* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Promotion = Communication - HSB-LHS
Visual merchandising wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Planned obsolescence wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Social media marketing wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Internal communications wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Product lifecycle wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Product placement wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Sales process engineering wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Sports marketing wikipedia , lookup
Predictive engineering analytics wikipedia , lookup
Supermarket wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
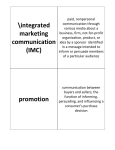
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Promotion = Communication Project #4 :: Promo Blitz Principles of Marketing Mrs. Schroeder Promotion What are some examples of promotion? Sales associate helping customers TV commercials Billboards Direct mail Ads in the newspaper and magazines Public service announcements Corporate sponsorship of sporting events Promotion is Marketing Communication: Goals of Promotion Promotion can be broadly described as the communication from an organization to its customers, potential customers, and the public. Also called marketing communication. The role of promotion is to help a business achieve its marketing goals. The basic marketing goals of most businesses are to sell products and make a profit. Promotion helps a business reach these goals by communicating. Inform Businesses want to keep customers informed about: Existing products New products New features on existing products Safety issues that may affect the use of a product Charities and cultural organizations the business supports Events the business sponsors in the community Another important aspect of informing is to remind. Express Promotional messages use words, pictures, color, motion, and music to express and entertain. TV commercials are often built around emotion and entertainment. Coke Pepsi Persuade Persuasion is the use of logic, argument, or pleading to get another person to agree with you or to act in a certain way. The ultimate goal of promotion is to persuade potential customers to buy the product. Promotional messages persuade people to buy through the use of information, reminders, expression, and entertainment. A promotional message might persuade might persuade you to buy a product, if the message did the following: Informed you about how the product meets your needs Provided a reminder that was timely Used expressive elements that made an impression and left you with a good feeling about the company and its product Promotion is Marketing Communication: The Communication Process and Promotion Promotion takes place through the communication process. An important part of developing the promotional message is choosing the best medium for the message. Promotion is Marketing Communication: The Communication Process and Promotion Noise Noise can interfere with promotional messages, just the same way noise can interfere with any communication. Promotional messages can encounter physical noise, technical problems, external distractions, and internal distractions. One of the major sources of noise is the sheer number of promotional messages that each person is exposed to every day. Marketers cannot control the environment where marketing messages are received, but, they have two methods to try to counteract these distractions: Repeat the same promotional message many times, often using several mediums Make the message stand out from all others Feedback Once the message reaches the receivers (target market), the decode, understand, and act on (or ignore) the message. Effective promotion, like effective communication, is promotion that achieves its goals. Most obvious sign is increase in sales. Promotion is Marketing Communication: Types of Promotion There are many ways to categorize promotion. Three common ways are: 1. The target market 2. What is being promoted 3. The elements of promotion Target Market: Business or Consumers Business-to-business (B2B) promotion is the promotion that occurs when a business promotes its products to another business. Business-to-consumer (B2C) promotion is promotion that occurs when a business promotes its products directly to the consumer market. What: Product or Institution Product promotion is marketing communication that focuses on the product and selling the product. Institutional promotion is communication that focuses on the image of the organization. The Four Elements of Promotion 1. Personal selling 2. Advertising 3. Sales promotion 4. Public relations These elements fall into two categories: personal promotion and nonpersonal promotion. Personal Promotion In personal promotion, the marketer and the customer communicate in person. The main feature of personal selling is that the seller can customize the message, based on the immediate response (feedback) from the customer. Nonpersonal Promotion Nonpersonal promotion is promotion that communicates the same message to all potential customers. Mass communication and the mass media are used to send nonpersonal promotion. Nonpersonal Promotion: Advertising Advertising is nonpersonal promotion paid for by an identified sponsor. Includes print ads in newspapers/magazines, commercials on radio/TV, Internet ads, outdoor ads (billboards), and transit ads on buses/subway cars. Also includes direct marketing, or direct mail. Nonpersonal Promotion: Sales Promotion Sales promotion consists of marketing activities designed to entice customers to buy a company’s products. Ex. – coupons, contests, free samples, etc. Have goal of getting customer to buy the product. Most are short-term activities and are designed to be used with other forms of promotion. Business-to-Consumer Sales Promotion Visual Merchandising: Visual merchandising is the physical presentation of merchandise and the design of a place of business for the purpose of increasing sales. Includes displays in store windows Purpose is to attract the customer to the merchandise Used to create atmosphere for service businesses Coupons and Rebates: A coupon is a printed piece of paper that indicates the product and the amount of price reduction when the coupon is used. A rebate is the return of a portion of the money paid for a purchase. (Ex.: cars = cash back) Free Samples: Free samples (trial samples) are small amounts of the product that are given to the customer at no charge. Premiums: A premium is an item given to the customer for free or at a reduced price along with the purchase of a product. Acts as an incentive by offering a reward or prize if the customer buys the product. Contests and Sweepstakes: Contests and sweepstakes are competitions that offer participants a chance to win a prize Contests usually require you to do something. A sweepstakes is a game of chance. Promotional Tie-In: A promotional tie-in is promotion involving the products of two or more companies. Product Placement: In product placement, the advertiser works with a media company to place one of its products in a movie or TV show, so that the brand name can be clearly seen. Business-to-Business Sales Promotion B2B sales promotion (trade promotion) is sales promotion that occurs between members of a distribution channel. The purpose is to get members of the distribution channel to buy the product, and then sell it to the next member of the channel. Many companies spend more on trade promotions than on consumer sales promotions. Trade Shows: A trade show is an exhibit of interest to a specific industry. Trade Allowance: A trade allowance is a discount or money paid to the intermediary who buys the product. Trade Allowances: A buying allowance is a discount given to retailers for the goods purchased. A promotional allowance is money that the manufacturer pays to the reseller to cover costs of promotion done by the reseller. A slotting allowance I money that the manufacturer or wholesaler pays to the retailer to cover the costs of carrying a new product. Point-of-Purchase Advertising: A promotional display located at the place where the customer makes the buying decision is called point-of-purchase advertising. Sales Incentives: Sales incentives consist of contests and rewards used by manufacturers and other channel members to motivate wholesalers and retailers to sell more of the product. Ex. – vacations for salespeople Nonpersonal Promotion: Public Relations Public relations consists of promotional activities designed to create goodwill between a company and the public. Is mostly institutional promotion A positive image often influences people to buy products from the company Proactive public relations consists of communications initiated within the company for the purpose of image building. Info on new products, charitable events, etc. Reactive public relations consists of communications in response to negative events or damaging information that appears in the media. Recalls, accidents, etc. Publicity: Publicity is information about a company and its products that appears in the media. The company does NOT pay for it. A press release is a story about the company that the public relations specialist writes and sends to the media. A press kit consists of information about the company and its products. A press conference is a meeting called by a business to which the media is invited. Philanthropy: Philanthropy consists of actions that improve human welfare and spread goodwill. The Marketing Concept and Promotion Promotion has been criticized for manipulating people into buying things that they do not really want or need. Marketers that follow the marketing concept do not run into these sorts of problems. The needs and wants of the customers should always be kept in mind.