* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 9/06 Pedigrees and Human Genetics
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Human–animal hybrid wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of autism wikipedia , lookup
Biology and sexual orientation wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Dual inheritance theory wikipedia , lookup
Genome-wide association study wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Irving Gottesman wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
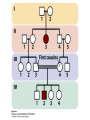
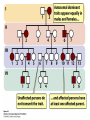
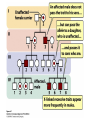
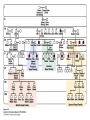
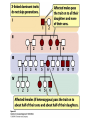
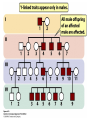
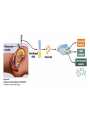
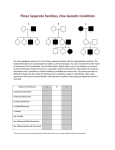
Chapter 6 Outline • 6.1 The Study of Genetics in Humans Is Constrained by Special Features of Human Biology and Culture, 135 • 6.2 Geneticists Often Use Pedigrees to Study the Inheritance of Characteristics in Humans, 136 • 6.3 Analysis of Pedigrees Requires Recognizing Patterns Associated with Different Modes of Inheritance, 136 • 6.4 The Study of Twins Can Be Used to Assess the Importance of Genes and Environment on Variation in a Trait, 142 Chapter 6 Outline • 6.5 Adoption Studies Are Another Technique for Examining the Effects of Genes and Environment on Variation in Traits, 145 • 6.6 Genetic Counseling Provides Information to Those Concerned about Genetic Diseases and Traits, 146 • 6.7 Genetic Testing Provides Information about the Potential for Inheriting or Developing a Genetic Condition, 147 • 6.8 Comparison of Human and Chimpanzee Genomes Is Helping to Reveal Genes That Make Humans Unique, 151 6.1 The Study of Genetics in Humans Is Constrained by Special Features of Human Biology and Culture • Special features: • Controlled mating is not possible • Long generation time • Small family size 6.2 Geneticists Often Use Pedigrees to Study the Inheritance of Characteristics in Humans • Pedigree: pictorial representation of a family history, a family tree that outlines the inheritance of one or more characteristics • Proband: the person with whom the pedigree is initiated 6.3 Analysis of Pedigrees Requires Recognizing Patterns Associated with Different Modes of Inheritance • Autosome Recessive Traits 6.3 Analysis of Pedigrees Requires Recognizing Patterns Associated with Different Modes of Inheritance • Autosomal Dominant Traits 6.3 Analysis of Pedigrees Requires Recognizing Patterns Associated with Different Modes of Inheritance • X-Linked Recessive Traits 6.3 Analysis of Pedigrees Requires Recognizing Patterns Associated with Different Modes of Inheritance • X-Linked Dominant Traits 6.3 Analysis of Pedigrees Requires Recognizing Patterns Associated with Different Modes of Inheritance • Y-Linked Traits 6.4 The Study of Twins Can Be Used to Assess the Importance of Genes and Environment on Variation in a Trait • Dizygotic twins = non-identical twins • Monozygotic twins = identical twins • Concordant trait: the trait shared by both members of a twin pair • Concordance: the percentage of twin pairs that are concordant for a trait 6.4 The Study of Twins Can Be Used to Assess the Importance of Genes and Environment on Variation in a Trait • Twin Studies and Obesity 6.6 Genetic Counseling Provides Information to Those Concerned about Genetic Diseases and Traits • Genetic counseling: provides information related to hereditory conditions 6.8 Comparison of Human and Chimpanzee Genomes Is Helping to Reveal Genes That Make Humans Unique • Microcephalin 1 to microcephalin 6 regulates human brain size. • FOXP 2 regulates human speech.