* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Division and Genetic material
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Transformation (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
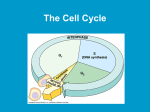
4.1 Cell Division and Genetic Material SBI3U Genetics: The study of how genetic information is passed from one generation to the next. Recall: Cell Theory 1) All living things are composed of one or more cells 2) Cells are the smallest units of living organisms 3) New cells come only from pre-existing cells by cell division DNA Structure DNA is the genetic information that an individual inherits from his/her parents. DNA is double stranded and is called a double helix During cell division (mitosis), DNA is replicated so that each new cell (daughter cell) receives an identical copy of the genetic information from parent cells DNA Structure DNA is made up of many nucleotides joined together as a chain. This chain is known as polynucleotide. DNA Structure Made up of 3 main parts 1)Phosphate group: -Binds to the deoxyribose (phosphodiester bond) to form the backbone of the DNA 2)Nitrogenous base: -Carbon ring (s) -bound to the sugar (A,C,T,G) 3)Pentose Sugar: -5 carbon ring -Deoxyribose The Deoxyribose sugar on the DNA does not have an oxygen on the 5th carbon. RNA has a ribose sugar, which has an oxygen atom on the 5th carbon.. Nitrogenous Bases: 1) Pyrimidine: - Cytosine, Thymine and Uracil( only in RNA) 2) Purine: - 2 ring structure - Adenine & Guanine Complementary base-pairing: Adenine – Thymine Guanine - Cytosine U DNA Structure Genome: Complete DNA sequence of an organism. Test your Understanding…. Complementary Base Pairing What would the complementary strand be? A T T C G A A CT a) T A A G G T C A G b) T A A G C T T G A c) G C C A T G G T C Recall: Key Terms Chromatin: uncoiled, uncondensed DNA Chromosome: coiled DNA (many strands of chromatin) Video https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xUrlreMaUrs The Cell Cycle 5-6 hours 3 main stages: Interphase, Mitosis, Cytokinesis 10 – 12 hours 4-6 hours Less than 1 hour Which phase does the cell spend most of its time? The Cell Cycle Process of growth and cell division for somatic cells ( body cells) One complete cycle produces 2 new daughter cells One cycle takes approx. 12-24 hours Function = Growth, Repair & Maintenance of cells INTERPHASE Stage where the cell grows and makes copies of genetic information and prepares the cell for division. 3 Stages G1 (First Growth Phase) : synthesizes new molecules S (Synthesis Phase): DNA is copied and in the form of chromatin. G2 (Second Growth Phase): synthesizes more proteins that prepare for cell division. MITOSIS The copied genetic material separates and prepares for the separation of two new daughter cells. The splitting of genetic information allows each new daughter cell to have identical genetic information. Subdivided into 4 main phases: Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase ( PMAT) 4 stages of Mitosis 1) Prophase Chromatin condenses into chromosome The chromosome arms are sister chromatids and are joined at the center by the centromere. Nuclear membrane breaks down and nucleus disappears. Spindle fibres are formed and migrate to opposite poles 2) Metaphase Spindle fibers attach to the centromere of the sister chromatids The sister chromatids line up at the equator of the cell forming a metaphase plate. 3) Anaphase Each centromere separates, causing the sister chromatids to separate. Each chromatid migrates to the opposite pole. One complete set of chromosomes is now on both poles of the cell. 4) Telophase Chromosomes unwind into chromatin Spindle fibers break down Nuclear membrane forms around the new set of chromosomes Cleavage Furrow Nucleolus forms within each new nucleus. CYTOKINESIS Process of nuclear division The cytoplasm divides and creates two new daughter cells The microfilaments on the cytoskeleton of the cell wall pinch and separate the cytoplasm. The cytoplasm divides equally between the two cells. Cytokinesis in Plant Cells Have a cell wall that is rigid A cell plate forms between the two nuclei and separates the two daughter cells. A new cell wall then forms around the cell plate. HOMEWORK Read & Make notes pgs. 160-165 Complete Pg. 164 Q# 1-4, 6