* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Developmental psychology wikipedia , lookup
Psychometrics wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Index of psychology articles wikipedia , lookup
Educational psychology wikipedia , lookup
Dual process theory wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive development wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Music psychology wikipedia , lookup
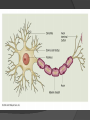
AP REVIEW Today’s Class Announcements: MANDATORY AP ASSEMBLY NEXT WEEK DURING CONFERENCE PERIOD IN THE AUDITORIUM: ○ Monday, April 20 Freshmen & Sophomores: 7:45 – 8:30 am Juniors & Seniors: 8:45 – 9:15 am Not that you would know it, but TUSD Stats is current (except for 13-14 Exam) ○ If you missed the exam on Units 13-14, please schedule a makeup ASAP Connections Assignment: Friday, April 24 AP Info & Review Schedule Units 1-2 Review Final Exam Info Part 1: Thursday, April 30 Part 2: Friday, May 1 Cheat sheets ARE allowed. 1 piece of 8.5x11” paper, but only one side of the paper this time Nothing that unfolds or somehow gives you more space. You don’t have to make a cheat sheet. AP Psychology Exam Info Monday, May 4 (afternoon session) bring photo ID, pens/pencils, & DO NOT BE LATE 2 hour, 10 minute exam Part 1: Multiple choice ○ 100 questions (A-E) ○ 70 minutes ○ ANSWER EVERY QUESTION! GUESS GUESS GUESS! 10 minute break Part 2: Free response ○ 2 questions ○ 50 minutes ○ ANSWER DIRECTLY! AP Psychology Exam Info 150 total possible points (100 multiple choice, 50 free response) Composite Score AP Grade (approx.) 96-150 5 74-95 4 55-73 3 36-54 2 0-35 1 Terms/Ideas psychology phrenology empiricism dualism tabula rasa structuralism ○ Unit 1 Review Topics introspection functionalism Gestalt psychology ○ perceptual units psychodynamic/psychoanalytic theory ○ unconscious behaviorism humanistic psychology cognitive psychology social psychology nature vs. nurture psychology vs. psychiatry Important People to Know John Locke Rene Descartes Hippocrates Sir Frances Bacon Wilhelm Wundt William James Sigmund Freud Unit 2 Review Topics Terms/Ideas hypothesis theory operational definition population sample (random sampling) Descriptive research ○ case study ○ surveys ○ naturalistic observation Correlational research ○ correlation coefficient (r) ○ direction and size of correlations ○ limitations? Experimental research ○ independent & dependent variables ○ experimental & control conditions ○ confounds Terms/Ideas, cont. random assignment reliability validity (internal & external) demand characteristics placebo effect double-blind design Descriptive statistics ○ measures of central tendency ○ measures of variability Inferential statistics ○ statistical significance ○ meta-analysis informed consent debriefing Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) Unit 3 Review Topics Terms/Ideas glial cells Neuron ○ cell body/soma ○ nucleus ○ dendrites ○ axon ○ myelin sheath Nodes of Ranvier, Schwann cells ○ terminal buttons/terminal branches resting potential action potential threshold (“all or none law”) synapse/synaptic cleft Neurotransmitters ○ vescicles ○ receptors ○ reuptake (SSRIs) Terms/Ideas, cont. agonists & antagonists Nervous system ○ central and peripheral ○ Peripheral Skeletal and Autonomic ○ Autonomic Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Endocrine system ○ hormones ○ pituitary gland Mapping Brain Functions ○ EEG ○ CT scan ○ PET scan ○ MRI & fMRI Unit 3 Review Topics Terms/Ideas Hindbrain ○ medulla ○ pons ○ reticular formation ○ cerebellum Midbrain ○ thalamus Forebrain ○ limbic system hippocampus hypothalamus amygdala Terms/Ideas, cont. Forebrain, cont. ○ cerebral cortex frontal lobe parietal lobe temporal lobe occipital lobe ○ corpus callosum ○ anterior cingulate plasticity Important People to Know Phineas Gage H.M. Unit 4 Review Topics Terms/Ideas sensation vs. perception bottom-up & top-down processing absolute threshold ○ just-noticeable difference (JND) ○ Weber’s Law priming signal detection theory sensory adaptation transduction Visual Sensation & Perception ○ amplitude & frequency of light waves ○ parts of the eye ○ theories of color vision trichromatic theory opponent-process theory (afterimages) ○ feature detector neurons Terms/Ideas, cont. Visual Sensation & Perception, cont. ○ cues to depth perception (monocular vs. binocular) ○ motion perception stroboscopic effect phi phenomenon ○ change blindness ○ Stroop task Auditory Sensation & Perception ○ amplitude & frequency of sound waves ○ parts of the ear ○ pitch theories (place theory, frequency theory) ○ cocktail party effect gate-control theory of pain synesthesia Unit 5 Review Topics Terms/Ideas consciousness (normal/waking vs. altered states) Sleep ○ circadian rhythm (roles of hypothalamus, pineal gland, melatonin) ○ stages of sleep brain wave activity ○ Why do we sleep? ○ Why do we dream? Freud (manifest vs. latent content) activation-synthesis theory memory consolidation Sleep, cont. ○ sleep disorders insomnia narcolepsy (hypocretin) sleep apnea night terrors Hypnosis ○ absorption ○ applications of hypnosis Psychoactive drugs ○ addiction, tolerance, & withdrawal ○ 3 classes: depressants stimulants hallucinogens Near-death experiences Unit 6 Review Topics Terms/Ideas Classical conditioning ○ 4 aspects: unconditioned stimulus (US) conditioned stimulus (CS) unconditioned response (UR) conditioned response (CR) ○ acquisition ○ extinction ○ reacquisition ○ spontaneous recovery ○ stimulus discrimination ○ stimulus generalization ○ biological preparedness ○ taste aversion (Garcia & Koelling study) ○ systematic desensitization Operant conditioning ○ ○ ○ ○ Law of Effect shaping positive & negative reinforcement 4 schedules of partial reinforcement: fixed ratio variable ratio fixed interval variable interval ○ positive & negative punishment Other types of learning besides conditioning ○ latent learning ○ insight learning ○ social/observational learning (modeling) ○ mirror neurons Unit 6 Review Topics Important People to Know Ivan Pavlov John Watson Edward Thorndike BF Skinner Wolfgang Kohler Albert Bandura Robert Rescorla Unit 7 Review Topics Terms/Ideas Terms/Ideas, cont. Memory Memory, cont. ○ 3 steps to forming a memory ○ retrograde & anterograde (encoding, storage, retrieval) amnesia ○ Atkinson & Shiffring (1968): 3 Stage ○ long-term potentiation Model of Memory ○ flashbulb memories sensory memory short-term ○ memory interference (working) memory long-term (proactive & retroactive) memory ○ repression ○ rehearsal ○ mnemonic devices ○ chunking ○ levels/depth of processing ○ primacy & recency effects ○ types of memories explicit vs. implicit episodic, semantic, procedural Unit 7 Review Topics Terms/Ideas Thinking ○ linguistic relativity (Whorf) ○ algorithms vs. heuristics heuristics: availability, representativeness, anchor & adjust ○ confirmation bias Language ○ phonemes, morphemes ○ grammar (syntax, semantics) ○ Broca’s aphasia, Wernicke’s aphasia Important People to Know Hermann Ebbinghaus Elizabeth Loftus Benjamin Whorf Noam Chomsky Unit 8 Review Topics Emotion Terms/Ideas Motivation ○ drive-reduction theory ○ law of optimal arousal (aka. Yerkes-Dodson Law) ○ Maslow’s hierarchy of needs ○ basic emotions ○ catharsis ○ 3 important theories of emotion 1. James-Lange 2. Cannon-Bard 3. two-factor theory (Schacter & Singer) ○ polygraph tests ○ effects of stress self-actualization ○ hunger (lateral & ventromedial hypothalamus) anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa ○ evolutionary perspective on mating habits ○ flow General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS) Important People to Know Abraham Maslow Paul Ekman Schacter & Singer Hans Selye Unit 9 Review Topics Terms/Ideas Physical/Prenatal Development ○ zygote embryo fetus ○ teratogens Cognitive Development ○ schemas (assimilation & accomodation) ○ Piaget’s stage model object permanence conservation egocentrism/theory of mind ○ autism Terms/Ideas, cont. Psychosocial Development ○ attachment styles ○ critical period/imprinting ○ Baumrind’s parenting styles ○ Erikson’s stage model Moral Development ○ Kohlberg’s stage model dementia/Alzheimer’s Disease Important People to Know Jean Piaget Harry Harlow Mary Ainsworth Konrad Lorenz Lawrence Kohlberg Erik Erikson Unit 10 Review Topics Terms/Ideas Psychoanalytic theory (aka. Terms/Ideas, cont. psychodynamic) Trait approach ○ the unconscious ○ factor analysis ○ Ways to access the unconscious: ○ five-factor theory of dreams (manifest vs. latent content) personality (“the Big Five”) free association hypnosis learned helplessness projective tests Important People to Know ○ id, superego, & ego Sigmund Freud ○ Freud’s stage model of Anna O. psychosexual development Carl Jung ○ Oedipus complex Gordon Allport ○ defense mechanisms: Alfred Adler repression, displacement, projection, regression, reaction formation, sublimation Unit 11 Review Topics Terms/Ideas Intelligence ○ general intelligence (g) ○ emotional intelligence ○ convergent vs. divergent thinking (creativity) ○ crystallized vs. fluid intelligence Intelligence testing ○ Intelligence quotient (IQ) ○ famous IQ tests: Binet-Simon Stanford-Binet WAIS/WISC ○ standardization ○ reliability (test-retest; split-half) ○ validity (criterion/predictive) Terms/Ideas, cont. stereotype threat Important People to Know Alfred Binet & Theodore Simon Lewis Terman Charles Spearman Howard Gardner Robert Sternberg Unit 12 Review Topics Terms/Ideas Diagnostic & Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th edition (DSM-IV) ○ 5 axes of the DSM Anxiety Disorders ○ Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) ○ Panic disorder (PD) ○ Agoraphobia ○ Phobias ○ Social anxiety disorder (SAD) (aka. social phobia) ○ Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) ○ Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) Terms/Ideas, cont. Mood disorders ○ Major depressive disorder (MDD) Seasonal affective disorder (SAD) ○ Bipolar disorder (BD) Schizophrenia ○ delusions, hallucinations, language disruptions Personality disorders ○ especially borderline (BPD) and antisocial (APD) Dissociative Identity Disorder (DID) Somatoform disorders Important People to Know David Rosenhan Unit 13 Review Topics Terms/Ideas Psychoanalytic Therapy ○ resistance ○ transference Humanistic Therapy ○ client-centered therapy ○ active listening Behavioral therapy ○ counterconditioning ○ token economies ○ systematic desensitization Cognitive therapy/cognitivebehavioral therapy (CBT) ○ rational-emotive therapy Terms/Ideas, cont. Types of Medication ○ antipsychotics, antidepressants, antianxiety, mood-stabilizers “Alternative” Therapies ○ electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), rTMS, EMDR, lobotomy Important People to Know Sigmund Freud Carl Rogers Albert Ellis Unit 14 Review Topics Terms/Ideas Hindsight bias Fundamental attribution error Social roles (Stanford Prison Study) Cognitive dissonance Conformity ○ Informational & normative social influence Obedience to authority Helping behavior ○ Bystander effect, diffusion of responsibility Terror Management Theory Terms/Ideas, cont. Stereotypes, prejudice, & discrimination ○ Explicit vs. implicit attitudes (IAT) ○ outgroup homogeneity, ingroup favoritism Persuasion ○ Elaboration Likelihood Model (ELM) ○ persuasion techniques: foot-in-the-door door-in-the-face Attraction & relationships ○ mere exposure effect ○ halo effect ○ Sternberg’s triangle theory Group processes ○ social facilitation, social loafing, group polarization, groupthink Unit 14 Review Topics Important People to Know Phil Zimbardo Leon Festinger Solomon Asch Stanley Milgram Robert Sternberg