* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plate Tectonics - ESL Consulting Services
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
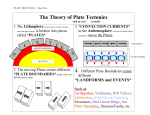
The Important Thing About Geoscience By Jody Decker- Bader The important thing about geoscience is that there are processes that continually change the surface of the Earth. ► The structure of the Earth is in layers. ► The top layer is called the crust. ► Below the crust is the mantle. The mantle is made up of a different kind of rock than the crust. ► The upper rigid part of the mantle, together with the crust, is called the lithosphere. It is broken into sections called plates, much the same way as the shell of a hard boiled egg can be cracked into sections. ► On the crust there are oceanic plates and continental plates. ► Below the lithosphere is the part of the upper mantle called the asthenosphere. The asthenosphere contains magma. ► The lithosphereic plates float and move on top of the moveable asthenosphere. This is the process that continually changes the surface of the Earth. ► Movement happens along plate boundaries. ► Geologists classify these movements into three categories. ► The first is a divergent boundary, where two plates move away from each other. ► On the ocean floor a midocean ridge is created when magma from the asthenosphere rises upward. ► The magma fills in the gap where the sea floor spread. Divergent Boundary Mid-ocean ridge ► When the asthenosphere rises beneath a continent, the lithosphere bulges upward and is stretched sideways forming long cracks that eventually fall into themselves creating a rift valley. ► The East African Rift Valley is an example of a divergent boundary on a continental plate. This is a process that continually changes the surface of the Earth. ► The second is a convergent boundary, where two plates move toward each other. ► A subduction zone is formed when the denser heavier oceanic plate is pushed under a continental plate. ► Off the coast of the Pacific NW the Juan de Fuca plate is subducting underneath the North American Plate. Convergent Boundary Subduction Zone ► Convergent boundaries can also happen between two continents. ► When two continents collide and are welded together a suture zone is formed. ► An example of a continentalcontinental convergent boundary is the collision of India and Asia, which began about 45 million years ago, producing the majestic Himalayan mountains. Convergent Boundary Suture Zone This is a process that continually changes the surface of the Earth. ► Volcanoes are also common ► Magma is produced above the subducted plate, and rises toward the surface because it is less dense than the surrounding rock. The “Ring of Fire” around the Pacific Ocean is caused by this melting at subduction zones all around the Pacific. ► Hot spot volcanoes, like along subduction zones, where they form volcanic arcs. Hawaii, are produced when narrow plumes of unusually hot mantle material rise up through the lithosphere, creating pools of magma. This is a process that continually changes the surface of the Earth. ► The third classification of plate boundary movement is a transform boundary, where two plates slide parallel to each other. Transform Boundary ► The surface along which the plates slide is called a transform fault. The longest and most famous transform fault is the San Andreas Fault in California. When plates move past each other the movement is not always smooth. Earthquakes happen when the rocks at plate boundaries can no longer withstand the pressure and move suddenly. This is a process that continually changes the surface of the Earth. ► Geoscientists believe that the process of thermal convection moves the plates. ► Geoscientists divide Earth into five main layers: the inner core, the outer core, the lower mantle, the upper mantle or asthenosphere, and the lithosphere. ► The core is made mostly of iron and is so hot that the outer core is molten. ► This heat from the core is also what keeps the mantle moving in a slow viscous manner, much like melted plastic. ► Heat from deep in the Earth rises toward the surface. It spreads out horizontally, cools, and sinks back into the interior. ► These extremely slow moving flows are called convection cells. ► Scientists hypothesize that convection cells are what help move the lithospheric plates. This is the process that continually changes the surface of the Earth. In conclusion, Plate Tectonics Theory states that 225 million years ago the Earth’s lithosphere was combined into one supercontinent named Pangaea. Over million of years the lithospheric plates assemble, break up, and reassemble. Thermal convection cells distribute heat from deep inside the Earth. This enables the plates to float upon and move on top of the viscous asthenosphere. But, the important thing about geoscience is that there are processes that continually change the surface of the Earth.