* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
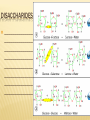
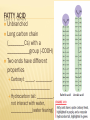
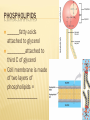
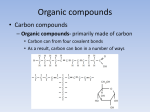
Unit 1 FOUNDATIONS OF BIOLOGY Biochemistry is the branch of science that explores the ____________processes within and related to ________organisms. It is a laboratory based science that brings together biology and chemistry. By using chemical knowledge and techniques, biochemists can understand and solve ______________ problems Chapter 3 BIOCHEMISTRY SECTION 1 CARBON COMPOUNDS Objectives Distinguish between organic and inorganic compounds Explain the importance of carbon bonding in biological molecules Identify functional groups in biological molecules Describe how the breaking down of ATP supplies energy to drive chemical reactions SECTION 1 Vocabulary Organic compound Functional group Monomer Polymer Vocabulary Macromolecule Condensation reaction Hydrolysis Adenosine triphosphate CARBON COMPOUNDS Water is primary medium for life… Living organisms’ molecules are based on the element ______________ Can form _______and __________molecules CARBON BONDING Organic compounds: ______________________ ________________________________________ Most matter in living orgs (not water) Inorganic compounds: ____________________ Few exceptions CARBON BONDING __ electrons in outermost energy level Stable when… _____________________ _____________________ Carbon can bond with other carbon atoms forming ____________________ _____________________ ____________________ CARBON BONDING 1 line represents a _______________________: ___________________________________________ 2 lines represents a ______________________ ___________________________________________ 3 lines represents a ______________________ ___________________________________________ FUNCTIONAL GROUPS Clusters of atoms that influence the ___________of the molecule they compose __________________________(________________) LARGE CARBON MOLECULES Carbon compounds are made of smaller units – ___________that bind together to form ____________(molecule made of repeated, linked units) Macromolecule: ______________________ Monomers link together through a process called _______________________________. CONDENSATION REACTION Each time a monomer is added to a polymer, a __________ molecule is released. Two monomers become linked by a _______________________ One monomer releases a __________ion (H+) and the other releases a __________ion (OH-), these two ions combine to form ___________ HYDROLYSIS REACTION _______________________________________ Water mol breaks bond between monomers Reverse of C.R. ENERGY CURRENCY Life requires energy Energy is available in compounds that ______________________________________ Covalent bond When covalent bond breaks, _______________________ HOMEWORK SECTION 1 Answer Section 1 Review in your homework book Answer all questions Start on a new page Please write the date at the top Heading: Carbon Compounds SECTION 2 MOLECULES OF LIFE Objectives Distinguish between monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides Explain the relationship between amino acids and protein structure Describe the induced fit model of an enzyme action Compare the structure and function of each of the different types of lipids Compare the nucleic acids of DNA and RNA SECTION 2 Vocabulary Carbohydrate Monosaccharide Disaccharide Polysaccharide Protein Amino acid Peptide bond Polypeptide Enzyme Substrate Vocabulary Active site Lipid Fatty acid Phospholipid Wax Steroid Nucleic acid DNA RNA Nucleotide MOLECULES OF LIFE 4 main classes of organic compounds essential to life: ______________ ______________ ________________ __________________ Made in different ratios of ________________ Each class has different __________________ CARBOHYDRATES Organic compounds Made of ____________ in a ratio __________ Number of carbons vary Some used for _________ Some used as __________________ _______________, _________________, ___________________ MONOSACCHARIDES _______________________________ Simple sugar Contains C,H,O in ratio 1:2:1 General formula ___________________ n = any whole number _____________ Example: (CH2O)6 → C6H12O6 Most common: _________, _______, _________ Glucose=main source of _____________ Fructose=found in _____________ Galactose=found in ____________ MONOSACCHARIDES Compounds with the same chemical formula but different structural forms are called isomers. DISACCHARIDES _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ POLYSACCHARIDES Complex molecule ____________________________________ Animals stores glucose in a polysaccharide called _______________ (100s of glucose mols strung together) Plants store glucose in a polysaccharide called ________________ Plants also make cellulose (a polysaccharide which gives strength) (1000s of glucose mols) POLYSACCHARIDES PROTEINS Organic compound Made mostly of ___________ Monomer: ________________ Proteins are made by linking monomers (amino acids) ________, _________, _________, ___________ are made mostly of proteins AMINO ACIDS 20 different amino acids, shares a basic structure Each contains: Central C atom, covalently bonded to 4 other atoms/functional groups _______________________________ ________________________________ ________________________________ ________________________________ AMINO ACIDS DIPEPTIDES ________________________________________ ____________________(__________________) POLYPEPTIDES Very long chain of ________________ Proteins are 1/more ______________________ 100s of amino acids Bent and folded due to bonding between ______________________ ENZYMES RNA or protein mols that act as _____________ ___________ (a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without itself undergoing any permanent chemical change) Enzyme actions depend on a physical fit between the enzyme and the __________(reactant being catalysed): ___________________________ INDUCED FIT MODEL 1. Enzyme has ___________________ where specific substrate fits 2. Linkage of enzyme and substrate causes slight change in enzyme ___________, which reduces the _________________________ (energy required to start reaction) 3. Enzyme releases ________________ 4. Enzyme is unchanged, ______________________________ INDUCED FIT MODEL LIPIDS Large, _______________, organic mols ________________________________ Includes: ___________________ _________________________ _______________ _______________ Higher ratio of C,H to O than carbs Stores more ___________________ FATTY ACID Unbranched Long carbon chain (________Cs) with a ___________group (-COOH) Two ends have different properties Carboxyl: _____, _________, ______________________ Hydrocarbon tail: _________, not interact with water, ____________(water fearing) FATTY ACID Saturated fatty acid: each C atom is covalently bonded to _____________, ______________________ Unsaturated fatty acid: has C atoms not bonded to max number of atoms, _______________________ TRIGLYCERIDES ________________________________________ ________________________________________ SATURATED TRIGLYCERIDES Composed of ____________________________ _____________ melting point Hard at ___________________ ___________________________________ UNSATURATED TRIGLYCERIDES Composed of _________________________ ______________ at room temp Found in ____________________ PHOSPHOLIPIDS ______fatty acids attached to glycerol _________attached to third C of glycerol Cell membrane is made of two layers of phospholipids = _______________ WAXES __________________________________________ ___________________ _____________________on plants’ outer surface ____________ protects animals’ ears STEROIDS ________________________________________ ______________________________________ Male hormone ________________ is a steroid ______________ is a steroid NUCLEIC ACIDS Very large, complex, organic mols Store and transfer ________________________ Two major types: Deoxyribonucleic acid: ______ _________________________________ _________________________________ Ribonucleic acid: _______ ________________________________________________ ______________________________________ DNA & RNA are polymers, made from the monomers ______________ HOMEWORK SECTION 2 Answer Section 2 Review in your homework book Answer all questions Start on a new page Please write the date at the top Heading: Molecules of Life