* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Earthquakes and Seismic Waves
2009–18 Oklahoma earthquake swarms wikipedia , lookup
Earthquake prediction wikipedia , lookup
Reflection seismology wikipedia , lookup
1880 Luzon earthquakes wikipedia , lookup
Seismic retrofit wikipedia , lookup
1992 Cape Mendocino earthquakes wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
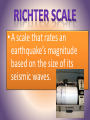
• Is the shaking that results from the sudden movement of rock along a fault. • Is the shaking that results from the movement of rock beneath Earth’s surface • The forces of plate movement causes earthquakes. Plate movement produces stress in Earth’s crust, adding energy to rock and forming faults. Stress increases along a fault until the rock breaks. An earthquake begins. In seconds, the large amount of stored energy is released. • The point beneath Earth’s surface where rock breaks under stress and causes an earthquake • The point on Earth’s surface directly above an earthquake’s focus • There are three types of seismic waves: P waves, S waves, and Surface Waves. • An Earthquake sends out two types of waves from its focus: P waves and S waves. When these two reach the surface at the epicenter, surface waves develop. • Also known as Primary Wave • A type of seismic wave that compresses and expands the ground like an accordion. P waves can travel through solids and liquids • Also known as Secondary Waves or Shear waves • A type of seismic wave that moves the ground surface up and down or side to side S waves can not travel through liquids • A type of seismic wave that forms when P waves and S waves reach Earth’s surface. Surface waves can be shakers (side to side) or rollers (up and down) • A Scale that rates earthquakes according to their intensity and how much damage they cause at a particular place. Twelve steps of the Mercalli scale (pg 185). The same earthquake can have different Mercalli ratings because intensity varies in different locations. • A scale that rates an earthquake’s magnitude based on the size of its seismic waves. • A device that records ground movements caused by a seismic waves • The record of an earthquake’s seismic waves produced by a seismograph • The measure of an earthquake’s strength based on seismic waves and movement along faults. • A scale that rates an earthquake by estimating the total energy released. Video • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Yukp0bP kQxs • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_YLjIvJXh pg