe other students are doing – what is the norm Why peer influence is so powerful during college years Time of personal development Time of Forming and Norming lifetime attitudes Distance from family Availability of peers Low influence of campus adults Mechanisms that cause and perpetuate the false norm Media Attention to sensational, atypical events Images from popular culture Causes of false norm (cont.) Public conversation: “Did you see Jack at the party last night …” Vividness effect Attribution error Perception vs. Actual: False Norm at K-State? 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 Perceived Actual Dr in ks /p Ni g ar ty ht s/ w ee k How a False Norm Can Function in a Social Group Pluralistic Ignorance When one falsely believes one’s private attitudes, judgments, or behaviors are different from the majority. Individual adjusts actions to fit in; increases participation in what he/she thinks is socially desirable. Social Norms Model Alcohol-Related Harm Alcohol Use Misperceptions Alcohol Use Behaviors Harmful Consequences The Opportunity College students’ actual drinking norm is much less than what they perceive it to be Social Norms theory hypothesis If students know the true norm of their peers their own behavior will be more consistent with this behavior than with the false norm. Social Norms Model Reducing Harm Correct Information on Alcohol-Use Norms More Moderate Alcohol Use Less Harmful Consequences Applying Social Norms Method: Media Campaign Procedures Get information from target population -Survey student body Inform target population about alcohol use norms of students through consistent media messages Project Wellness 2003 Survey Data Responsible drinking is the norm at K-State! • K-Staters average about one drink per hour when they party. • Most (56%) party one or fewer nights per week. 2003 Survey Data (cont.) K-Staters know how to keep themselves and others safe when they use alcohol! Of those who drink: 88% choose to drink in places they know they will be safe 88% report they never pressure someone to drink 84% report they usually or always have a designated driver 62% report they keep track of the number of drinks they have 2003 Survey Data (cont.) Alcohol-related harm is low 98% Report they have not required medical attention because of their drinking 90% Report they have not been in a physical fight due to their drinking 85% Report they have not damaged property due to their drinking 82% Report they have not done poorly on a test or important project because of their drinking Getting information on norms Classroom Survey Media Testing Focus Groups Poster Incentive Project Freshman Focus Groups Seminar: Investigating The Student Experience VIP/Influential Students Project (Tippers) On-line Journaling & Discussion Group With Leadership Students What We Learned Consequences Students Want to Avoid Doing something embarrassing, humiliating Hangovers Late for or miss class/work Weight gain & decrease physical fitness Assault, accident, DUI: terrible, but not likely What We Learned Protective Behaviors Utilized by Students Designated drivers “Buddy system” Time management Limit money Idiosyncratic ways of “knowing” when to stop Upperclassmen learned how to drink more safely from experience What We Learned What’s Important to Students Academic success Graduating, getting desired job Physical health Healthy relationships and friendships Fun, stress relief, letting go Delivering Social Norms Messages 127 advertisements (~ 27 Fall, 12 Spring) Posters (2000, 2001) Flyers Give-away items Banner Web site Advertising in the Collegian Progression of Media Development Give basic consumption messages Advertising in the Collegian Progression of Media Development Highlight protective behaviors Advertising in the Collegian Progression of Media Development Link drinking with important issues & emphasize safer partying Advertising in the Collegian Progression of Media Development Improve the link between other health/important issues and drinking Characteristics of Social Norms Marketing Positive – Promotes, supports, and affirms the healthy behaviors of students Motivates them to use the skills they already possess Inclusive – No one is excluded from access to wellness Empowering – Encourages people to act on their own behalf and identifies what they can do to realize wellness Measuring Outcomes of Intervention Survey data Focus group data Mall intercept data Auxiliary data Qualitative interviews with KSU student services personnel Data from KSU student services Outcome measures Data on Perception of Consumption (Nights Party/Week) Perception of Nights Party 2.8 Nights Party (mean) 2.75 2.7 2.65 2.6 2.55 2.5 2000 2001 2002 Year - - - - - No media 2003 Outcome measures Data on Perception of Protective Behaviors Perception Drink in Safe Environments 80 Percent Usually or Always 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 2000 2001 2002 Year 2003 Outcome measures Harmful Consequences Harmful Consequences Percent One or More Times in Last Year 25 20 Poor Test/Project Performance 15 Damaged Property 10 5 0 2000 2001 2002 2003 Year - - - / - - - No media Other Social Norms Implementations Injunctive (Attitudinal) Norms Addressing students’ attitudes about and comfort with high risk health behaviors. Can Social Norms be used for Physical Activity Promotion? Combine Social Norms and Theory of Reasoned Action Recall: Subjective norm = perceived social pressure to to perform or not perform the behavior Normative beliefs = perceived expectations of important others Motivation to comply with normative beliefs Theory of Reasoned Action Behavioral Beliefs Evaluation of B. B Attitude Intention Subjective Norm Normative Beliefs Motivation to Comply Behavior Example: PA in Older Adults (50+) Godin and Shephard (1990): Adult population held favorable impression of physician’s attitude toward exercise. People had desire to comply with such beliefs. Possible Social Norms Marketing Strategies To increase normative beliefs that important others (physician and peers) approve of regular PA and to increase motivation to comply -Advertise normative beliefs of physicians and older adults toward PA for older adults Possible Social Norms message: Most Physicians in Sometown strongly approve of regular exercise for older adults. Most seniors in Sometown believe staying PA is important. Here are typical ways Sometown seniors stay active: Attend water aerobics at YMCA Walk the mall with mall walkers group Engage in 20-30 minutes of yard and house work Participate in movement classes at community center