* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SCIENCE 10: (7.1) ATOMIC THEORY, ISOTOPES
Gamma spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Valley of stability wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Fallout shelter wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear transmutation wikipedia , lookup
Radioactive decay wikipedia , lookup
Technetium-99m wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
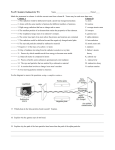
SCIENCE 10: (7.1) ATOMIC THEORY, ISOTOPES AND RADIOACTIVE DECAY Name: Date: Block: (Textbook Reference pp. 286-301 in BC Science 10) Natural background radiation: __________________________ _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ It has the ability to interact with an atom and turn it into an _______ Radiation: __________________________________________ _______________________________________________ When atoms lose high-energy particles and waves, ions or even new atoms can be formed. High-energy waves and particles are called radiation when they leave the atom. Radioactivity: _______________________________________ _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ Being exposed to radioactive materials can be beneficial or harmful. Beneficial: __________________________________ Harmful:____________________________________ ISOTOPES AND MASS NUMBER Isotopes:__________________________________________ _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________. Remember that an atom of an element will have the same number of protons and electrons (___________________) Not all atoms of an element have the same number of neutrons (_______________). Remember the mass number tells you the total number of __________ and _______________ in an isotope. Isotopes of an element have the same __________ and same ___________ _________________ Mass number = ______________ + _____________ Atomic mass = ____________________________ _____________________________________. REPRESENTING ISOTOPES http://www.colorado.edu/physics/2000/isotopes/index.html Isotopes are written using standard atomic notation. The standard atomic symbol (or nuclear symbol) for the following isotopes of potassium would be: o Potassium-39 o Potassium-40 o Potassium-41 In nature, most elements are found as a mixture of isotopes. http://www.chem4kids.com/files/atom_isotopes.html Complete the Practice Problems on p. 291 RADIOACTIVE DECAY Radioactive decay: ___________________________________ _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ Radioactive atoms release energy until they become __________, often as different atoms. Ex. Uranium -238 undergoes 14 different radioactive decay steps before forming stable lead-206. An element may have only certain isotopes that are radioactive. Isotopes that are capable of radioactive decay are called _______________________. THREE TYPES OF RADIATION Rutherford identified three types of radiation using an electric field. Positive _______________________ were attracted to the negative plate. Negative ______________________ were attracted to the positive plate. Neutral __________________ did not move towards any plate. ALPHA RADIATION Alpha radiation is a stream of ________ particles. They are _______________ charged, and are the _______ massive of the radiation types. Alpha particles are essentially the same as __________ atoms. Alpha particles are represented by the symbols: Because it has two protons, it has a charge of ___ The release of alpha particles is called __________ ____________. Alpha particles are _______ and penetrate materials much _______ than the other forms of radiation. A sheet of __________ will stop an alpha particle. Example: ***Note: The equation is balanced! (The sum of the atomic numbers and the sum of the mass numbers are equal on both sides of the arrow. Also the product nucleus has an atomic number that is lower by two and a mass number that is lower by four due to the alpha particle) Complete the Practice Problems on p. 295 BETA RADIATION A beta particle is an _____________ and is _______________ charged. Beta particles are represented by the symbols: Electrons are very tiny, so beta particles are assigned a mass of ____. Since there is only an electron, a beta particle has a charge of _____. Beta decay occurs when a ______________ changes into a ___________+ an _______________. The proton stays in the nucleus, and the electron is ________________. It takes a thin sheet of ___________________ to stop a beta particle. Example: ***Note: The equation is balanced! (The sum of the atomic numbers and the sum of the mass numbers are equal on both sides of the arrow. Also the product nucleus has an atomic number that is greater, making it an atom of the next higher element and a mass number that equal to the reactant because the beta particle emitted was an electron) Complete the Practice Problems on p. 296 GAMMA RADIATION Gamma radiation is a _______ of high-energy, short-wavelength radiation. Gamma radiation has ______ charge and _____ mass, and is represented by the symbol Gamma radiation is the _____________-energy form of electromagnetic radiation. It takes thick blocks of _______ or ___________ to stop gamma rays. Gamma decay results from __________ being released from a high-energy nucleus. Often, other kinds of radioactive decay will also release gamma radiation. Uranium-238 decays into an alpha particle and also releases gamma rays. Example: ***Note: The equation is balanced! (The sum of the atomic numbers and the sum of the mass numbers are equal on both sides of the arrow. Also the product nucleus has an atomic number and a mass number that are equal to the reactant because gamma decay involves energy, not particles.) SUMMARY: Type ALPHA BETA GAMMA RADIATION RADIATION RADIATION ALPHA DECAY BETA DECAY GAMMA DECAY Symbol Particle or Ray Description of Radiation Charge Relative mass Chemical symbol Can be stopped by: Particle emitted Change in mass of starting nucleus. Change in atomic number of starting nucleus. Remember the following rules when you write a nuclear equation: 1. _____________________________________________________ 2. _____________________________________________________ More Practice: Complete p. 301 #4, 7, 11-13