* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Circulation -core notes File
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
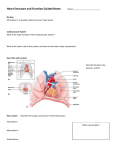
6.2 The Transport System 1. Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the heart. 2. State that coronary arteries supply heart muscle with oxygen and nutrients. 3. Explain the action of the heart in terms of collecting blood, pumping blood, and opening and closing of valves. A. the heart: composed mainly of contractile muscle tissue, supported by connective, nerve, and epithelial tissues B. collecting of blood: deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium from the inferior and superior vena cava oxygenated blood enters the left atrium from the pulmonary vein C. pumping of blood: contraction of the atria (right and left) pumps the blood into the ventricles (right and left) contraction of ventricles (right and left) pumps the blood into the pulmonary artery(right) and aorta (left) D. opening and closing of valves: as a function of pressure differences, one-way valves prevent backflow of blood atrioventricular valves prevent backflow from ventricles into atria semilunar valves prevent backflow of blood from pulmonary artery into right ventricle and from aorta into left ventricle 3. Outline the control of the heartbeat in terms of myogenic muscle contraction, the role of the pacemaker, nerves, the medulla of the brain and epinephrine (adrenaline). A. heartbeat: electrical impulses cause regular contractions of, first the two atria, and then the two ventricles B. pacemaker and myogenic muscle contraction: the sino-atrial node (SAN), known as the pacemaker, is a specialized set of cells located on the right atrium SAN, not the brain, generates regular electrical impulses autonomously SAN impulses spread throughout both atria, causing simultaneous contraction impulse spread to ventricles only at the atrio-ventricular node (AVN) with a delay of about 0.1 seconds AVN transmits electrical signals to heart apex via bundles of His signals trigger powerful contractions of both ventricles from the apex toward the atria bundle of His transmits electrical signals throughout ventricles via Purkinje fibers, causing simultaneous contraction of ventricles C. nerve stimulation: sympathetic nerves from brain release epinephrine, increasing heart rate parasympathetic nerves from brain via vagus nerve decrease heart rate D. hormone stimulation: adrenaline (epinephrine) from adrenal medulla increase heart rate 5. Explain the relationship between the structure and function of arteries, capillaries, and veins. vessel Artery Structure -inner endothelium -thick walls of smooth muscle with elastic fibers Function move blood away from heart under very high pressure & high speed (10-40 cm/sec) -outer layer of connective tissue with elastic fibers Veins -inner endothelium -thin walls of smooth muscle with elastic fibers -outer layer of connective tissue with elastic fibers move blood toward the heart under very low pressure fiber (10 mm Hg) & moderate speed (5-20 cm/sec) -prevent backflow of blood -valves -thin single layer of endothelium of dissolved capillary & tissues -surrounded by basement membrane -numerous allow diffusion materials between blood under low pressure (20- 40 mm Hg) & low speed (< 1 cm/sec) 6. State that blood is composed of plasma, erythrocytes, leucocytes (phagocytes and lymphocytes), and platelets 7. State that the following are transported by the blood: nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, antibodies, urea and heat.