* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What Is Promotion?
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Visual merchandising wikipedia , lookup
Targeted advertising wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Advertising management wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Advertising wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Internal communications wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Supermarket wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
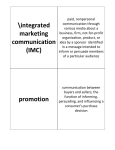
What Is Promotion? Promotion Is Marketing Communication Promotion is communication from an organization to its customers potential customers the public Marketing communication is another term for promotion. Goals of Promotion Goal of promotion to help a business achieve its goals by communicating with customers and the public Promotion informs expresses persuades Inform Businesses want to keep customers informed about existing products new products new features on existing products how to use or assemble products safety issues charities, cultural organizations, and community events that the business supports Express Promotional messages express and entertain. attracts customer attention to products creates demand for products Messages that entertain or create emotion are more likely to be remembered. Persuade Persuasion use of logic, argument, or pleading to get another person to agree with you or act in a certain way the ultimate goal of promotion is to persuade people to buy the product occurs through information, reminders, expression, and entertainment The Communication Process The communication process in promotion the marketer is the sender the target market is the receiver Noise Noise can interfere with promotional messages. Noise can include physical noise, technical problems, external distractions, and internal distractions Two methods to counteract distractions repeat the same message many times make the message stand out from all others Feedback How do marketers determine whether a promotion message was effective? effective promotion is promotion that achieves its goals Customer feedback can be obtained by monitoring sales performing market research Types of Promotion Types of Promotion Promotion can be categorized based on the target market businesses or consumers what is being promoted product promotion: focuses on selling the product institutional promotion: focuses on creating an image of the organization the four elements of promotion Promotion is either personal or nonpersonal. personal promotion occurs directly between customer and marketer personal selling is the only type of personal promotion nonpersonal promotion communicates the same message to the entire target market Examples: advertising, sales promotion, and public relations Four Elements of Promotion The four elements of promotion personal promotion personal selling non-personal promotion advertising sales promotion public relations Personal Selling Personal selling seller communicates in person with buyer a selling message can be customized for each buyer based on immediate feedback from the customer can occur on-site, over the phone, and over the internet used in both B2C and B2B sales Advertising Advertising includes print ads commercials Internet ads outdoor advertising transit advertising direct marketing e.g., sales flyers Sales Promotion Sales promotion marketing activities designed to entice customers to buy a company’s products Examples: coupons, contests, free samples can be categorized as B2C and B2B B2C sales promotion coupons and rebates free samples premiums contests and sweepstakes promotional tie-ins product placement visual merchandising B2B sales promotion trade shows trade allowances point-of-purchase advertising sales incentives Public Relations Public relations promotional activities designed to create goodwill between a company and the public proactive public relations communications initiated within the company for the purpose of image building reactive public relations communications in response to negative events or damaging information Publicity information about a company and its products that appears in the media company does not pay for articles to be written company also has no control over article content main tools of publicity: press release, press kit, and press conference Philanthropy supporting a charity, sport, or cultural activity public relations department makes the sure public knows about these activities potential customers will feel good about a company that supports causes they care about