* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lifestyle/Chronic Diseases ( Non
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
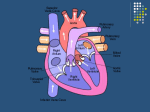
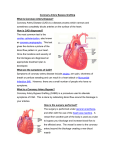
Lifestyle/Chronic Diseases ( Non-Communicable) Unit 8 In The Book Page 514 Lifestyle/Chronic Diseases - diseases caused by lifestyle choices, genetics, and/or environment and not communicable. Factors That Have An Influence Cardiovascular Diseases (diseases of the CV system) p.515 Heart Diseases- any disease of the heart muscle or other working parts of the heart. Coronary Heart Disease- A disease in which the coronary arteries are narrowed or blocked. Coronary Artery- is a blood vessel that carries blood to the heart muscles. Plaque- hardened deposits of fat. Factors which could lead to CVD -gender, heredity, smoking, hypertension, high cholesterol, poor diet, diabetes, obesity, lack of exercise & stress. Leading Causes of Death Types of Diabetes 523 InsulinGlucose- Heart Attack (Myocardial Infarction) P. 517 - Death of heart muscle (no O2) Blood Vessels p.210 1. Arteries- carry blood away from the heart, largest blood vessels with thick muscular walls. 2. Veins- carry blood towards the heart. 3. Capillaries- connect arteries to veins. Blood Vessel Problems Thrombus- a stationary clot in the blood. Embolus- a traveling blood clot. Aneurysm- the ballooning out of an artery at a point where it has become weak. Hemorrhage- the breaking of an artery wall at a point where it has grown weak. Atherosclerosis p.516 - a disease in which plaque collects on artery walls. Arteriosclerosis- tends to occur naturally as people age. Other Types of Heart Disease p.515 Congenital- “born with” Murmur- a heart sound that reflects damaged or abnormal heart valves. Pacemaker- a device that is implanted in the heart to stimulate normal heart contractions. Rheumatic Fever- occurs chiefly in children and teens and includes inflammation of the heart valves. Blood Pressure p.519 Hypertension- high blood pressure, “silent Killer”. Hereditary 120 systolic- contraction ( good BP) 80 diastolic- relaxation 140/90 ( High BP) PrehypertensionStage IStage IISphygmomanometer- used to measure BP High Cholesterol • Below 200 milligrams per deciliter is desirable (total) Two types 1. High Density Lipoproteins (HDL) 2. Low Density Lipoproteins (LDL) LDL • • • • Bad Builds up on artery walls (atherosclerosis) LDL levels should be below 130 mg/dl Raises by consuming Sat. Fat HDL • • • • Good Takes fat out of blood HDL levels should be above 45 mg/dl Raises w/exercise and fruits, veg & whole grains Stroke (Brain Attack)P. 516 - a condition caused by a blocked or broken blood vessel in the brain, basically shutting off all blood flow to the brain. Causes: Thrombus, Embolus, Hemorrhage, Aneurysm, compression from a tumor. Symptoms of a Stroke • • • • • • Sudden weakness, numbness, tingling Loss of speech Dizziness, unsteadiness Dimness, loss of vision Paralysis Disability or death In a major stroke, part of the brain will die causing mental & physical damage & loss of functioning. Diagnosis & Treatment P. 520 Electro-CardiogramCardiac CatheterizationStress TestEchocardiogramNuclear Stress TestAngioplastyStent- Cancer P. 531 -An uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells which spreads into surrounding tissue and other body parts. Tumor P.531 Tumor- an abnormal mass of tissue that can live and reproduce itself, but performs no service to the body. Benign- non-cancerous, as does not spread to other parts of the body. Malignant- is a cancerous tumor, that may spread to other parts of the body. Stages P.531 Metastasis- is the spread of cancer. “In Situ”- cancer not spreading, in its original location. How Cancer Develops 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Exposure to Carcinogen or initiator Initiator enters cell Cells’ genetic material changes Promoter may be present Multiplication of cells Tumors develop Malignant tumor grows & spreads to surrounding tissue 8. Metastasis occurs Warning signs of Cancer p.534 C A U T I O N Common Cancers P.532 & 533 (Table 49.1) Male- lung, prostate, colon-rectum Female- lung, breast, colon-rectum, uterus Initiators (Causes): 1.Heredity(lung,colon,rectal,breast,uterine) 2.Carcinogens 3.Radiation 4.Viruses 5.Lack of Exercise or Poor Diet Reducing Your Risk of Cancer P.534 & 535 Treatment Approaches P. 536 • • • • Surgery Radiation Therapy Chemotherapy Immunotherapy