* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Atom
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
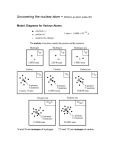
THE CHEMISTRY OF LIFE The Nature of Matter What do all of These Pictures Have in Common? And last, but not least… GEICO’S Gecko! MATTER • All matter is made up of different combinations of elements. • Atom = the smallest quantity of an element that still has the characteristics of it. • Atoms are made up of even smaller (subatomic) particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons. THE NUCLEUS • The core of an atom. • It holds 99.9% of the mass of the atom. • It is small compared to the whole atom. – Most of atom is empty space around the nucleus. – If nucleus of one atom were 1cm wide, the size of the atom would cover 30 football fields. • It is made up of Protons and Neutrons. • Electrons orbit around the nucleus. PROTONS • Have a positive (+) charge. • Found inside the nucleus of an atom. • Each element has a different number of protons. • Atomic Number = the number of protons in an atom. • Proton # never changes in an element. NEUTRONS • Have no charge = “neutral” • Found in the nucleus of an atom. • Atoms of an element don’t always have the same # of neutrons. • These atoms are called isotopes. ELECTRONS • • • • • Have a negative (-) charge. Orbit around the nucleus. It is always in motion. Travels at the speed of light. It is 2,000 times smaller than a Proton or a Neutron. – If the nucleus is 1cm wide, the Electrons would be smaller than the width of a strand of hair. THE ATOM • ProtonsHave a positive charge (+) • NeutronsHave no charge • ElectronsHave a negative charge (-) • The nucleus = Protons + Neutrons. • Surrounding the nucleus = Electrons. ATOMIC NUMBER • The number of Protons in the nucleus of an atom. • The number of Protons = the number of Electrons. ATOMIC MASS • The number of Protons + the number of Neutrons. – Find the atomic mass of an atom that has 10 protons, 8 neutrons, and 10 electrons. – An atom has: • Atomic Number = 8 • Atomic Mass = 20 How many Protons, Neutrons and Electrons does it have? THE ATOM • The nucleus = + • “Opposites Attract” charge. • The electron cloud = - charge. • Nucleus and electron cloud are attracted to each other. ATOMIC STRUCTURE ELECTRON ORBITS • • • • 1st orbit = 2 e2nd orbit = 8 e3rd orbit = 8 e4th orbit = 16 e- • The atom is always looking to fill up its outermost orbit. ELEMENTS • Element = A pure substance made up of only one kind of atom. • Each element has a unique atomic number. • Which one of these is an element? PERIODIC TABLE OF ELEMENTS • Elements are categorized by atomic number = number of protons. • Who created the Periodic Table of Elements? ISOTOPES • IsotopesAtoms of an element that have different number of neutrons. – Ex. Carbon-12, Carbon-13, Carbon-14 • All isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties: – Same number of electrons. STOP AND REVIEW • • • • • • • ATOM ATOMIC NUCLEUS PROTONS NEUTRONS ELECTRONS ATOMIC NUMBER ATOMIC MASS • ATOMIC STRUCTURE • VALENCE ELECTRONS • ELEMENT • PERIODIC TABLE • ISOTOPES COMPOUNDS • Compound = Substance made up + of atoms of two or more different elements. • Compounds are joined by chemical bonds. • They can be broken down into simpler Sodium Chloride = Table salt substances. Sodiu m Chlorine CHEMICAL BONDS • Covalent Bond = Forms when two or more atoms share electrons to form a molecule. • If the electrons are shared equally = nonpolar bond. • If electrons are NOT shared equally = polar bond. – Ex. H2O (hydrogen bonds) – Who does it remind you of? MOLECULES • Molecules = The structure that results when two atoms are joined by covalent bonds. • Physical and chemical characteristics are different from the elements that make it up. CHEMICAL BONDS • Ionic Bond = One atom pulls the shared electrons away from the other atom. (greedy) • Ion = An atom or molecules that has gained or lost one or more electrons. • Ex. Na+, Cl- --Ionic bond between sodium (Na) and Chlorine (Cl) = Na+ and Cl- ions http://www.visionlearning.com/library/module_viewer.php?c3=&mid=55&ut=&l=e http://www.sciencejoywagon.com/chemzone/lessonch/03bonding/dogbond/default.htm IONIC BOND • Na+ + Cl- = NaCl (Sodium Chloride) • Sodium Chloride = Table salt • Salt crystal STOP AND REVIEW • COMPOUNDS • CHEMICAL BONDS • COVALENT BOND – NONPOLAR – POLAR • IONIC BOND • ION QUESTIONS • What is the basic structure of an atom? • Give one example of a compound? • What is the difference between a covalent bond and an ionic bond? • Why do all isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties? QUESTIONS • Two or more different atoms are combined in definite proportions in any: – A. Symbol – B. Isotope – C. Element – D. Compound QUESTIONS • An atom may have a positive charge, a negative charge, or be electrically neutral. How does an atom develop a negative charge? – A. by gaining a neutron – B. by gaining an electron – C. by losing an electron