* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Aplastic Anemia
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency wikipedia , lookup
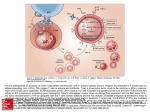
Aplastic Anemia Tissue Conference 1/19/00 Brad Kahl, MD Pancytopenia • Reduction of counts in all three cell lines • Differential Diagnosis – aplastic anemia – myelodysplasia – marrow replacement • leukemia, lymphoma, carcinoma, myelofibrosis – B12, folate – chemotherapy induced Pancytopenia • Differential Diagnosis continued – – – – splenomegaly (any cause) PNH SLE Congenital • Fanconi’s, Schwamann-Diamond, Folate uptake def Pancytopenia • Presentation varies with degree of cytopenia – anemia – thrombocytopenia – neutropenia fatigue bruising/bleeding infection • Approach – history • constitutional symptoms, pain, early satiety, etc... • diet, EtOH, exposures, occupation Pancytopenia • Approach – PE • nodes, spleen, sensory, portal htn – Labs • B12, folate, LFT’s, PNH, ANA • view smear (macrocytosis, megaloblastosis, tear drops, nuc RBC’s, malignant cells) • abdominal imaging • bone marrow evaluation Aplastic Anemia • Bone Marrow Failure – WHY?????????? • Stem cell defect (seed) • Stromal cell defect (soil) • Growth Factor defect (fertilizer) – Evidence suggests that majority of cases of idiopathic AA are due to immune suppression of the hematopoietic stem cell Aplastic Anemia Classification • Direct Toxicity – Iatrogenic (radiation, chemotherapy) – Benzene – Drug metabolites • Immune Mediated – – – – Drug metabolites transfusion associated hepatitis associated idiopathic Aplastic Anemia Pathophysiology • Evidence for an immunological basis arose from observations after BMT – unexpected improvement of pancytopenia in some patients after allogeneic graft failure – successful BMT of identical twins generally requires some sort of immunosuppressive conditioning regimen Aplastic Anemia Pathophysiology • Evidence for stem cells (seed) as targets – in vitro colony forming assays are used to define the stem cell compartment – two papers in 1996 showed profound deficits in the stem cell population in patients with AA – at the time of clinical presentation the absolute number of stem cells is < 1% of normal Aplastic Anemia Pathophysiology • What about the stroma (soil) and growth factors (fertilizer)? – successful BMT implies intact stroma since it is not replaced in the transplant – laboratory studies have shown the stroma of AA patients is able to support normal stem cell growth – stromal cells of AA patients tend to make increased levels of several growth factors (EPO, TPO, G-CSF) – clinical studies using factor replacement haven’t worked Aplastic Anemia Pathophysiology • Laboratory Evidence for Immune Destruction of Hematopoietic Stem Cells – mononuclear cells from blood and marrow of AA patients suppress hematopoietic colony formation by normal marrow stem cells – if selectively remove T cells from the sample, generally improve in vitro colony formation Aplastic Anemia Pathophysiology • What are the T cells doing? – Direct cellular cytotoxicity • blood and marrow of AA patients contain increased numbers of activated cytotoxic lymphocytes • the number and activity of these cells decreases after successful treatment with ATG Aplastic Anemia Pathophysiology • Cytokines – T cells of AA patients overproduce both IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha – both of these cytokines inhibit colony formation in vitro • IFN-gamma induces nitric oxide synthase (NOS) and production of nitric oxide (NO) • both induce expression of Fas receptor on CD34+ cells and activation of this receptor by its ligand induces apoptosis – both appear to inhibit mitosis • IFN-gamma increases IFN regulatory factor 1 which inhibits transcription of cellular genes and entry into the cell cycle Aplastic Anemia Pathophysiology Aplastic Anemia Pathophysiology • Inciting Events – much less clear, most cases--no clue – a few cases clearly associated with a non-A, non-B, non-C, non-G hepatitis • severe pancytopenia 1-2 months after an apparent viral hepatitis • patients tend to have a marked activation of cytotoxic lymphocytes and tend to respond favorably to immunosuppressive therapy Aplastic Anemia Pathophysiology • Drugs – – – – – implicated in 15-25% cases (difficult to study) no animal model some cases may be a direct toxic effect some cases appear immune mediated in general patients have similar characteristics as idiopathic AA and respond similarly to immunosuppression Aplastic Anemia Treatment • Options – BMT from donor vs. immunosuppression with ATG, CSA, or ATG/CSA combination – steroids, androgens generally ineffective • Trend towards separating severe AA and non-severe AA in current clinical trials Aplastic Anemia Treatment • Severe Aplastic Anemia Criteria – blood: • neutrophils < 500/mm3 • platelets < 20k • retics < 1% (corrected) – marrow • severe hypocellularity • moderate hypocellularity with hematopoietic cells representing < 30% of residual cells • need 2/3 blood and one marrow criteria Aplastic Anemia Treatment • Non-severe AA (Blood, April 99) – patients randomized to CSA vs. ATG/CSA – Overall Response Rate at 6 months • CSA 46% ATG/CSA 74% – Similar early toxicity/infections P=.02 Aplastic Anemia Treatment • Severe AA (Ann Int Med 1997) • Allo BMT vs. Immunosuppression ORR 15 Yr OS allogeneic BMT 89% 69% Immunosuppression 44% 38% – 40% BMT patients clinically extensive chronic GVHD – 1/227 receiving immunosuppression got ATG/CSA – 50/227 received ATG + mismatched bone marrow Aplastic Anemia Treatment • Severe Aplastic Anemia – NEJM 1991 ATG/Pred ATG/Pred/CSA ORR 31% 65% – Blood 1992 ATG/LDM/oxymethalone ATG/HDM/oxymetholone 36% 48% – Blood 1995 ATG/CSA 78% Aplastic Anemia Treatment • Future – High Dose Cyclophosphamide vs. ATG – Addition of MMF to ATG/CSA combinations – ? allo BMT vs optimal immunosuppression? Aplastic Anemia Summary – idiopathic AA appears to be an AI disorder directed against hematopoietic stem cells – mediated by cytotoxic T cells and cytokines – allo BMT is the gold standard treatment – intensive immunosuppressive therapy has improved the outlook for patients ineligible for BMT due to age or lack of a suitable donor – expect further refinements in therapy as the pathophysiology is further elucidated























![Aplastic Anemia [PPT]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000248384_1-5c39883593ffaaa864ec61d1eb51b312-150x150.png)