* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MeiosisVocabularyladder
Survey
Document related concepts
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
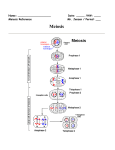
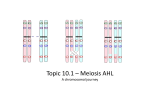
Vocabulary Ladder A Meiosis A process where one diploid cell divides into four haploid cells(sex cells) Haploid Cells that have only one chromosome from each pair Diploid Cells that have pairs of chromosomes (one from each parent) Gamete A male or female sex cell Homologous Chromosomes that have genes for the same traits chromosomes arranged in the same order Sister Two identical chromatids joined by a centromere chromatid Crossover When homologous pairs of chromosomes exchange genetic information Interphase The stage in the cell cycle when the DNA/organelles make copies of themselves Prophase Chromosomes become visible, nuclear membrane dissolves, spindle fibers attach to sister chromatids. (in meiosis, homologous pairs come together and crossover occurs) Metaphase Spindle fibers pull the sister chromatids(mitosis/ metaphase II) or homologous pairs (meiosis) to the middle of the cell. Anaphase Sister chromatids are pulled apart (mitosis) Homologous pairs are pulled to the opposite sides of the cell (meiosis I) Telophase A nuclear membrane forms around the chromosomes cytokinesis The cytoplasm and its contents divide. Sexual A type of reproduction where the offspring are reproduction genetically different than the parents Vocabulary Ladder B Crossover Sister chromatid Diploid cytokinesis Homologous chromosomes Haploid Meiosis Telophase Prophase Sexual reproduction Anaphase Interphase gamete Metaphase When homologous pairs of chromosomes exchange genetic information Two identical chromatids joined by a centromere Cells that have pairs of chromosomes (one from each parent) The cytoplasm and its contents divide. Chromosomes that have genes for the same traits arranged in the same order Cells that have only one chromosome from each pair A process where one diploid cell divides into four haploid cells(sex cells)When homologous pairs of chromosomes exchange genetic information A nuclear membrane forms around the chromosomes Chromosomes become visible, nuclear membrane dissolves, spindle fibers attach to sister chromatids. (in meiosis, homologous pairs come together and crossover occurs) A type of reproduction where the offspring are genetically different than the parents Sister chromatids are pulled apart (mitosis) Homologous pairs are pulled to the opposite sides of the cell (meiosis I) The stage in the cell cycle when the DNA/organelles make copies of themselves A male or female sex cell Spindle fibers pull the sister chromatids (mitosis/ metaphase II) or homologous pairs (meiosis) to the middle of the cell.