* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download New and Improved: How Computer Graphics
Hold-And-Modify wikipedia , lookup
Ray tracing (graphics) wikipedia , lookup
Color vision wikipedia , lookup
Solid modeling wikipedia , lookup
Waveform graphics wikipedia , lookup
BSAVE (bitmap format) wikipedia , lookup
Computer vision wikipedia , lookup
Apple II graphics wikipedia , lookup
Mesa (computer graphics) wikipedia , lookup
Tektronix 4010 wikipedia , lookup
Free and open-source graphics device driver wikipedia , lookup
Framebuffer wikipedia , lookup
Molecular graphics wikipedia , lookup
Rendering (computer graphics) wikipedia , lookup
Graphics processing unit wikipedia , lookup
General-purpose computing on graphics processing units wikipedia , lookup
Bedrich Benes, Ph.D.,
Computer Graphics Technology
About the Speaker
Bedrich Benes, Ph.D
• Ph.D from Computer Science (1998)
• Associate Professor of Computer Graphics Technology
• Assistant Head of Department
• Director of High Performance Computer Graphics Lab
• Cuda Teaching Center
• Purdue University Faculty Scholar
• Over 50 peer reviewed publications including
•
•
•
ACM Transaction on Graphics,
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics,
IEEE Computer Graphics & Applications.
• Funding from Adobe Research, NASA, NSF, NVIDIA, etc.
Overview
• What is Computer Graphics
• Application areas
• Computer Graphics as a discipline
• Human perception system
• Rendering
• Modeling
• Procedural modeling
• Modern GPUs
• Take-home messages
Computer…Graphics
Computer
ehm… what?
!
Def 1:
Computer graphics are graphics created using computers and,
more generally, the representation and manipulation of image
data by a computer with help from specialized software and
hardware.
Def 2:
Computer graphics is a sub-field of computer science which
studies methods for digitally synthesizing and manipulating
visual content. It encompasses three-dimensional graphics as
well as two-dimensional graphics and image processing.
Computer Graphics – Application Areas
Two Dimensional (2D):
• Desk Top Publishing (DTP)
• Video Editing
• Digital Cameras
• Graphical User Interfaces
Computer Graphics – Application Areas
Three Dimensional (3D)
• Movie industry
• Gaming
• Scientific Visualization
• Computer Graphics Itself
© EA
Is Computer Graphics a Science?
CG is about visual simulation of real world
Color
perception
Light source
properties
Tristimulus
value
Reflected
light
Material
properties
Cone sensitivity
Need for Speed?
Real-Time Computer Graphics
• Sacrifice quality for speed
• Usual requirement 60 frames per second
• About 160ms to render the image
Photorealistic Computer Graphics
• As realistic as possible
• No time restrictions
© V. Stejskal
Need for Speed?
Can
Real-Time Computer Graphics
be
Photorealistic at the same time?
CG as a Visual Simulation of Real World
Color
perception
Light source
properties
Tristimulus
value
Reflected
light
Material
properties
Cone sensitivity
Perception
Human visual perception system
• is complex and not well-understood,
• some phenomena are used by CG, but
• many open questions still to be answered.
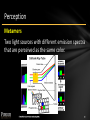
Perception
Metamers
Two light sources with different emission spectra
that are perceived as the same color.
© 2005 Bruce MacEvoy
Perception
Perception
Selective attention - applications
© M.F. Cohen
Level of Detail and Scene Simplification
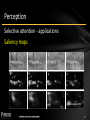
Perception
Selective attention - applications
Saliency maps
© Dashan Gao 2008
Perception
Selective attention - applications
Discarding irrelevant phenomena
CG as a Visual Simulation of Real World
Color
perception
Light source
properties
Tristimulus
value
Reflected
light
Material
properties
Cone sensitivity
CG as a Visual Simulation of Real World
Color
perception
Light source
properties
Tristimulus
value
Reflected
light
Material
properties
Cone sensitivity
Rendering
1. A depiction or interpretation,
as in painting or music.
2. A coat of plaster or cement
applied to a masonry surface.
3. The act or an instance of performing a play,
piece of music, etc.
4. A translation of a text from a foreign language.
5. A perspective drawing showing an
architect's idea of a finished building, interior, etc.
Rendering
We have
• a model in the computer memory (objects),
• its material description (texture),
• light properties.
Rendering means visualizing the model.
Rendering
Real-Time Rendering
simplifies the light-material interaction
Photorealistic rendering
attempts for a precise physics-based evaluation
Rendering
The rendering problem
can be formulated mathematically
by means of so-called rendering equation.
𝐿𝑆 𝒙, 𝜔 = 𝐿𝑒
𝒙,𝜔
′
cos
𝜃
cos
𝜃
′
+ 𝑔 𝒙, 𝒙′ 𝑓𝑟 𝒙, 𝜔, 𝜔 ′ 𝐿𝑓 𝒙, 𝜔 ′
𝑑𝜔
′|
|𝒙
−
𝒙
𝐴
Rendering – Evaluation
Cornell Box
C. M. Goral, K. E. Torrance, and D. P. Greenberg
Rendering
• Rendering is considered a solved problem in
computer graphics.
• We can simulate nearly any effect we want.
• The remaining task is to make it faster.
© Guile3D
Non Photorealistic (Stylized) Rendering
Wait a second…
Do we always need a photorealistic rendering?
Abstraction can deliver unbiased message.
© Kiss
Non Photorealistic (Stylized) Rendering
Application areas:
• Architecture
• Biology
• Medicine
• Computer Aided Design
© Electronic Arts
© S. Eikland
• Gaming
© O. Deussen
Non Photorealistic (Stylized) Rendering
© O. Deussen
CG as a Visual Simulation of Real World
Color
perception
Light source
properties
Tristimulus
value
Reflected
light
Material
properties
Cone sensitivity
Modeling
Color
perception
Light source
properties
Tristimulus
value
Reflected
light
Cone sensitivity
Objects
Modeling
3D Object Creation
is one of the most important problems in CG
Modeling
Various ways:
• manual editing,
• existing object reconstruction,
• procedural modeling,
• simulations,
• …and their combinations.
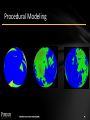
Procedural Modeling
Starting from a set of parameters
a procedure generates the model.
Example:
1. take an object
2. divide it into two parts
3. increase the elevation of one and decrease the
other one (change color, etc.)
4. decrease the intensity of changes 2x
5. apply this step many times
Procedural Modeling
Procedural Modeling
Inverse Procedural Modeling
But can we do it in reverse?
Find a procedure that generates an object!
Very difficult problem…
If solved, could be a solution
to a lot of modeling troubles.
Inverse Procedural Modeling
Inverse Procedural Modeling
CG as a Visual Simulation of Real World
Color
perception
Light source
properties
Tristimulus
value
Reflected
light
Cone sensitivity
Objects
CG as a Visual Simulation of Real World
Color
perception
Light source
properties
Tristimulus
value
Reflected
light
Cone sensitivity
Objects
Where are we now?
Computer Graphics is one of the fastest evolving
areas of technology that affects everyone.
The need for realism and speed is reflected as a
need for processing larger dataset faster.
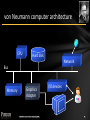
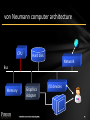
von Neumann computer architecture
CPU
Hard disk
Network
Bus
Memory
Graphics
Adapter
I/O devices
von Neumann computer architecture
CPU
Hard disk
Network
Bus
Memory
Graphics
Adapter
I/O devices
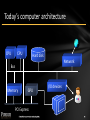
Today’s computer architecture
CPU
CPU
Hard disk
Network
Bus
Memory
GPU
PCI Express
I/O devices
Modern GPUs
Modern GPUs :
• are fully programmable,
• have their own programming languages
and compilers,
• have their own memory, and
• work together with CPUs.
Modern GPUs
NVIDIA GTX 580:
Intel i7 Extreme Edition:
• 3.0 billion transistors
• 774 million transistors
• 1.5 GB memory
• 16 GB memory
• 512 Cuda Cores (CPUs)
• 4 Cores
• Running @ 1.5GHz
•
Running @ 3.5GHz
Modern GPUs
This comparison is not exactly correct…
CPU is effective
for problems with high flow control demand.
GPU is effective
in data-parallel computations.
Modern GPUs
© NVIDIA
Modern GPUs
© NVIDIA
Modern GPUs
But GPUs are only for gaming, aren’t they?
Well. Not exactly….
Modern GPUs
GPUs are extremely powerful co-processors
suitable for data parallel and
computationally extensive tasks.
A new way of computational thinking is
required to fully utilize their potential.
Modern GPUs
NVIDIA CUDA™ is NVIDIA's parallel computing
architecture that enables dramatic increases in
computing performance by harnessing the power
of the GPU.
AMD, INTEL, and NVIDIA have OpenCL
that is a parallel computing API for
CPUs and GPUs.
GPU Programming
App
C for
CUDA
OpenCL
Fortran
DirectX
Compute
NVIDIA driver
NVIDIA hardware
CUDA architecture
CUDA
Python
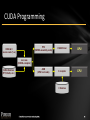
CUDA Programming
CUDA & C
source code (*.cu)
PTX
(NVIDIA assembly code)
CUDA Driver
GPU
ASM
(CPU host code)
C compiler
CPU
nvcc.exe
(NVIDIA compiler)
CUDA libraries
(FFT, BLAS, etc.)
C libraries
CUDA Programming
VecAdd<<<256,256>>>(d_A, d_B, d_C, n);
__global__ void VecAdd(float* a, float* b,
float* c, unsigned int n)
{
int stride=blockDim.x*gridDim.x;
int i= threadIdx.x+blockIdx.x*blockDim.x;
while (i<n){
c[i] = a[i] + b[i];
i+=stride;
}
GPU Systems
The Tianhe-1A Supercomputer, located at National
Supercomputer Center, Tianjin
GPU Systems
• Couples GPUs with multi-core CPUs
• 7,168 NVIDIA® Tesla™ M2050 GPUs and 14,336 CPUs
• The same performance on the CPUs only would need
50,000 CPUs and 2x much floor space
• 2.507 petaflop system built entirely with CPUs would
consume more than 12 megawatts.
• Thanks to the use of GPUs it consumes only 4.04
megawatts, (3 x more power efficient)
GPU Systems
Do we need anything really special?
Most of GPUs are CUDA or OpenCL enabled!
Better systems use
high-end GPUs
Or dedicated “personal supercomputers”
GPU Applications
Computational Fluid Dynamics
GPU Applications
Nanomaterials
Simulation of electromagnetic field
near a quantum well
+
=
GPU Applications
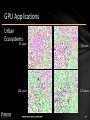
Urban
Ecosystems
25 years
75 years
100 years
125 years
GPU Applications
Urban Ecosystems
Conclusions
• Computer Graphics is one of the fastest evolving
areas of technology.
• It affects everyone’s life.
• Computer Graphics technology (GPUs) seem as
an intermediate step towards a massively parallel
data intensive computing platform.
• We need computational thinking to use it.
Bedrich Benes, Ph.D.,
Computer Graphics Technology