* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
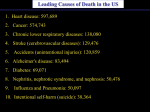
Medical Terminology: Cardiovascular Disease Angi/o: blood Arteri/o: artery Brad/y: slow Cardi/o: heart Cereb/o: cerebrum Cor: heart Cyan/o: blue Gram/o: Hemangi/o: blood vessels My/o: muscle Orrhex’s: Phleb/o: vein Scler/o: hard Tach/y: fast Thromb/o: clot Vas/o: blood vessel Varix: swollen vein Vena: vein Xanta/o: yellow Cardiovascular Diagnostic Terms Aneurysm: the dilation and bulging of smooth muscle usually found at the points where cerebral arteries divide or split Arteriosclerosis: general term for thickening of the walls of the blood vessels with a resulting loss of vascular elasticity and narrowed lumen Atheroma: degeneration of the walls of the arteries caused by accumulated fatty acid deposits and scar tissue leading to the restriction of circulation and risk of thromlous Atherosclerosis (AS): Thickening of the blood vessel walls specifically caused by the presence of plaque Cardiac Arrest: sudden unexpected loss of heart function Cardiac Cachexia (CVD): associated malnutrition/wasting syndrome characterized by extreme skeletal muscle wasting, fatigue, and anorexia Cardiomegaly: enlarged heart Cerebrovascular accident (CVA): a stroke, rapid developing loss of brain function due to disturbance of blood supply to the brain Congestive heart failure (CHF): impairment of the ventricles’ capacity to eject blood from the heart or to fill with blood Coronary heart disease (CHD): coronary arteries narrow from accumulation of plaque and decrease blood flow Dyslipidemia: conditions in which LDL levels are elevated and HDL levels are low Embolism: obstruction in blood vessel due to a blood clot Fatty Streaks: composed of macrophage white blood cells; early stage of atherosclerosis Homocysteine: naturally occurring amino acid found in blood plasma, high levels may cause heart attacks, vascular disease and strokes Hypercholesterolemia: presence of abnormal amount of cholesterol in cells and plasma in the blood Hyperlipoproteinemia: any various disorder of lipoprotein and cholesterol metabolism that result in high levels of lipoprotein and cholesterol circulating in the blood Hypertension (HTP, HTN): condition of chronically elevated blood pressure Ischemia: inadequate supply of oxygen Myocardial infarction (MI): necrosis of the myocardial cells as a result of oxygen deprivition Myocarditis: inflammation of heart muscle Plaque: the noncalcified accumulation of oral microorganisms and their by-products that adhere to the teeth Thrombus: blood clot Cardiovascular Symptomatic Terms Angina syndrome/anginapectoris: Angina: chest pain caused by oxygen deficit to the heart. Two forms are stable and unstable Anoxia: absence or lack of oxygen in tissues and organs Asystole: failure of the ventricles of the heart to contract, leads to no heartbeat Bradycardia: abnormally slow heart action Cardia edema: results from congestive heart failure; lungs fill with fluid because the ventricle is not able to pump out blood it receives from the lungs Claudication: pain in the arms and legs due to inadequate blood flow to those muscles Palpitation: rapid, strong, irregular heartbeat due to illness or exertion Systole: contraction phase of the cardiac cycle; during this phase blood is ejected from the ventricles into the aorta and pulmonary artery. Tachycardia: abnormally rapid heartbeat Vasoconstriction: constriction of blood vessels, which increases blood pressure Vasodepression: dilation of blood vessels, which decreases blood pressure Xanthoma: an irregular yellow patch or nodule on skin caused by deposition of lipids Cardiovascular Chart Abbreviations AHA: American Heart Association AI: Adequate Intake ASHD: Arteriosclerotic heart disease Atr: atrophy AV: arteriovenous BP: blood pressure Brady: bradycardia BV: blood vessel CAD: coronary artery disease Cardio: hear CBC: complete blood count CCCR:closed chest cardiac reconstruction CABG: coronary artery bypass graft CCU: coronary care unit CHD: coronary heart disease CHF: congestive heart failure Chol: cholesterol CP: cardiopulmonary CPR: cardiopulmonary resosutation CVA: cerebrovascular accident ECG/EKG: electrocardiogram FFA: free fatty acid Fib: fibrillation HCVD: hypertensive cardiovascular disease HTN/HPT: Hypertension MI: myocardia infarction MS: multiple sclerosis, morphine sulfate MVR: mitral valve repair HTG: hypertriglyceridemia OHS: open heart surgery PA: pulmonary artery PT: physical therapy/prothrombintime RHD: round heart disease SOB: shortness of breath Tach: tachycardic TG: triglycerides/test guidelines Throm: thrombis Vent: ventras