* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 23-3 Stems
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
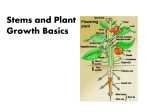
23–3 Stems I) ______________ Structure and Function Stems have ________________ important functions: • they produce ____________________, branches and _________________ • they hold leaves up to the ___________________ • they transport substances between ______________ and _________________ A) Stems make up an essential part of the water and __________________ transport systems of the plant. B) Xylem and __________________ form continuous tubes from the roots through the stems to the ___________________. 1) This allows water and ___________________ to be carried throughout the plant. C) Stems are surrounded by a layer of ______________ cells that have thick cell walls and a _____________ protective coating. 1) Leaves attach to the stem at structures called _________________. (a) The regions of stem between the nodes are ______________________. (b) Small ____________ are found where leaves attach to __________________. • Buds contain _____________________ tissue that can produce new stems and leaves. D) In larger plants, stems develop ________________ tissue that helps support leaves and _____________________. II) Monocot and _________________ Stems A) The arrangement of __________________ in a stem differs among _______________ plants. PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com 1) In _________________, vascular bundles are _________________ throughout the stem. In ________________ and most gymnosperms, vascular bundles are arranged in a ____________________ pattern. B) ___________________ Stems 1) Monocot stems have a distinct _________________, which encloses vascular bundles. 2) Each ___________________ bundle contains ______________ and phloem tissue. 3) Vascular bundles are _________________ throughout the __________________ tissue. 4) Ground tissue consists mainly of ______________________ cells. C) _________________ Stems 1) Dicot stems have vascular bundles arranged in a ________________ pattern. 2) The ____________________ cells inside the vascular tissue are known as ___________. 3) The parenchyma cells outside of the vascular tissue form the _____________ of the stem. III) _____________________ Growth of Stems A) All seed plants undergo ________________ growth, which is an increase in _________________. B) For the entire life of the plant, new _____________ are produced at the tips of roots and shoots. C) Primary growth of stems is produced by cell divisions in the apical _________________. It takes place in all seed plants. IV) ____________________ Growth of Stems A) The method of growth in which stems increase in ________________ is called secondary growth. PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com 1) In ____________________ and _______________, secondary growth takes place in the __________________ cambium and _______________ cambium. (a) Vascular cambium produces vascular ________________ and increases the ___________________ of stems over time. (b) Cork cambium produces the outer __________________ of stems. • The addition of new tissue in these cambium layers increases the thickness of the stem. B) Formation of the Vascular _______________________ 1) Once ___________________ growth begins, the vascular cambium appears as a thin layer between the ______________ and ________________ of each vascular bundle. 2) The vascular cambium divides to produce _____________ cells toward the _______________ of the stem and phloem cells toward the ______________. 3) These different tissues form the ____________ and wood of a mature stem. C) Formation of _______________ 1) Wood is actually layers of ______________. These cells build up year after year. 2) As woody stems grow ________________, older xylem cells near the center of the stem no longer conduct ______________. (a) This is called __________________. Heartwood supports the tree. (b) Heartwood is __________________ by sapwood. (c) ___________________ is active in water and mineral transport. D) Formation of Bark 1) On most trees, bark includes all of the tissues _________________ the vascular cambium — phloem, the ____________ cambium and cork. 2) The ___________________ cambium produces new xylem and phloem, which increase the width of the stem. 3) The phloem transports _______________ produced by __________________. PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com 4) The cork cambium produces a protective layer of ____________________. 5) The cork contains old, nonfunctioning __________________ that protects the tree. PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com