* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Review Notes
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary mismatch wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Vestigiality wikipedia , lookup
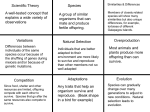
Class 2: Evolution Review • Mechanisms of Evolution • Types of Evidence • Hominids Mechanisms of Evolution • Darwin (mid 1800’s) – Naturalist = biologist who made observations about plants and animals – HMS Beagle Galapagos Islands – Found species similar to those in Central and South America … but slightly different on the different islands. • Natural Selection = organisms with traits best suited for a given environment are more likely to survive and reproduce • Artificial Selection = humans select for desired traits and purposely breed plants and animals for these traits 2 Types of Selection: Artificial Selection -> manmade • Plants • Animals – Dog Breeds Natural Selection –> natural • Galapagos Islands • http://www.youtube.com/w atch?v=n3265bno2X0 Principles of Natural Selection 1. Organisms produce more offspring than can survive 2. Genotypic variations are found among off-spring. Sources of variation include: – – – Mutations Transpositions (Barbara McClintock) Sexual Reproductions 3. Variations are passed on to offspring 4. Some variations allow members of a population to survive and reproduce … while others do not. 5. Over time, offspring with beneficial adaptations survive and reproduce more often more and more of the population exhibit the beneficial phenotype “Evolution” in Our Classroom! • Pick a tool – Knife – Fork – Spoon • Why did you pick the one you did? • Task 1 Results? • Pick a tool – Knife – Fork – Spoon • Task 2 Results? How fast does evolutionary change occur? KEY IDEA: It depends … on the environment! How fast does evolutionary change occur? Types of Evidence • Fossil Record – Dating • Stratigraphy • Radiometric – Geological Timeline • • • • Similarities in genetic make-up Homologous structures Vestigial structures Embryology Fossil Record – Paleontology/ Geology • Dating • Stratigraphy • Radiometric • Geological Timeline http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SY3MZ_wNFW8 Similarities in Genetic Make-up – Molecular Biology • All living organisms have DNA • The more closely related the more commonalities in the sequence and pairs Humans and Chimps share 98 % Humans and other Humans share 99% Commonalities Structures - Anatomy • Homologous structures = Body parts that are similar in origin and structure • Vestigial structures = body part that doesn’t seem to have a function, anymore Embryology • Comparative Embryology Class __: Evolution Review • Mechanisms of Evolution • Types of Evidence • Hominids Mechanisms of Evolution • D________________________ (mid 1800’s) – Naturalist = biologist who made observations about plants and animals – HMS Beagle Galapagos Islands – Found species similar to those in Central and South America … but slightly different on the different islands. • Natural Selection = organisms with t_______________ best suited for a given e_____________________ are more likely to survive and r____________________ • Artificial Selection = h____________________ select for desired traits and purposely breed plants and animals for these traits 2 Types of Selection: A______________________ Selection -> manmade • Plants • Animals – Dog Breeds N________________________ Selection –> natural • Galapagos Islands • http://www.youtube.com/w atch?v=n3265bno2X0 Principles of Natural Selection 1. Organisms produce more o__________ than can survive 2. Genotypic variations are found among off-spring. Sources of variation include: – – – M_______________________________ T______________________________ (Barbara McClintock) S_________________________ Reproduction 3. V_____________________ are passed on to offspring 4. Some variations allow members of a population to s______________ and reproduce … while others do not. 5. Over time, offspring with b______________ adaptations survive and reproduce m________________ often more and more of the population exhibit the beneficial p____________________________ “Evolution” in Our Classroom! • Pick a tool – Knife – Fork – Spoon • Why did you pick the one you did? • Task 1 Results? ___________________________________ • Pick a tool – Knife – Fork – Spoon • Task 2 Results? ___________________________________ How fast does evolutionary change occur? KEY IDEA: It depends … _________________ How fast does evolutionary change occur? Types of Evidence • F____________________ Record – Dating • Stratigraphy • Radiometric – Geological Timeline • • • • Similarities in g_______________ make-up H_________________ structures V_________________ structures Embryology Fossil Record – Paleontology/ Geology • Dating • S__________________ • R__________________ • G_________ Timeline http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SY3MZ_wNFW8 Similarities in Genetic Make-up – Molecular Biology • All living organisms have _______________ • The more closely r____________________ the more commonalities in the sequence and pairs Humans and Chimps share 98 % Humans and other Humans share 99% Commonalities Structures - Anatomy • Homologous structures = Body parts that are ________________ origin and ________________ • Vestigial structures = body part that doesn’t seem to have a ______________, anymore E_________________ • Comparative Embryology