* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 1:
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
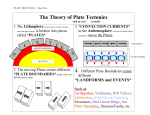
Geology 101 Lecture Outline Lecture #3 Basic Plate Tectonics & Plate Boundaries 1. Another look at the Earth’s uppermost layers a) Separate by behavior instead of composition b) Lithosphere - a brittle layer of rock that is approx. 100 km thick i) therefore, this layer includes all of the crust and the uppermost part of the mantle c) Asthenosphere - a plastic-behaving layer that lies directly under the lithosphere; from 100 km depth to maybe 700 km? i) therefore, it is still within the upper part of the mantle 2. A Plate a) An “independent” piece of lithosphere that is “floating” on the asthenosphere b) Earth outer region is composed of a number of these plates c) Each plate moves somewhat independently, but at its edges it will be greatly effected by the adjacent plates 3. Tectonics - Study of the deformation of the Earth’s lithospheric plates 4. Plate Boundaries - line along with two adjacent plates are in contact - There are 3 types of boundaries: a) Divergent boundary (also called a Spreading Center) - Occurs when two plates are moving away from each other (e.g. the middle of the Atlantic Ocean) i) New lithosphere is created to fill the gap they leave through nearly continuous volcanic activity b) Convergent boundary - Occurs when two plates move toward each other: Two types i) Subduction zone - where one plate, it must have oceanic crust, is pushed beneath another other(e.g. off the WA and OR coast) a) Earthquakes and volcanic activity ii) Continent-Continent collision - where both plates have continental crust and they push upward to form huge mountains (e.g. Himilayas) a) Earthquake activity, but no active volcanoes c) Transform boundary(also called a Strike-slip boundary) - Occurs where two plates slide past one another (e.g. San Andreas fault) i) Very active earthquake zone 1