* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Rise of the Roman Republic
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Factorum ac dictorum memorabilium libri IX wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Conflict of the Orders wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Legislative assemblies of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Executive magistrates of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Roman Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Demography of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
Early Roman army wikipedia , lookup
Treaties between Rome and Carthage wikipedia , lookup
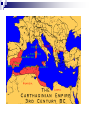
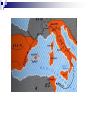
Rise of the Roman Republic I. Geography of Italian Peninsula Mountainous Alps (north) Apennines (backbone) East = poor West = attractive Proximity to Mediterranean Sea Easy access MILITARY!!! Fertile land, great harbors!!! II. Early History of Rome Legend of Romulus & Remus 1200 BCE: Indo-Euros. invaded peninsula 1000 BCE: Latins founded settlements on 7 Hills (Palatine Hill) Overlooked Tiber River Became Rome Strategic location Farming-based society A. The Etruscans 8th cent. BCE: from Anatolia Lived north of Tiber River 6th cent. = moved south, conquered Rome Set up monarchy Contributed to Roman civ. Arch Drained swamps Forum Phoenician alphabet Roman Forum Public meeting place and the heart of Roman political life Examples of Etruscan art Note the Greek alphabet Romans borrowed Etruscan building techniques. B. The Greek Influence 750-500 BCE: Greek colonization Southern Italian city-states Syracuse & Naples Spread Greek culture into Italy! Art, Mythology, & Religion III. Establishing the Republic 509 BCE: overthrow of Etruscan monarchy Tarquin the Proud (tyrant) Est. a republic (lasted almost 500 yrs.) res publica = “public affairs” A. Roman Govt. 3 Groups: The Senate (aristocratic) Popular Assemblies (democratic) The Magistrates/Consuls (monarchy) 1. The Senate (aristocratic) Most important & powerful of 3 bodies 300 members (upper class) Senate seats for life (continuity) Controlled foreign policy & public funds Elected dictator (for times of crisis) Absolute power (make laws & command army) 2. Popular Assemblies (demo.) Citizens voted on laws & elected officials Had 10 tribunes – protected interests of plebeians—could veto Senate 3. The Magistrates (monarchy) 2 consuls – 1 yr. terms (no reelection for 10) Commanded army & directed govt. Each could veto the other Checks & balances Praetors—8 judges (1 year term) B. Social Structure Patricians consuls, senators, assembly 10% of pop. Plebeians farmers, merchants, laborers, artisans Roman laws were unwritten C. Plebeian Struggle of Reform Advantage of Plebeians? Will not fight w/out reforms!! 494 BCE: Council of Plebeians (Tribal Assembly) Elected 10 tribunes Could veto Senate or consuls 451 BCE: Twelve Tables Advertised Roman law Posted in Forum Est. that ALL free citizens had protection of the law Plebeians did not change govt. much Patricians exercised most power Roman politics = undemocratic “the people were not to govern, but to be governed” Senate ruled w/great authority IV. Extending the Republic By 265 BCE: Romans controlled all of Italy south of Rubicon River A. The Army Conscription for adult male citizens Legion (Legionaires) Auxilia (non-citizens) B. Wise Policies Romans shared citizenship w/conquered peoples = ensured loyalty Made alliances w/distant cities Remained independent Provided military assistance to Rome C. Religion Spirits inhabit everything Identified Roman gods w/Greek gods Zeus = Jupiter Hera = Juno Poseidon = Neptune Aphrodite = Venus Hades = Pluto V. Rome vs. Carthage Carthage = powerful city on N. Af. coast Empire spanned the western Med. Both were expansionistic Carthage feared Rome would take Sicily Rome feared Carthage would stand in way Fought 3 wars (264-146 BCE) Punic Wars A. First Punic War (264 BCE) Rome built up navy Used land tactics at sea 241: Rome prevailed Indemnity (war reparations) B. Second Punic War (218 BCE) Hannibal (Carthaginian General) Won numerous victories (Romans retreated) Had no siege equipment to sack cities Rome’s allies remained loyal Scipio Invaded Carthage Hannibal went home 202 BCE: Battle of Zama – defeat of Hannibal Ensured supremacy of Greco-Roman civ. C. Third Punic War Lasting hatred towards Carthage 149 BCE: declare war on Carthage!!! 146 BCE: Carthage fell, was burned, inhabitants enslaved Rome = dominates W. Med. 197 BCE: Rome defeated Macedonia Took control of Greek cities 133 BCE: Roman supremacy over Med. completed