* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PHARMACOLOGY AND PRINCIPLES OF DRUG ACTION
Specialty drugs in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Psychedelic therapy wikipedia , lookup
Environmental persistent pharmaceutical pollutant wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Toxicodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Environmental impact of pharmaceuticals and personal care products wikipedia , lookup
Orphan drug wikipedia , lookup
Theralizumab wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Prescription drug prices in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
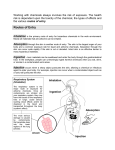
PHARMACOLOGY AND PRINCIPLES OF DRUG ACTION What is pharmacology? • Medical pharmacology is the science of chemicals (drugs) that interact with the human body. • Pharmacology deals with all aspects of the actions of drugs on living tissues, particularly their effects on man. • The effect of chemicals may be beneficial (therapeutic) or harmful (toxic). The pure chemicals or mixtures may be of natural origin (plant, animal, or mineral) or may be synthetic compounds. • In Pharmacology drugs are tested, first in vitro (in the laboratory) for biochemical activity and then in vivo (on animals, human volunteers, and patients) for safety, effectiveness, side effects, and interactions with other drugs and to find the best dose, timing, and route (mouth, injection, etc.) The categories of pharmacology Chemotherapy • the use of chemicals to destroy invading organisms Pharmacotherapy • the use of drugs to restore or replace normal function in various tissue cells, organs. Toxicology • the study of the poisonous effects of chemicals. Psychopharmacology • the study of the effects of chemicals on the behavior of humans or animals. Biochemical pharmacology • the effects of chemicals on biochemical reactions in living systems, and the effects of these systems on the chemicals and their metabolism. Clinical Pharmacology • the study and evaluation of the effects of drugs in humans The main branches of pharmacology The interactions of chemicals are divided into two categories:- • Pharmacodynamics • Pharmacokinetics PHARMACODYNAMICS • the effects of the drug on the body • how the effects of a drug are generated Pharmacokinetics • The way the body affects the drug with time considering absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion. DRUG ABSORPTION, DISTRIBUTION, EXCRETION Absorption Most drugs are given orally passing through the gut wall to enter the bloodstream Absorption… Depends on:- Formulation Stability to acid and enzymes Food in stomach Lipid solubility Routes of administration • Orally or parentally ( nongastrointestinal route) ORAL…. Convenient Some drugs are destroyed by acid or enzymes in gut Parenterally:Intravenous injection… Drugs enter circulation and bypass the absorption barriers Intramuscular/ subcutaneous injection Inhalation (asthma inhalers) Topical (lotions, ointments) Sublingual rectal DISTRIBUTION • When drug reaches the circulation and penetrates tissues EXCRETION • Renal Most drugs are eliminated via kidneys • Biliary Some drugs concentrated in bile excreted into intestine and may be reabsorbed