* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Tutorial - 3: Diuretics
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of beta-blockers wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of cephalosporins wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of antiandrogens wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Toxicodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of non-nucleoside reverse-transcriptase inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of direct Xa inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of neuraminidase inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of integrase inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotease inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
NK1 receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of proton pump inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of ACE inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
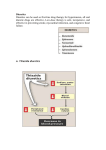
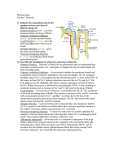
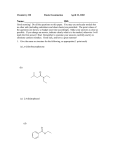
Medicinal Chemistry-III, Tutorial - 3 Medicinal Chemistry – III Tutorial – 3 (Home Work) DIURETICS 1. Define and classify diuretics. Give two examples of each class of diuretics. 2. What is the site of action and mechanism of action of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (CAIs)? Give two examples. 3. Write the mechanism of action, three (3) clinical indications and three (3) side effects of Methazolamide. 4. What the site of action and mechanism of action of loop diuretics? Give two examples of drug as loop diuretics. Write three (3) clinical indications and three (3) side effects of loop diuretics. 5. What is the advantage of loop diuretics over carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (CAIs)? 6. Write the structure activity relationship (SAR) of 5-Sulfamoyl-2- and -3-aminobenzoic acid derivatives. 7. What is the advantage of ethacrynic acid over other sulfamoyl containing diuretics? 8. Write the site of action and mechanism of action of thiazide diuretics. Give two examples of thiazide diuretics. Write clinical indications and side effects of thiazide diuretics. 9. Write the structure activity relationship (SAR) of thiazide diuretics. 10. What is the difference and similarity between thiazide diuretics and thiazide-like diuretics? Give one example of thiazide-like diuretics. 11. Write the site of action and mechanism of action of potassium-sparing diuretics. Give two nexamples. Write clinical indications and side effects of potassium-sparing diuretics. 12. What are osmotic diuretics? Give two examples.Write four features of osmotic diuretics. Medicinal Chemistry-III, Tutorial - 3 A CH3 B H2NO2S N C CH3 H O S H2NO2S C N C CH3 O S Cl D CL Cl NH CH2 O CH2COOH O CH2 C H2NO2S H3CH2C COOH C O Cl N H2NO2S S E O F H 21 19 11 10 3 4 5 8 7 6 S H2N NH O 8 1 7 N N 6 N 4 5 S NH2 N3 15 H 2 20 16 9 2 O 17 13 14 1 H2NO2S O O 12 18O H N NH O G Cl NH2 CH3 O OH I J OH OH HO OH OH 3 Cl 2 4 OH 1 H2NO2S 5 6 1 HN 2 3 O 13. Compound ______ and _______ are carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (CAIs). Compound ___ is more potent CAI than compound _______. 14. Compound _______ acts as diuretic at site _________ and causes metabolic acidosis as one of the major side effect. 15. The name of the compound C is ____________________ and acts at site ________ in the ______________________________________ of nephron. The advantage of compound C as compared to compounds A and B is that it does not cause ______________________. 16. Compound ____________ can be given as a diuretic to those patients who are hypersensitive to sulphur containing drugs. 17. Compound/s __________ can be given as a diuretic to a patient suffering from hyperuricemia. 18. Compound/s ______________ is/are not preferred drug of choice for a patient suffering from hyperuricemia because they can cause ________________________ as side effect. Medicinal Chemistry-III, Tutorial - 3 19. Compound ____________ is an example of hydrothiazide and its name is _____________. 20. The name of the compound J is ____________________ and it is an example of _________________________ diuretics and it acts at site _________ in the __________________________________________ and __________________________ of the nephron. The efficacy, electrolyte excretion pattern, and adverse effects of compound J is similar to _______________________ diuretics. 21. The metabolites of compound ___________ is equiefficacious diuretics. The name of the metabolites are ___________________________________________________________. 22. Diuretic drug/s ________________ can also be used for the treatment of anion overdose, hyperkalemia and hypercalcemia. 23. Compounds ________________ can block Na+ / K+ / 2Cl- cotransporter at site ________ in the _____________________________________________ of the nephron. 24. The diuretics drug/s _____________ can also be used for urinary alkalinization to increase the excretion of uric acid and also for the treatment of Glaucoma and acute mountain sickness. 25. Compound ____________ is an example of thiazide and its name is __________________ and it acts at site ____ in the __________________________________________ and ____________________________________________ of the nephron. 26. Compounds __________ are generally given in combination with other diuretics to reduce their hypokalemic (potassium loss) side effects. 27. The name of the compound G is ____________________ and it shows diuretic effect by antagonizing _________________ in the _____________________________ of kidney. 28. Compound _____ is metabolized to _____________________ which is an active aldosterone antagonist. 29. Compound ________ has structural similarity to folic acid and certain dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) inhibitors but cannot be used as an anticancer agent. 30. Compound ________ has structural similarity to folic acid and certain DHFR inhibitors but used as a diuretic agent mainly in combination with other diuretics __________________ to reduce ________________________________________. 31. Compounds _________________________ and _____ show hypokalemic side effect which can be reduced if they are used in combination of compound ________ or ______. 32. Compound _____ can prevent the reabsorption of up to 28% of the filtered load of water. 33. The name of the compound I is ________________ and it is an _____________ diuretic.