* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Metabolism
Survey
Document related concepts
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
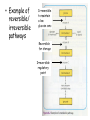
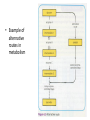
Cell Metabolism Higher Human Biology Unit 1 – Section 6 Metabolic Pathways Learning Intentions By the end of this section you should be able to: • State what is meant by cell metabolism • State that metabolic pathways are controlled at each step by enzymes and can also be controlled by intracellular and extracellular signalling molecules. • Describe the difference between anabolic and catabolic processes, and explain how metabolic pathways can be reversible and irreversible steps as well as alternative processes. • The key role played by specific enzymes in regulating rates of reactions. What is Cell Metabolism? • This is the collective term for all chemical reactions that take place cell. These are usually connected integrated into pathways that catalysed by enzymes. the in a and are Metabolic Pathways • There are two types of metabolic pathways: • Catabolic – these bring about the breakdown of complex molecules to simpler ones, usually releasing energy and often producing building block molecules • E.g. aerobic respiration. • Anabolic – these bring about the synthesis of complex molecules from simpler building block molecules and as such require energy. E.g. protein synthesis • E.g. protein synthesis • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iIW5SPY-vwI The two types of metabolic pathway Carbon Dioxide e.g. Amino Acids ATP Energy + Energy Water Catabolic – Aerobic Respiration Glucose + Oxygen Respiration Catabolic Energy ENERGY TRANSFER ADP + Anabolic – e.g. Protein synthesis Energy Protein molecule Pi Protein Synthesis Anabolic Synthetic (anabolic) reactions Another example: glucose-1-phosphate phosphorylase starch This reaction requires the input of energy to proceed (anabolic reaction). Breakdown (catabolic) reactions Another example: starch amylase maltose This reaction releases energy (catabolic reaction). What else do you need to know? • Metabolic pathways can have reversible and irreversible steps. AND • Alternative pathways may exist that can bypass steps in a pathway. • Example of reversible/ irreversible pathways Irreversible to maintain a low glucose conc Reversible for storage Irreversible regulatory point • Example of alternative routes in metabolism