* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Heart Physiology
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
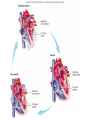
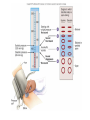
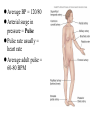
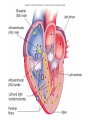
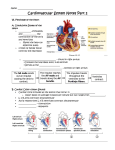
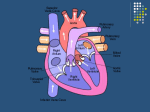
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Heart Physiology CARDIAC CYCLE Systole *Atria Contract, Ventricles Fill *Ventricles Contract, Blood Forced into Aorta and Pulmonary Trunk Diastole *Atria Relax & Fill *Ventricles Passively Receive Blood from the Atria BLOOD PRESSURE BP = pressure blood exerts on inner blood vessel walls BP keeps blood moving between heart contractions BP rises & falls in response to heart contraction & relaxation BLOOD PRESSURE Systole - Contraction of ventricles causes arterial pressure to rise - Systolic pressure (SBP) is the maximum pressure during contraction BLOOD PRESSURE CONTINUED Diastole - Relaxation and refilling of ventricles while semilunar valves are closed - Arterial pressure drops as blood flows “downstream” - Diastolic pressure (DBP) is the minimum pressure just before the next systole Average BP = 120/80 Arterial surge in pressure = Pulse Pulse rate usually = heart rate Average adult pulse = 60-80 BPM CONDUCTION SYSTEM OF THE HEART Specialized Cardiac Muscle Tissue Capable of Generating & Conducting Action Potentials Autorhythmic Stimulates Contraction of Myocardial Tissue CONDUCTION SYSTEM OF THE HEART continued 5 Components: - Sinoatrial Node (Pacemaker) * Right Atrium * Spontaneously Depolarize * Activates Atrial Contraction * Origin of Heart Beat * Action Potential Spreads to: CONDUCTION SYSTEM OF THE HEART continued - Atrioventricular (AV) Node * Rt. atrium (interatrial septum) * Action potential spreads to: - Atrioventricular Bundle (Bundle of His) * Only electrical pathway between atria & ventricles (C.T.Block) * Interventricular septum * Carries action potential through interventricular septum to: CONDUCTION SYSTEM OF THE HEART continued - Bundle Branches (Left & Right ) * Interventricular septum * Carries action potential toward respective ventricles - Purkinje Fibers * Myocardium of Ventricles * Conduct action potentials to ventricular myocardium ELECTROCARDIOGRAM (ECG/EKG) Record of Electrical Changes in Heart Muscle Electrical Changes due to Depolarization & Repolarization of Cardiac Muscle Fibers Metal Electrodes Applied to Skin, Attached to Physiograph, Pick-up Electrical Activity Normal Cardiac Cycle Gives Rise to Characteristic “Waves” ELECTROCARIDOGRAM (ECG/EKG) continued P Wave - SA Node Stimulates Atrial Depolarization - Occurs Prior to Atrial Contraction QRS Complex - Ventricular Depolarization - More Tissue, More Electrical Activity, Larger Wave - Occurs Prior to Ventricular Contraction T Wave - Ventricular Repolarization HEART SOUNDS Caused by Closing of Heart Valves AV Valves - prevent blood from flowing backwards into atria - “Lubb” Semilunar Valves - prevent blood from flowing backwards into ventricles - “Dupp” HEART MURMURS Abnormal sound Often indicates valve disorder Causes: - Congenital defects - Scarring - Insufficiency/Backflow