* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Stems
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
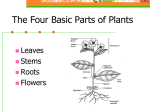
Stems Stems • A stem is the other structural axis for the plant after roots. • It is composed of nodes and internodes. • Nodes hold buds which can grow into leaves, flowers, cones, branches, etc… • Internodes are the spaces between nodes. Stems • A shoot is not the same as a stem! Shoots are any new plant growth, not just new stems. • Stems are usually located above the surface, but there are some plants with underground stems. Stem functions • 1) 2) 3) 4) Stems have four main functions: Support and elevation for leaves, flowers and fruits Transport of materials between the roots and the shoots Nutrient Storage Annual, lateral, plant growth Types of Stems • Herbaceous: softer texture stems that die at the end of the growing season; nonwoody. • Woody: hard textured stems with secondary xylem • Woody stems longer than 5m with a trunk make the plant a tree. Dicot Stems • Pith in the center • Outside of stem is still the epidermis • Lateral growth is due to the vascular bundles in a ring Dicot Stems IF WOODY STEM: • Each vascular bundle has a meristem between the xylem and phloem • Secondary xylem grows to the inside, while secondary phloem grows to the outside • The epidermis and cortex get destroyed as the secondary xylem and phloem grow. Dicot Stems The plant produces a cork cambium layer on the outside which replaces the epidermis. • The outer region develops into the bark which protects the outside of the woody dicot. • Secondary Xylem is known as heartwood, while secondary phloem is known as sapwood. Monocot Stems • Have vascular bundles throughout, though usually concentrated near the edge. • Rarely produce secondary growth as they are rarely woody. • Grow laterally due to anomalous growth. Specialized Stems • Bulb: short underground stem with fleshy leaves attached (tulip, onion, daffodil) • Climbing: stems that cling to or wrap around other plants or structures (ivies, vines) Specialized Stems • Corm: short, enlarged, underground stem (gladiolus, crocus) • Rhizome: a horizontal, underground stem used mainly in reproduction, but also in storage (ferns, iris) Specialized Stems • Stolons/Runners: horizontal, above ground stems to produce new rooted plantlets when they touch the surface (strawberries, spider plants) • Tuber: swollen, underground stems used for storage (potatoes)