* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary mismatch wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
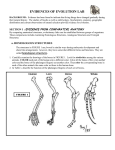
Around the World Activity- Evolution Name: Class Period: 1. We have evidence for evolution. True or False 2. The fossil record supports the theory of evolution. True or False 3. Evolutionary theory teaches that humans evolved from apes. True or False 4. Species can change over time. True or false 5. Mutation is a driving force of evolution. True or False 6. Individual organisms can evolve. True or false 7. How old is the earth? 8. Evolution is still occurring. True or False 9. Evolution cannot be observed. True or False 10. Evolution leads to the eventual formation of a perfect organism. True or False 11. In Science, evolution is referred to as? A. More speculation B. An explanation of why species become extinct C. Change over time D. An explanation for the rate of population growth 12. Individuals that are better able to cope with the challenges of their environment tend to A. Decrease in population over time B. Leave fewer offspring than those more suited to the environment C. Leave fewer offspring than those less suited to the environment D. Leave more offspring than those less suited to the environment 13. Natural selection is the process by which A. The age of Earth is calculated B. Organisms with traits well suited to the environment survive and reproduce at a greater rate than other organisms C. Acquired traits are passed from one generation to the next D. All of the above 14. What do geologic and fossil records, DNA relationships, structure similarities, homologous structures, and vestigial structures all provide? A. Evidence for biological evolution B. Interesting questions to study C. Proof that whales once lived on Earth D. All of the above 15. Natural selection could not occur without A. Genetic variation in species B. Environmental changes C. Competition for unlimited resources D. Gradual warming of Earth 16. Since natural resources are limited, all organisms A. Must migrate to new habitats B. Face a constant struggle for existence C. Display vestigial structures D. Have a species half-life 17. Strong evidence for evolution comes from A. Forensic biology B. Works of philosophy C. Phylogenetic trees D. The fossil record 18. Structures that are present in an organism but are reduced in size and have little or no function are called A. Pharyngeal pouches B. Vestigial structures C. Convergent structures D. Embryological homologies 19. Reproductive Isolation is a result of: A. Geographic barriers B. Different mating seasons C. Other reproductive barriers D. All of the above 20. In his experiment with peppered moths, Kettlewell found that A. The color of the moths was not important B. Birds preferred the flavor of the light colored moths C. Moths whose color matched that of the tree trunks were more likely to survive D. Natural selection did not affect moth survival 21. The beak of a bird and the beak of a giant squid have the same function, but are different in structure. The beaks are: A. Convergent structures B. Vestigial structures C. Homologous structures D. Analogous structures 22. Which of the following is an example of selective breeding? A. A male elk rounds up a herd of female elk B. Breeders use the same male with desirable traits to breed many females C. A cold winter reduces the elk population to just a few very strong individuals D. A dog owner raises several litters of puppies with mixed breeding 23. Occasionally a mutation produces a fish with a new characteristic. What determines whether this fish will be the beginning of a new species? A. The mutations must make the fish very different from other fish B. The fish must be able to live in the usual environment for that fish C. The mutation must provide some type of an advantage to the fish D. The fish must not dominate the other fish 24. Organisms that are the most alike in body structure, reproductive processes and feeding patterns are most likely to share what other relationship? A. A three or four chambered heart B. A common ability to live in water C. A similar evolutionary past D. Ability to make their own food Define or give an example of the following terms: Fossil EvidenceComparative anatomyHomologous StructuresAnalogous StructuresVestigial StructuresEmbryological EvidenceComparative DNABiogeographyAllele FrequencyMutationsVariationNatural SelectionFitnessArtificial SelectionSexual Selection-