* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download blood flow - OCPS TeacherPress
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
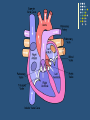
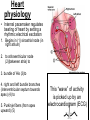
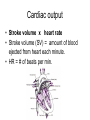
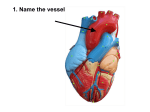
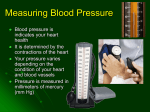
(HOW THE HEART WORKS) HEART PHYSIOLOGY HEART SOUNDS HEART SOUNDS Blood turbulence from closing valves 2 sounds: Lubb (closing of valves between atria and ventricles) Dupp (closing of valves after ventricles) HEART SOUNDS Heart physiology • Internal pacemaker regulates beating of heart by setting a rhythmic electrical excitation 1. Begins in (1) sinoatrial node (in right atrium) 2. to atrioventricular node (2)(between atria) to 3. bundle of His (3)to 4. right and left bundle branches (interventricular septum towards apex) (4) to 5. Purkinje fibers (from apex upward) (5) This “wave” of activity is picked up by an electrocardiogram (ECG) ELECTROCARDIOGRAM (ECG or EKG) Recorded electrical currents of heart Determine healthy heart P wave: atrial depolarization (contraction follows) QRS complex: ventricular depolarization T wave: ventricular repolarization (start relaxing) BLOOD FLOW pulse • Alternating expansion and recoil of an artery • Wrist pulse = radial artery • Neck pulse = carotid artery Blood pressure • Generated by contraction of ventricles • Pressure exerted by blood on walls of a blood vessel • Highest in aorta; falls as distance from left ventricle increases • Bp, as a vital sign, measures pressure in aorta/large arteries Blood pressure • 2 measurements: systolic (heart contraction) and diastolic (relaxation) pressure. EX. 120/80 • Affected by cardiac output and peripheral resistance Cardiac output • Stroke volume x heart rate • Stroke volume (SV) = amount of blood ejected from heart each minute. • HR = # of beats per min. resistance • Affected by – diameter of blood vessel: – Blood viscosity (ratio of rbc to fluid): increase by dehydration, polycythemia; decrease to anemia, hemorrhage – Total blood vessel length: obesity • What does blood pressure measure? • What factors can raise blood pressure? Systolic Diastolic FACTORS AFFECTING BLOOD FLOW Vol. of blood through any tissue for a given time period. Factors: Cardiac output: heart rate x stroke volume (amount of blood per minute) Blood pressure Resistance Size of vessel diameter Blood viscosity Total blood vessel length HYPERTENSION High blood pressure Major cause of heart failure and stroke Causes: Overweight Excessive alcohol Lack of exercise Diet: high saturated fat (meat/butter)*****, high salt, low minerals (potassium, calcium) Stress ******** newest science indicates processed food is to blame, not saturated fat