* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mechanism underlying anti-apoptotic activity of a
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
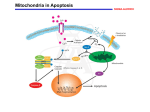
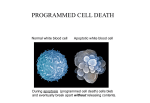
Mechanism underlying anti-apoptotic activity of a (-)deprenyl-related propargylamine, rasagiline by Maruyama W, Yamamoto T, Kitani K, Carrillo MC, Youdim M, Naoi M. Department of Basic Gerontology, Laboratory of Biochemistry and Metabolism, National Institute for Longevity Sciences, Gengo, Morioka-cho, Obu 474-8522, Aichi, Japan. [email protected] Mech Ageing Dev. 2000 Jul 31;116(2-3):181-91. ABSTRACT A potent inhibitor of type B monoamine oxidase, (-)deprenyl, is known to protect or rescue dying neurons, independent of inhibition of the enzyme activity. After long term administration to rodents, a propargylamine structurally related to (-)deprenyl, (R)(+)-N-propargyl-1-aminoindan (rasagiline) increased the activities of antioxidative enzymes, superoxide dismutase and catalase. Rasagiline protected in vitro dopamine cells from apoptosis induced by oxidative stress or neurotoxins. The mechanism of the anti-apoptotic effect was studied by in vitro experiments using human dopaminergic neuroblastoma, SH-SY5Y cells. Peroxynitrite-generating Nmorpholino sydonimine (SIN-1) induced apoptosis in SH-SY5Y cells via disruption of mitochondrial membrane potential (DeltaPsim), followed by caspase 3 activation. Rasagiline prevented the loss of DeltaPsim, the initial step to apoptosis, and also following caspase 3-activation and DNA fragmentation. The results suggest that rasagiline may interact with the specific molecule in the mitochondria and suppress the death signal transduction. By the anti-apoptotic function, rasagiline may rescue or protect declining neurons in aging and neurodegenerative disorders, such as Parkinson's disease.