* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pathophysiology Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Common cold wikipedia , lookup
Urinary tract infection wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Autoimmunity wikipedia , lookup
Inflammatory bowel disease wikipedia , lookup
Acute pancreatitis wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Inflammation wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
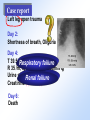
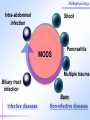
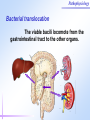
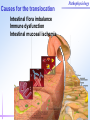
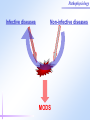
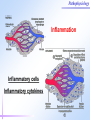
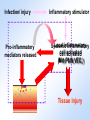
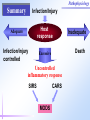
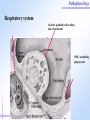
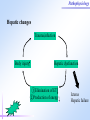
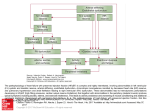
Pathophysiology Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome Pathophysiology Department, Tongji Medical College, HUST World War One Circulatory failure, hypovolemic shock World War Two Korean War Viet Nam War Post-traumaticacute acute Post-traumatic renal insufficiency respiratory insufficiency Seventy’s 70’s syndrome 1991 Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome Case report Left leg open trauma Day 2: Shortness of breath, Oliguria Day 4: 9/L) ↑ T 39.5 ℃↑WBC (18×10 Respiratory failure R 35 /m, cyanosis, PaO2<60mmHg Urine <100ml/d Renal failure Creatinine ↑↑ BUN ↑↑ Day 6: Death Pathophysiology Definition Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome (MODS) is dysfunction of two organs (initially two or more organs initially uninvolved developing within a short short period period of time. Cor pulmonale? Causes Multiple system organ failure. The role of uncontrolled infection . 1980,115(2):136-140. They studied multiple parameters in 553 consecutive emergency surgical patients. MSOF is primarily due to infection. MSOF is the most common fatal expression of uncontrolled infection. Pathophysiology Why did anti-biotic strategies fail in some of the patients with MODS? Intra-abdominal infection Shock MODS Pancreatitis Multiple trauma Biliary tract infection Infective diseases Burn Non-infective diseases Pathophysiology Intra-abdominal infection Shock MODS Pancreatitis Multiple trauma Biliary tract infection Infective diseases Burn Non-infective diseases Pathophysiology Bacterial translocation The viable bacili locomote from the gastrointestinal tract to the other organs. Causes for the translocation Intestinal flora imbalance Immune dysfunction Intestinal mucosal ischemia Pathophysiology Pathophysiology What exactly is "leaky gut" or "increased intestinal permeability"? To understand the importance of increased intestinal permeability, you must first understand the basic concepts that: 1) the intestines are supposed to absorb nutrients, and 2) the intestines are supposed to exclude (not absorb) potentially harmful substances like bacteria, toxins, food proteins (which cause food allergy). Therefore, when we talk about "leaky gut" and "increased intestinal permeability" we are describing a condition where in these basic functions are failing. The intestines are failing in the ability to absorb nutrients, and the intestines are absorbing too many toxins. Pathophysiology Infective diseases Non-infective diseases MODS Pathophysiology Mechanism Uncontrolled inflammatory response Microcirculatory hypo-perfusion Ischemia/reperfusion injury Pathophysiology Causes Q1 Uncontrolled inflammatory response Q2 MODS Pathophysiology Inflammation Inflammatory cells Inflammatory cytokines Pathophysiology Anti-inflammatory reaction IL-10, IL-4, TGF-β IL-1ra ,Lipoxin Cell elimination Pro-inflammatory reaction TNF-a, IL-1, IL-6, IFN TXA2, PAF Cell activation Pathophysiology MODS is the failure of the balance Uncontrolled inflammatory response Pathophysiology Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS) 【Definition】 Anti-inflammatory reaction IL-10, IL-4, TGF-β IL-1ra ,Lipoxin Cell eliminate An uncontrolled inflammation process Pro-inflammatory signals exceed its normal domain or degree Pro-inflammatory reaction TNF-a, IL-1, IL-6, IFN TXA2, PAF ResultCell in activation end-organ damage failure. and multi-system Infection/ injury Pro-inflammatory mediators released Inflammatory stimulator Local inflammatory Systemic inflammatory cell cell activated activated (M,PMN,VEC,) (M,PMN,VEC,) Tissue injury Pathophysiology 【SIRS Clinical manifestations】 Body temperature above 38℃ or less than 36℃. Heart rate >90 beat/min. Respiration rate >20/min or PaCO2 <32 mmHg. WBC >12,000/mm3 or <4000 cells/mm3, or >10% immature cells. Pathophysiology Case review Left leg open trauma SIRS Respiratory failure Renal failure Pathophysiology Compensatory Anti-inflammatory Response Syndrome( CARS) 【Definition】 Anti-inflammatory reaction IL-10, IL-4, TGF-β IL-1ra ,Lipoxin Cell eliminate anti-inflammation process An uncontrolled Anti-inflammatory signals exceed its normal domain or degree Result in end-organ damage and multi-system failure. Pro-inflammatory reaction TNF-a, IL-1, IL-6, IFN TXA2, PAF Cell activation Immune paralysis Pathophysiology Infection/Injury Uncontrolled inflammatory response SIRS Controlled inflammatory response CARS MODS Infection/injury controlled Pathophysiology Summary Infection/Injury Adequate Host response Infection/injury controlled Excessive Death Uncontrolled inflammatory response SIRS CARS MODS Inadequate Pathophysiology Alternations in Functions and Mechanism in different organs Pathophysiology Respiratory system Alveolar epithelial cell swelling lack of surfactant WBC assembling phagocytosis Pathophysiology Highest incidence earliest occurring Mechanism inferior vena cava superior vena cava Respiratory circulation Systemic circulation Pathophysiology Permeability WBC Leukotriene Neutrophils adhesion WBC assembling Main manifestation Pulmonary edema pulmonary hemorrhage Dyspnea death Pathophysiology Urinary system Acute renal failure Mechanism Acute necrosis of tubular cells Decreased perfusion of kidney Pathophysiology Hepatic changes Trauma,infection Body injury Hepatic dysfunction ①Elimination of ET ②Production of energy Icterus Hepatic failure Pathophysiology Isaac Newton (1642-1727) “No great discovery was ever made without a bold guess.” Pathophysiology THANK YOU!