* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 6th - inside earth study guide1
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
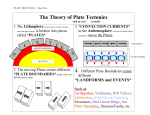
Name: ____________________________________ Test Date: ____________________________________ 6th Grade Earth Science – Earth Layers, Magnetism & Plate Tectonics Understand the following vocabulary terms: crust – the layer of rock that forms Earth’s outer surface lithosphere – a rigid layer made up of the uppermost part of the mantle and crust mantle – the layer of hot, solid material between Earth’s crust & core asthenosphere (convecting mantle) – the soft layer of the mantle on which the lithosphere floats outer core – a layer of molten iron and nickel that surrounds the inner core of the Earth inner core – a dense sphere of solid iron and nickel at the center of the Earth magnet – a material that attracts steel, iron, cobalt, and nickel Earth as a magnet – the Earth acts like a magnet because of the liquid outer core made of iron and nickel which spins as the earth rotates and creates a magnetic field and the north & south poles on earth compass – an instrument composed of a small, light-weight magnet called a needle, that is balanced on a frictionless bearing continental drift – the hypothesis that the continents slowly move across the Earth’s surface sea-floor spreading – the process by which molten material adds new crust to the ocean floor subduction – the process by which ocean floor sinks beneath a deep-ocean trench and back into the mantle. plate tectonics – the theory that pieces of Earth’s lithosphere are in constant motion, driven by convection currents in the mantle divergent boundary – a plate boundary where two plates move away from each other convergent boundary – a plate boundary where two plates move toward each other transform boundary – a plate boundary where two plates move past each other in opposite directions earthquake – when plate boundaries slide past each other , build up pressure & cause a sudden, violent shift volcano – forms where plates diverge and magma reaches earths surface & where plates collide and one subducts into the mantle forming molten material mountain building – when two plates collide & crush together causing land to be pushed up, resulting in the folding and breaking of Earth’s crust Be prepared for questions similar to those below: See bold for suggested answers. 1. In the table below, study what you know about each layer including its location, composition (iron, nickel, rock, crust & upper mantle) and state of matter (solid or liquid). Also, be able to identify where each layer is located (from an image). Crust Location on Earth: Top layer also part of the lithosphere Composition (made of): Rock State of Matter: Solid Lithosphere Location on Earth: part crust, what the tectonic plates are made of Composition (made of): crust & upper mantle, rock (hard like jolly rancher) State of Matter: Solid Upper Mantle Location on Earth: part of the lithosphere Composition (made of): Rock State of Matter: Solid Middle Mantle/ Asthenosphere Location on Earth: Under the lithosphere, the lithosphere floats on this (where the convection currents are) Composition (made of): Rock (soft like laffy taffy) State of Matter: Solid Lower Mantle Location on Earth: Below the asthenosphere Composition (made of): Rock State of Matter: Solid Outer Core Location on Earth: Under the mantle Composition (made of): Metal (iron & nickel) State of Matter: Liquid Inner Core Location on Earth: Under the mantle Composition (made of): Metal (iron & nickel) State of Matter: Solid 2. List all the ways in which the Earth is like magnet. i. both have poles (north & south) ii. both are composed of (nickel & iron) iii. both create a magnetic field iv. both attract iron & nickel 3. What creates Earth’s magnetic field? The rotational forces within the Earth’s liquid iron layer (the outer core) 4. Why is a compass composed of a frictionless bearing & a lightweight magnet? To allow the needle to turn easier because Earth’s magnetic field is very large 5. Where can a compass be used for navigation & why? On land & at sea because the magnetic field of earth is so large it can be used by a compass anywhere 6. The tectonic plates are part of this Earth layer Lithosphere 7. On average, the Earth’s lithospheric plates move about how far each year? A few centimeters Complete the plate boundary table below: Plate Boundary Definition Is crust created or destroyed? destroyed What geologic event occurs? Volcanoes and Earthquakes Mountain Building Convergent Where two plates come together, collide, when one goes beneath the other it is subduction Divergent Where two plates move away from one another, divide, separate created Volcanoes, Earthquakes Mountain building Transform Where two plates move past each other, slide neither Earthquake 8. At what type of plate boundary do mountains form? Convergent, (underwater – divergent) 9. At what type of plate boundary do volcanoes occur? Convergent & Divergent 10. What is the cause of an earthquake? When plates slide past one another at a transform boundary and energy stored in the Earth’s crust is suddenly released. 11. What is it called when an oceanic plate dives beneath a continental plate? Subduction Use the map below to answer the questions that follow. 12. Describe what happens at the two plate boundary locations between the Pacific Plate & the North American Plates? Where the arrows move in opposite directions past one another, this is a transform boundary and earthquakes may occur here. Where the arrows move towards one another, the plates are converging (i.e. colliding) & one must subduct (the pacific) beneath the other (the North American). A mountain range occurs here. 13. Describe what happens between the American Plate and the Eurasian plates? Where the arrows move away from one another, the plates are diverging (separating) & new crust is created here (and possibly volcanoes). 14. Compare what happens between the Cocos & Caribbean Plates to what is happens between the Antarctic & South American Plates. Both plate relationships are convergent. One plate in each will subduct beneath the other causing volcanic activity or mountain formation.