* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mapping Fire Regimes Across Time and Space:
Climatic Research Unit documents wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change denial wikipedia , lookup
Climate resilience wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
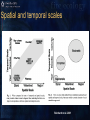
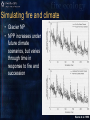
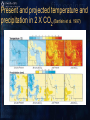
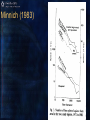
Fire-climate-vegetationtopography-land use Part II: Simulation models as research tools Models of vegetation succession following fire Reinhardt et al. 2001 Simulation models as a research tool • With multiple runs, we can conduct replicated, controlled experiments with novel treatment conditions • One of the few research tools that integrate both space and time • Our uncertainty is higher for the coarse temporal and spatial scales where models are the most useful • Models are abstractions of reality Spatial and temporal scales Reinhardt et al. 2001 Simulating fire and climate • Glacier NP • NPP increases under future climate scenarios, but varies through time in response to fire and succession Keane et al. 1998 Landscape composition • Landscape composition would be greatly affected by both fire occurrence and climate change • Is there synergy between fire and climate? Keane et al. 1998 Present and projected temperature and precipitation in 2 X CO2 (Bartlein et al. 1997) Implications of 2 X CO2 climate for some species ranges (Bartlein et al. 1997) What we’ve learned (Part I) • Climate is changing under human influence • Fire regimes have changed in response to both climate and human action • Fire regimes reflect both the physical and socio-political environment • Climate influences lightning ignitions, as well as fire behavior and effects, • The interrelationships between fire, climate, vegetation, land use, and topography are complex and scaled. What we’ve learned (Part I) • The effects of climate change on vegetation will be mediated through fire and other disturbances • Altered fire regimes will be important determinants of rates and directions of ecosystem change, • …and they have powerful feedback to global climate change through their influence on carbon and nitrogen cycles Fire management in a changed climate • Protecting life and property • Suppression • Pre-suppression • Fuels management • Managing wildlife habitat • Prescribed burning • Ecological restoration • Prescribed burning and other management activities • Fire as a natural process • Lightning and human ignitions Minnich (1983) Keeley et al. (1999)