* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download C06.InformationSecur.. - SIUE Computer Science
Unix security wikipedia , lookup
Airport security wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Cyberwarfare wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Information security wikipedia , lookup
Mobile security wikipedia , lookup
Security-focused operating system wikipedia , lookup
Cyber-security regulation wikipedia , lookup
Computer and network surveillance wikipedia , lookup
International cybercrime wikipedia , lookup
Social engineering (security) wikipedia , lookup
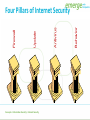
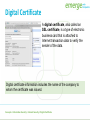
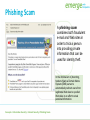
Bad Day in the Office Links: Bad Day in the Office Concepts > Information Security Information Security Information security refers to the protection of information systems and the information they manage against unauthorized access, use, manipulation, or destruction, and against the denial of service to authorized users. In this section: • Machine-Level Security • Network Security • Internet Security Concepts > Information Security Machine-Level Security Machine-level security refers to actions taken to protect information on a computer that may or may not be connected to a computer network or the Internet. In this section: • Authentication • Encryption • Data Backup Concepts > Information Security > Machine-Level Security Authentication Authentication is a security process in which the identity of a person is verified. Facial pattern recognition is a form of biometrics that uses a mathematical technique to measure the distances between points on the face. Links: Microsoft - Strong passwords: How to create and use them Concepts > Information Security > Machine-Level Security > Authentication IDTECK - Biometrics Links: IDTECK – Biometrics Concepts > Information Security > Machine-Level Security > Authentication Encryption Encryption is a security technique that uses highlevel mathematical functions and computer algorithms to encode data so that it is unintelligible to all but the intended recipient. Concepts > Information Security > Machine-Level Security > Encryption Encryption / Decryption code Turn sound down! Links: Encryption / Decryption code Concepts > Information Security > Machine-Level Security > Encryption Data Backup Data backup is a process in which copies of important computer files are stored in a safe place to guard against data loss. With the advent of cloud computing, users are storing increasing amounts of data on Internet servers. E-mail, calendars, documents, photos, and other data are being saved in services provided by Google, Yahoo!, Microsoft, Flickr, Facebook, and other Web 2.0 applications. Concepts > Information Security > Machine-Level Security > Data Backup Mac OS X Leopard – Time Machine Links: Mac OS X Leopard – Time Machine Concepts > Information Security > Machine-Level Security > Data Backup Network Security Network security is concerned with addressing vulnerabilities and threats in computer networks that may or may not be connected to the Internet. In this section: • Permissions • Interior Threats • Information Theft • Behavioral Targeting (Issues) Concepts > Information Security > Network Security • Network Usage Policy • Wireless Security Permissions Permissions, or file system permissions, refer to the specific access privileges afforded to each network user and each system resource in terms of which files, folders, and drives each user can read, write, and execute. Concepts > Information Security > Network Security > Permissions Interior Threats Types of Errors • Data-entry • Computer Programming • Installation & setup of systems • Mishandling of output • Inadequate planning & control of malfunctions Interior threats are network security threats that originate from within a network, typically from registered users. Concepts > Information Security > Network Security > Interior Threats Information Theft Information theft refers to the access of information by an unauthorized person for financial gain or other benefit. Concepts > Information Security > Network Security > Interior Threats Behavioral Targeting Behavioral targeting uses information about a person’s behavior to inform businesses and marketers so that they can offer products that are likely to be of interest to that person. Links: Web Users Push For More Privacy Issues > Privacy > Behavioral Targeting Network Usage Policy A network usage policy is a document, agreement, or contract that defines acceptable and unacceptable uses of computer and network resources for a business or organization. Policy Types Network & computer use E-mail use Internet use Links: SIUE ITS Policies: Responsible Use Policy Concepts > Information Security > Network Security > Network Usage Policy Wireless Security Wireless security refers to the unique threats and defenses associated with wireless computer networks. Concepts > Information Security > Network Security > Wireless Security How to secure your Wi-Fi network Links: How to secure your Wi-Fi network Concepts > Information Security > Network Security > Wireless Security Internet Security Internet security refers to the unique threats and defenses associated with computers connected to the Internet. In this section: • Hacker • Firewall • Software Patch • Malware • Antivirus Software • • • • Botnet Cyber Warfare Identity Theft Internet Fraud Concepts > Information Security > Internet Security • • • • Digital Certificate Phishing Scam Spam Virus Hoax Concepts > Information Security > Internet Security Behavior Antivirus Update Firewall Four Pillars of Internet Security Underground Economy Links: Symantec Guide to Scary Internet Stuff – Underground Economy Concepts > Information Security > Internet Security Hacker A hacker is an individual who subverts computer security without authorization. Key-logging software Packet-sniffing software Wireless network scanning software Port-scanning software Social engineering Concepts > Information Security > Internet Security > Hacker Firewall A firewall is network hardware or software that examines data packets flowing in and sometimes out of a network or computer in order to filter out packets that are potentially dangerous. A firewall acts as a barrier that examines and blocks specified data packets from a network or computer. Concepts > Information Security > Internet Security > Firewall Software Patch The vast majority of hacker exploits take advantage of the security holes in Internet software. Keeping this software up to date and using firewall software are two of the most important steps to take to ensure information security. A software patch, sometimes called a security patch, fixes software bugs and flaws, and is typically distributed to software users through online software updates. Concepts > Information Security > Internet Security > Software Patch Malware Malware is short for “malicious software,” and includes any software designed to damage, corrupt, or illegally manipulate computer resources. Common forms include viruses, worms, and spyware. Malware propagates itself through e-mail attachments, instant message attachments, and Web pages Concepts > Information Security > Internet Security > Malware Antivirus Software Antivirus software, also known as virus scan software, uses several techniques to find viruses, worms, and spyware on a computer system; remove them if possible; and keep additional viruses, worms, and spyware from infecting the system. Besides using antivirus software, knowledge and caution play a big part in protecting PCs against viruses and worms. Links: PC Magazine: Antivirus reviews Concepts > Information Security > Internet Security > Antivirus Software Fake Anti-Virus Software Scams Links: Fake Anti-Virus Software Scams Concepts > Information Security > Internet Security > Antivirus Software Botnet A botnet, or botnet army, refers to a collection of computers autonomously or automatically working together toward some goal; often zombie computers that are synchronized to perform illegal activities on the Internet. In 2007, a botnet was used to bring down the information infrastructure of the country of Estonia, in an act that the country viewed as a military attack. Concepts > Information Security > Internet Security > Botnet Botnets Links: Symantec Guide to Scary Internet Stuff – Botnets Concepts > Information Security > Internet Security > Botnet Cyber Warfare Cyber warfare extends traditional forms of warfare to the Internet and the Web including espionage, psychological warfare, and attacks. Cyberterrorism extends traditional forms of terrorism to the Internet and the Web. Concepts > Information Security > Internet Security > Cyber Warfare Identity Theft Identity theft is the criminal act of stealing information about a person to assume that person’s identity to commit fraud or other crimes. People can protect themselves from identity theft by being cautious with their personal information Concepts > Information Security > Internet Security > Cyber Warfare Citibank Identity Theft Commercials Links: Bustier Mud Flaps Babe Magnet Darrel Internet Fraud Internet fraud is the crime of deliberately deceiving a person over the Internet in order to damage them or to obtain property or services unlawfully. The most common form of Internet fraud is Internet auction fraud, accounting for a little more than one third of fraud cases. Auction fraud involves being swindled by sellers or buyers on auction sites like eBay. Concepts > Information Security > Internet Security > Cyber Warfare Internet Fraud Links: Internet Fraud Concepts > Information Security > Internet Security > Cyber Warfare Digital Certificate A digital certificate, also called an SSL certificate, is a type of electronic business card that is attached to Internet transaction data to verify the sender of the data. Digital certificate information includes the name of the company to whom the certificate was issued. Concepts > Information Security > Internet Security > Digital Certificate VeriSign SSL Certificates Links: VeriSign SSL Certificates Concepts > Information Security > Internet Security > Digital Certificate Phishing Scam A phishing scam combines both fraudulent e-mail and Web sites in order to trick a person into providing private information that can be used for identity theft. In the criminal act of pharming, hackers hijack a Domain Name System (DNS) server to automatically redirect users from legitimate Web sites to spoofed Web sites in an effort to steal personal information. Concepts > Information Security > Internet Security > Phishing Scam Spam Spam refers to unsolicited junk e-mail that makes up more than half of the amount of e-mail delivered. Concepts > Information Security > Internet Security > Spam Virus Hoax A virus hoax is an e-mail or popup window that warns of a virus that doesn’t exist in order to confuse or get users to take actions that harm their own computers. Links: Snopes: Virus Hoaxes & Realities Sophos: Hoaxes Concepts > Information Security > Internet Security > Virus Hoax Discussion Question Privacy issues include: the right to be left alone, to be free from surveillance, and to control the information collected and stored about you. To what extent are you willing to sacrifice your privacy for conveniences and to increase your personal safety and national security? Links: Digital Dossier Concepts > Information Security > Discussion Question