* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Darwin`s Case for Evolution
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
On the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
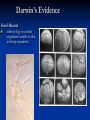
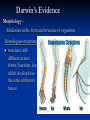
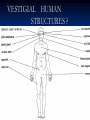
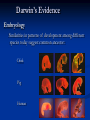
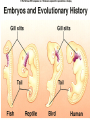
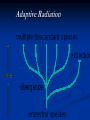
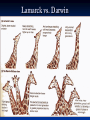
On the Origin of Species Charles Darwin’s book Published December, 1859 Sold out in one day “A century and a half later, it still argues the case for evolution better than any other book. “ Edward J. Larson, Evolution Darwin’s Case for Evolution Artificial Selection Darwin’s Case for Evolution - Artificial Selection An idea with which people were comfortable Farmers select for breeding only the animals or plants that have the traits they like Fast horses, plants with the biggest fruit Named this process “artificial selection” Darwin’s Case for Evolution – Variety also exists in nature – among species (interspecific) Darwin’s Case for Evolution -and within species (intraspecific) Darwin’s Case for Evolution In nature, many more individuals are born than can possibly survive. Thomas Malthus connection Darwin’s Case for Evolution Why can’t they all survive? Limiting Factors (factors that limit pop. size) Predation Food supply Shelter Mates Competition Darwin’s Case for Evolution A high rate of reproduction combined with competition for food, shelter, and mates creates a struggle for existence. The fiercest struggle is among individuals of the same species sharing the same niche, habitat, and dangers. Darwin’s Case for Evolution “Can we doubt that individuals having an advantage, however slight, over others, would have the best chance of surviving and procreating their kind?...This preservation of favorable conditions… I call Natural Selection.” In modern terms: DIFFERENTIAL REPRODUCTION OF SELECTED PHENOTYPES Natural Selection Measures the ability of a population to survive and reproduce Dependent upon environmental factors Genotypes (alleles) phentoypes (traits) survival/repro advantage! Darwin’s observations High reproductive potential Overall, population size is stable Limited resources Variation Darwin’s conclusions Competition drives selection Fitness level determined by adaptations! The more adaptations… the more evolutionary success! Natural Selection Summary Populations of organisms struggle for survival and reproductive success (fitness) Environment determines which genetic variations are most desirable in organisms/populations Populations of organisms adapt to their environment to improve fitness WHERE’S THE EVIDENCE? FOSSIL RECORD BIOGEOGRAPHY COMPARATIVE ANATOMY COMPARATIVE EMBRYOLOGY COMPARATIVE BIOCHEMISTRY Darwin’s Evidence Fossil Record Over millions of years, deposits compress older sediments below into layers Older layers, with older fossils, lie beneath younger layers, with younger fossils Darwin’s Evidence Fossil Record embryology in extinct organisms similar to that in living organisms Variation Darwin’s Evidence Morphology – Similarities in the form and structure of organisms Homologous structures: structures with different mature forms/functions, but which develop from the same embryonic tissues Darwin’s Evidence Morphology – similarities in the form and structure of organisms Analogous structures: structures with same mature forms/functions, but which develop from the different embryonic tissues Homologous vs. Analagous Darwin’s Evidence Morphology – Vestigial Organs – Homologous structures which no longer function VESTIGIAL HUMAN STRUCTURES ? Darwin’s Evidence Embryology Similarities in patterns of development among different species today suggest common ancestor: Chick Pig Human Darwin’s Evidence Geographic proximity of similar species – species on different Galapagos Islands were similar to one another, but different from those on mainland Darwin’s Finches DIVERGENT EVOLUTION Adaptive Radiation Darwin’s Evidence Convergent Evolution Animals living on different continents had different ancestors; however, because some animals on each continent lived under similar ecological conditions, they had similar selection pressures and thus similar features Placental Mammals Australian Marsupials Lamarck vs. Darwin Remaining 19th Century Questions Natural Selection Special Creation The complexity and perfection of structures such as the human eye indicates the work of a supernatural Designer. William Paley Natural selection results in better-adapted organs and organisms, not perfect ones. Charles Darwin Remaining 19th Century Questions What about gaps in the fossil record? What about these “great leaps” forward? Is the Earth old enough for the slow process of natural selection? How did human mental and moral attributes evolve? How does inheritance work? Where do varieties come from?