* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slides Gene Group Analysis
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
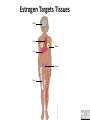
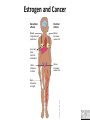
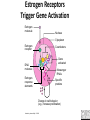
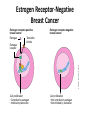
GeneGroupAnalysis 1.0.0-BetaCS Alejandro Quiroz-Zárate John Quackenbush lab http://compbio.dfci.harvard.edu/compbio The “usual” analysis Molecular profile Shark Run GSEA DAVID Nemo The Key Idea • This methodology was developed with Dr. John Quackenbush Genes as repeated measurements Prior Knowledge Genes Gene Group Samples (pa ents) Gene Groups (KEGG, GO) Repeated measurements (genes) The model T Functional Gene Group Data Base Applications Linear Model on the Mean of the Gene Groups High dimensionality on the number of gene groups Gene Groups Genes The proposed methodology Sparness priors are used to control for multiple comparison Two or more group comparison(cross-sectional design) Time series data design GeneGroupAnalysis 1.2.0 Go to • Example (real data set) – Gene expression from tumor samples • 209 ER+ and 135 E• GEO reference accession numbers:GSE2034,GSE5327 – Affymetrix U133A – Conceive the data set with a Cross-Sectional Design – Question of interest: • What are the biological mechanisms that drive the differences in Estrogen Receptor status? Estrogen Targets Tissues Brain Heart Breast Liver Uterus Artwork by Jeanne Kelly. © 2010. Bone Estrogen and Cancer Beneficial effects Harmful effects Breast Programs milk production Breast Increases cancer risk Liver and heart Controls cholesterol Uterus Prepares for fetus Uterus Increases cancer risk Artwork by Jeanne Kelly. © 2010. Bone Preserves strength Estrogen Receptors Trigger Gene Activation Estrogen molecule Nucleus Cytoplasm Estrogen receptor Coactivators Gene activated DNA molecule Messenger RNAs Estrogen response elements Specific proteins Change in cell behavior (e.g., increase proliferation) Artwork by Jeanne Kelly. © 2010. Estrogen Receptor-Negative Breast Cancer Estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer Estrogen Estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer Tamoxifen inhibits Artwork by Jeanne Kelly. © 2010. Estrogen receptor Cell proliferation • Controlled by estrogen • Inhibited by tamoxifen Cell proliferation • Not controlled by estrogen • Not inhibited by tamoxifen Analysis