* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
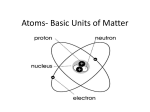
Download 1. The central core of the atom, containing protons and usually
Colloidal crystal wikipedia , lookup
Crystal structure wikipedia , lookup
Electromigration wikipedia , lookup
Low-energy electron diffraction wikipedia , lookup
Halogen bond wikipedia , lookup
Heat transfer physics wikipedia , lookup
Metastable inner-shell molecular state wikipedia , lookup
State of matter wikipedia , lookup
Tight binding wikipedia , lookup
1. The central core of the atom, containing protons and usually neutrons NUCLEUS PROTON • Small positively charged particles that are found in the nucleus of an atom NEUTRON • Small uncharged particles that are found in the nucleus of an atom ELECTRON • Tiny, negatively charged, high-energy particles that move around outside the nucleus of an atom VALENCE ELECTRONS • The electrons that are farthest away from the nucleus of an atom and are involved in chemical interactions. ELECTRON DOT DIAGRAM A representation of the number of valence electrons in an atom, using dots placed around the symbol of an element ATOMIC NUMBER • The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom GROUP • Elements in the same vertical column of the periodic table. Also called family. PERIOD • Elements in the same horizontal row of the periodic table. HALOGEN REACTIVE NON METAL • An element belonging to Group 17 of the periodic table. ION • An atom or group of atoms that has become electrically charged. IONIC BOND • The attraction between oppositely charged ions. POLYATOMIC ION • An ion that is made of more than one atom. CRYSTAL • An orderly, three-dimensional pattern of ions or atoms in a solid. MINERAL • A naturally occurring solid that has a crystal structure and a definite chemical composition.


















![Properties of matter student notes[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009076956_1-3293fc3fecf578fd34e3f0f2700d471f-150x150.png)