* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bacteria vs. Viruses
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
Social immunity wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Herd immunity wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Plant disease resistance wikipedia , lookup
Vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
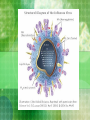
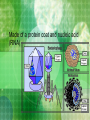
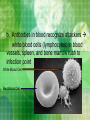
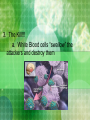
Bacteria vs. Viruses I. Bacteria and Viruses: Both can cause diseases Anthrax A. Bacteria are living organisms (have DNA): they can control functions and replicate on their own B. Viruses are not living organisms: they can not control their own functions or replicate on their own 1. Made of a protein coat and nucleic acid (RNA) 2. In order to replicate they must use a host cell’s organelles and enzymes C. Our Immune System 1. The Attackers (pathogens): Bacteria or Viruses enter the body through opening in skin or mucous membranes 2. The Defenders a. Skin b. Antibodies in blood recognize attackers white blood cells (lymphocytes) in blood vessels, spleen, and bone marrow rush to infection point White Blood Cell Red Blood Cell 3. The Kill!!! a. White Blood cells “swallow” the attackers and destroy them D. Primary and Secondary Immune Responses 1. The second time you are infected by a pathogen (foreign invader), your immune system works faster to fight it. WHY? 2. Memory Cells: Protect against reinfection by a specific pathogen E. Immunity and Vaccines 1. Immunity: resistant to a specific pathogen a. Acquire immunity by being infected by a pathogen and surviving the disease OR b. By a vaccine: contains pathogens or toxins that have been modified so they can’t cause the disease 2. How do Vaccines work? a. b. c. Pathogens contain antigens (protein name tags) that make immune system respond as if it were harmful Results in an increase in memory cells Now body is ready to fight off pathogen in the future