* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pharmacokinetics
Orphan drug wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical marketing wikipedia , lookup
Compounding wikipedia , lookup
Adherence (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Medical prescription wikipedia , lookup
Theralizumab wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Electronic prescribing wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
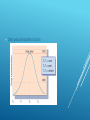
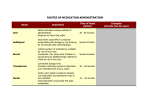
PHARMACOKINETICS ABSORPTION→DISTRIBUTION→METABOLISM→EXCRETION Chapter 26 – Fundamentals NUR 152 Denise Turner, MS-N.Ed, CCRN, RN Overview of the principles of pharmacotherapy Pharmacodynamics/pharmacokinetics Discuss half life and therapeutic levels Types of medication effects OBJECTIVES • Pharmaceutical Factors – Rate of dissolution – Lipid/water solubility - pH – Route • Clinician/Patient Factors – Blood flow – Route – Competition ABSORPTION PG 609/614 FIGURE 26-3 Elevation of gastric pH (makes it more alkaline) by antacids – Increases the absorbance of basic drugs; decreases that of acidic drugs • Laxatives – Increase peristalsis and decrease GI transit time PHARMACOKINETIC EFFECTS ON ABSORPTION Blood Flow – Target organ/area Protein binding Free drugs-body can use the “free or unbound” drug DISTRIBUTION (TRANSPORTATION) PG 614 Remaining unbound drug is chemically inactivated, broken into metabolites and excreted once it reaches its target organ and is finished doing its job First Pass Effect: Effectively, the drug has been metabolized before it ever reaches the systemic circulation and/or its target organ METABOLISM-BIOTRANSFORMATION PG 615 In order for a drug to “stop” performing its actions it must be excreted. Metabolism is the start of this process (which is dependent on “functioning” organs of metabolism). Liver, lungs, kidneys, GI tract EXCRETION PG 615 Decreased function in any of the areas of excretion can cause delays: Renal disease Dehydration/decreased fluid intake Increased creatinine Liver/GI tract disorders/probs Increased peristalsis = ↑ Decreased peristalsis Decreased activity, diet = ↑ Lungs disorders/probs EXCRETION DELAYS The client has been on a low-protein diet. This will most likely affect which pharmacokinetic process? a. Absorption b. Excretion c. Distribution d. Metabolism CLICKERCHECK Correct answer: C A low-protein diet may lead to an inadequate level of plasma proteins, which will affect availability of “free” drug. CLICKERCHECK (CONT’D) The nurse is having difficulty deciphering the medication prescription written by the provider. What is the best strategy to clarify the information? a. Ask the patient what medication the provider prescribed. b. Call the pharmacist and ask him or her to read the prescription. c. Ask the nurse who knows the provider’s handwriting to read the prescription. d. Call the provider and ask him or her to clarify the prescription. CLICKERCHECK Correct answer: D All other answers increase the risk of a medication error. CLICKERCHECK (CONT’D) When administering a drug via a parenteral route, the drug would be absorbed fastest if given per the IM route. a. True b. False CLICKERCHECK Correct answer: B Absorption refers to the “movement” of the drug from the site of administration into the bloodstream. Therefore, the IV, parenteral route leads to “instant” absorption. CLICKERCHECK (CONT’D) PHARMACODYNAMICS Pg 618 Onset, peak, and duration of action Agonists and antagonists Two Drug Agonists Attach to the Receptor Site. The drug agonist that has an exact fit is a strong agonist and is more biologically active than the weak agonist. Therapeutic Effects The desired effect we are expecting Side Effects Unintended but we are aware they can happen If the S/E is pronounced we will stop or decrease the dose Adverse Reactions: Harmful, not expected and unpredictable Usually end up stopping the medication Depending on reaction, may require contacting the FDA and filing a report PG 619 Toxic reactions: Must monitor therapeutic levels on some medications Nurses need to know what s/s of toxicity are for particular medications Allergic reactions: Blood levels are too high or not therapeutic Rash, anaphylaxis Idiosyncratic: Abnormal or odd response Sensitivity or an opposite effect of the therapeutic response expected. Cumulative effects: Client may not be able to metabolize or excrete a medication effectively with end result of too much medication in their system or toxicity.