* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 6 Grade Science Geology Unit Information
Provenance (geology) wikipedia , lookup
Surface runoff wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Marine geology of the Cape Peninsula and False Bay wikipedia , lookup
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Geology of Great Britain wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
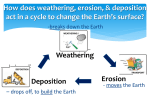
6th Grade Science Geology Unit Information Milestones Domain/Weight: Geology 40% Purpose/Goal(s): Students studying Geology in Grade 6 will investigate how Earth’s surface is formed, describe processes that change Earth, and explain the physical effects of these processes. Grade 6 students should be able to compare the physical and chemical composition of the crust, mantle, and core. They should describe the formation of rocks and fossils and the composition of soil. They should also explain how human activity causes erosion and describe methods of conservation. Content Map: Geology Content Map Geology Study/Resource Guide Content from Frameworks: Geology Content from the Frameworks Prerequisites: Elementary Standards for Geology Unit Length: Geology Concepts 1-3 approximately 22 days [Geology 1 Test] Geology Concept 4 approximately 14 days [Geology 2 Test] Geology Concept 4 approximately 17 days [Geology 3 Test] Geology 1 Unit Test Study Guide | Geology 1 Unit Test Study Guide KEY Geology 2 Unit Test Study Guide | Geology 2 Unit Test Study Guide KEY Geology 3 Unit Test Study Guide | Geology 3 Unit Test Study Guide KEY Click on the links below for resources by Essential Question: EQ 1: How are layers of the Earth different from one another? EQ 2: How does the constant movement of lithospheric plates cause major geological events on the earth’s surface? EQ 3: How is the ocean floor like the surface of the Earth? EQ 4: What is the composition of rocks and how are they formed? EQ 5: How do fossils show evidence of the changing surface and climate of the Earth? EQ 6: How do changes in the Earth’s surface occur over time? EQ 7: How is soil formed? EQ 8: How does human activity affect the Earth’s surface? TCSS 6th Science Geology Unit Standard(s) and Essential Question Standard(s): S6E5a. Compare and contrast the Earth’s crust, mantle, and core including temperature, density, and composition. 1. How are layers of the Earth different from one another? (temperature, density, composition) Textbook page 280,309 Vocabulary Essential* Core Mantle Crust Density Temperature Composition Supplemental** dense magma molten metallic geologic hot spots lithosphere radioactive decay convection currents lithospheric plates uranium (inner core) geothermal energy asthenosphere oceanic crust continental crust *Essential Vocabulary listed in the Standards Resources [Back to Top] The resources below are set up in a model lesson format. The ppt provides guidance for the entire lesson including activating, teaching and summarizing strategies. The activities listed below the ppt are used during the lesson and are identified in the ppt for use where they are most likely appropriate. The resources can be used as an entire lesson or pulled out for use separately. **Supplemental Vocabulary listed in the state frameworks and/or other state document TCSS Assessment S6E5a. Sample Assessment Items S6E5a. GOFAR CR Layers of the Earth Layers of the Earth ppt Layers of the Earth Foldable Earth Cross Section Diagram | Layers of the Earth Blank Diagrams [use these for formative assessment or quizzes] Layers of the Earth Slipcover Review – Put unlabeled earth diagrams in clear slipcovers. Give each student a slipcover, vis-à-vis or expo marker, and paper towel (a sock is also good and cheaper). Call out layers and have students mark the layer and hold up their slipcover when instructed. Layers of the Earth Review Layers of the Earth Summarizer Differentiation – after completing the Layers of the Earth Summarizer, place students in one of three differentiated groups. Students may be placed in groups of 2-3 to complete the activities. o Level 1 – Layers of the Earth Flashcards [could be used to play Kaboom or another game] o Level 2 – Layers of the Earth Tic-Tac-Toe o Level 3 – Layers of the Earth Cube Review o Layers of the Earth Differentiated Task Additional Models and Organizers o Earth’s Structure Model o Layers of the Earth Circle Model o http://www.education.com/science-fair/article/earth-layerschemical-physical-properties/ o Edible Models – If you do an edible model, be sure to have the students compare the layers in regards to temperature, pressure, and density as a review. Candy Earth Model Eating Earth’s Layers Songs about Layers of the Earth o https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RiHRI_Z2Kgs [linked in 2/21/2016 2 TCSS 6th Science Geology Unit Standard(s) and Essential Question Vocabulary Resources [Back to Top] Assessment ppt] Layers of the Earth Educational Rap with Images | Layers of the Earth Educational Rap | Lyrics Internet Resources o Annenberg Learning: Interactives Dynamic Earth [linked in ppt] o TCSS 2/21/2016 3 TCSS 6th Science Geology Unit Standard(s) and Essential Question Standard(s): S6E5e. Recognize that lithospheric plates constantly move and cause major geological events on the earth’s surface. 2. How does the constant movement of lithospheric plates cause major geological events on the earth’s surface? Textbook page 280-345 Vocabulary Essential* Geological Lithospheric plates Supplemental** Fault Rifting Volcanoes Normal Fault Subduction Fold Pangaea Transform Divergent Earthquakes Convergent Reverse fault Plate tectonics Plate boundary Strike-slip fault Mountain building Seafloor spreading Hydrothermal vent Mid-ocean ridge Convection currents Resources [Back to Top] *Essential Vocabulary listed in the Standards **Supplemental Vocabulary listed in the state frameworks and/or other state document TCSS Activator – Watch Ice Age: Scrat Continental Crack Up video clip and have students either answer individually or with a partner the following questions: (1) Which part(s) of Scrat’s adventure is accurate? (2) Which part(s) of Scrat’s adventure is not accurate? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zocutif0cQY Geological Events ppt Geological Events Notes – the ppt contains slides at the end of each type of boundary that illustrates how the diagrams should be completed on the notes chart Pangea Flipbook – only shows that the continents changed; it does not show evidence Continental Drift Evidence – Select one of the following or differentiate by giving higher groups the mystery and the lower groups one of the maps o Continental Drift Mystery o Puzzling Continental Drift Evidence o Continental Drift Continents Map Age of Ocean Crust Activity Seafloor Spreading Activities – select one o A Model of Seafloor Spreading – paper version o Seafloor Spreading Desk Model o http://www.education.com/science-fair/article/plate-tectonicsfloating-crustal-sections/ o https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OGi1h0qvMX4 Plate Boundary Analysis Activity Simple Convergent Boundary Models or Demonstrations o Give students or groups of students Aluminum Foil square approximately 20 cm X 20 cm. Students should draw a line down the center of the aluminum foil square with a marker. This line is the imaginary plate boundary. Students place their hands side by side on the aluminum foil with the line, or boundary, running between them. Students push their hands slowly toward each other while observing what occurs at the plate boundary. o http://thehomeschoolden.blogspot.com/2011/02/earth-sciencehow-fold-mountains-are.html Plate Boundary Activities – all activities are not necessary. Possibly select two activities and use others for reinforcement or 2/21/2016 Assessment S6E5e. Sample Assessment Items S6E5e. GOFAR CR Mountains S6E5e. GOFAR CR Tectonic Plate Boundaries 4 TCSS 6th Science Geology Unit Standard(s) and Essential Question Vocabulary Resources [Back to Top] TCSS Assessment extension. o Push Those Plates Activity or similar activity | Graham Cracker Earthquake (additional ideas and explanations for using the graham crackers) o Milky Way Plate Tectonics o Oreo Plate Tectonics o Peanut Butter Ridge o Plate Boundary Cootie Catcher o Plate Tectonics Vocabulary Match o Meet the Boundary Activity o Types of Plate Boundaries Map Identification – more for extension o Colliding Plates Inquiry Task Earthquake Activities o Earthquakes: They’re Definitely Not Your FAULT! Demonstration o Model of Three Faults Activity – Students do not have to know the different types of faults. Use the activity to demonstrate the effects of the different directions of movement o http://thehomeschoolden.blogspot.com/2011/02/earth-scienceplate-movement.html o Use a sponge to demonstrate the how the earth’s surface bends under stress. Use the link to help structure the quick activity, but do not require students to know the different types of stress on rocks that cause earthquakes. http://www.education.com/science-fair/article/crustal-bending/ o My Teacher Caused an Earthquake – conduct in a location other than the classroom that has been pre-approved Geological Events Formative Assessment [covers earthquakes and volcanoes] Geological Events Summarizer/Formative Assessment Differentiation – Use the summarizer as the formative assessment component to determine differentiated groups. These are possible tasks for each level if they have not already been used. o Level 1 – Geological Event Review Cards o Level 2 – Types of Plate Boundaries Map Identification A o Level 3 - Types of Plate Boundaries Map Identification B Videos 2/21/2016 5 TCSS 6th Science Geology Unit Standard(s) and Essential Question Vocabulary Resources [Back to Top] Assessment o TCSS http://www.sciencechannel.com/tv-shows/greatestdiscoveries/videos/100-greatest-discoveries-continental-drift/ [linked in ppt] o http://www.sciencechannel.com/tv-shows/greatestdiscoveries/videos/100-greatest-discoveries-sea-floorspreading/ [linked in ppt] o Short summary of divergent and convergent o Crust in Pieces Song [linked in ppt] o Plate Tectonics Song [linked in ppt] o How the Earth is Changing o Volcanoes How Volcanoes Formed [linked in ppt] 4:48 Ring of Fire Eruption Song [linked in ppt] o Earthquakes Earthquake is like a drip of water video It’s An Earthquake Song o Tsunami https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0NfKZAiWRoE [1:01] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tPQ5iTcnXW0 [14:49] This video is not necessary if you play the other video. It just shows a longer time period of the water receding and then slowly coming back until the larger waves come in flooding the area. Crust Rolls Up Tsunami Song [linked in ppt] Online Animations/Resources o http://www.geo.cornell.edu/hawaii/220/PRI/continental_puzzle. html - Try to reconstruct Pangea o Processes that occur along plate boundaries [linked individually in ppt] o Convergent: http://www.classzone.com/books/earth_science/terc/conten t/visualizations/es1105/es1105page01.cfm?chapter_no=vis ualization [Formation of the Himalayan Mountains linked in ppt] o Formation of Volcanic Islands over a hot spot [linked in ppt] o Earthquakes and Faults [linked in ppt] Savage Earth Animations Faults: Students do not have to identify the different faults 2/21/2016 6 TCSS 6th Science Geology Unit Standard(s) and Essential Question Vocabulary Resources [Back to Top] o o TCSS Assessment this is just for illustration http://www.classzone.com/books/earth_science/terc/conten t/visualizations/es1103/es1103page01.cfm?chapter_no=vis ualization [linked in ppt] Tsunami: http://www.nsf.gov/news/special_reports/tsunami/index_hig h.jsp?id=intro http://www.tsunami.noaa.gov/tsunami_story.html [click on the picture for animation; embedded in ppt] Earthquakes & Tsunamis Webquest 2/21/2016 7 TCSS 6th Science Geology Unit Standard(s) and Essential Question Standard: S6E3c. Describe the composition, location, and subsurface topography of the world’s oceans. 3. How is the ocean floor like the surface of the Earth? Textbook page 542-548 Vocabulary Essential* Subsurface Topography Resources [Back to Top] Seafloor Features Seafloor Foldable Notes [optional] Seafloor Vocabulary Flashcards The Ocean Floor Revealed [1:51] Assessment Supplemental** Trench Plains Valleys Geysers Seamounts Mountains Abyssal plain Continental slope Subduction zone Mid-ocean ridge Continental plain Continental shelf Hydrothermal vents S6E3c. Sample Assessment Items S6E3c. GOFAR CR World Ocean S6E3c. GOFAR CR Ocean Floor *Essential Vocabulary listed in the Standards **Supplemental Vocabulary listed in the state frameworks and/or other state document TCSS 2/21/2016 8 TCSS 6th Science Geology Unit Standard(s) and Essential Question Standard(s): S6E5b. Investigate the contribution of minerals to rock composition. S6E5c. Classify rocks by their process of formation. S6E5d. Describe processes that change rocks and the surface of the Earth. 4. What is the composition of rocks and how are they formed? Textbook page 63-109 Vocabulary Essential* Rocks Mineral Formation Composition Supplemental** Igneous Sedimentary (Sediment) Metamorphic Rock Cycle Magma Hardness Texture Compacted Foliation Cemented Lithification Volcanic ash Organic matter Fine-grained Coarse-grained Chemical compound Metamorphism Crystallizes Recrystallized Glassy Silicate Resources [Back to Top] *Essential Vocabulary listed in the Standards **Supplemental Vocabulary listed in the state frameworks and/or other state document TCSS Minerals and Rocks ppt Rocks Graphic Organizer - to take notes during ppt Mineral Resources o Designing Minerals with Legos o Mineral Mania Web Hunt o Bicycle Minerals | Bicycle Minerals Key o Cell Phone Minerals | Cell Phone Minerals Key o Soccer Minerals | Soccer Minerals Key o Television Minerals | Television Minerals Key Mineral Identification Activity – This optional activity will vary from school to school depending on resources; therefore, there are no specific directions. Sample Mineral Identification Activity | Sample Mineral Identification Activity 2 Another option is to take students to the computer lab and do a virtual mineral identification lab such as K12 Virtual Labs: Rocks and Minerals [have students View Walk-through first] *Note: Based on state documentation, students do not have to know specifics on minerals. The standard is about the contribution of minerals to rock composition. Therefore, if you do a mineral identification lab, focus on just the main tests such as hardness, streak, luster, cleavage/fracture, etc. Demonstrating Folds in Metamorphic Rocks | Hotwire High Jinks Demonstration (rocks changing due to heat, pressure, and folding) Types of Rock Sorting Activity Rock Cycle Label – the students will follow along with the teacher and the ppt to complete the rock cycle Locating the Types of Rock on Earth handout Weathering & Erosion Summary Handout – this is intended to provide a short summary for students on weathering and erosion. These concepts will be taught in-depth later in the unit. However, to understand the rock cycle, students need a basic understanding of the concepts. Rock Cycle Activities – possible activities, but all of the activities are not necessary o Ride the Rock Cycle (Journey on the Rock Cycle) o Rock Cycle Shuffle o Rock Cycle Formative Assessment 2/21/2016 Assessment GOFAR CR Minerals and Rock GOFAR CR Rock Formation GOFAR CR Rock Cycle GOFAR CR Rock Cycle 2 GOFAR CR PB&J Rock Model S6E5b. Sample Assessment Items S6E5c. Sample Assessment Items S6E5d. Sample Assessment Items 9 TCSS 6th Science Geology Unit Standard(s) and Essential Question Vocabulary Resources [Back to Top] Assessment o o o o o TCSS Sugar Rock Cycle Rock Wheel Cycle Crayon Rock Cycle Rock Cycle Roundabout Rock Cycle Vocabulary from http://mjksciteachingideas.com/rocks.html Rocks Summarizer Videos and Online Resources o Minerals A Brief Introduction to Minerals [10:21] Minerals Song o Igneous Rock How do Igneous Rock Form? Animation [linked in ppt] Igneous Rocks [4:15] o Metamorphic Rock Animation of Metamorphic Rocks Forming o Rock Cycle Study Jams: Rock Cycle Mr. Parr’s Rock Cycle Song [linked in ppt] Mr. Lee’s Rock Cycle Rap Rock Cycle Animation Rock Cycle Animation from Prentice Hall [linked in ppt] Annenberg Interactive Rock Cycle Interactive Rock Cycle Animation from McDougal Littell Rocks from BBC 2/21/2016 10 TCSS 6th Science Geology Unit Essential Question and Standard(s) Standard: S6E5g. Describe how fossils show evidence of the changing surface and climate of the Earth. 5. How do fossils show evidence of the changing surface and climate of the Earth? Textbook page 362-375 TCSS Vocabulary Essential* Supplemental** Resources [Back to Top] http://www.parents.com/blogs/homeschool-den/category/earthscience-unit/ My Dirty Laundry Relates to Geology? Analogy Examining Fossil Formation Lab Fossil Inferences Activity | Fossil Inferences Activity PPT Geologic Time Spiral Assessment GOFAR CR Fossils *Essential Vocabulary listed in the Standards **Supplemental Vocabulary listed in the state frameworks and/or other state document 2/21/2016 11 TCSS 6th Science Geology Unit Essential Question and Standard(s) Standard: S6E5f. Explain the effects of physical processes (plate tectonics, erosion, deposition, volcanic eruption, gravity) on geological features including oceans (composition, currents and tides). 6. How do changes in the Earth’s surface occur over time? Textbook page 180-241 Vocabulary Essential* Erosion Gravity Deposition Supplemental** “Agents of erosion” Exfoliation Frost wedging Weathering Dissolution Hydrolysis Oxidation Thermal expansion Chemical Weathering Biological Weathering Physical (Mechanical) Weathering *Essential Vocabulary listed in the Standards **Supplemental Vocabulary listed in the state frameworks and/or other state document TCSS Resources [Back to Top] Activator on first slide: Watch the next few slides. When the slides stop transitioning get with an elbow partner to discuss the events that caused the formation of the beautiful features. Be as specific as possible. [the slides are automatically timed to transition for the activator and will stop on the last slide of the activator] Weathering and Erosion ppt [Note: although the ppt and notes include specific names of weathering examples, it is more important for students to identify the processes as either an example of mechanical or chemical weathering. Do not stress over them knowing the names exfoliation, dissolution, hydrolysis, or oxidation. These processes are included in the state frameworks but not listed specifically in the standard. The student should use these processes to identify the type of weathering.] Weathering, Erosion, and Deposition Foldable – if space or time allows, you may want to have students draw images for the concepts on their foldable. It could possibly go on the top flap that opens. Weathering Activities o Weathering Sort o Weathering Gallery Walk o Modeling the Effect of Ice on Rock o Salt and Chalk Lab o Weathering a Snickers | Erosion and Weathering in my Mouth o Other demonstrations or lab stations: If you can get samples of limestone rock, have students use droppers to pour vinegar on the rock to demonstrate chemical weathering Chalk can be used to demonstrate physical and chemical weathering. Students can take two pieces of chalk and rub them or make them collide to observe physical weathering. Then, students can place a piece of chalk in a small, clear cup and add drops of vinegar to demonstrate chemical weathering. Use sandpaper to rub rock for physical weathering 2/21/2016 Assessment GOFAR CR Weathering, Erosion, Deposition 12 TCSS 6th Science Geology Unit Essential Question and Standard(s) Vocabulary Resources [Back to Top] TCSS Assessment You Crack Me Up! Weathering and Erosion Formative Assessment Activities o Weathering, Erosion, Deposition Cards o Weathering, Erosion, and Deposition Journey o What is It? Weathering, Erosion, or Deposition o Changing Mountains Constructed Response o Providence Canyon Tiered Task o A Glacier in a Milk Jug Demonstration Videos: o Weathering and erosion - Freeze thaw weathering [1:20 linked in ppt] o Rock Meets Lichen [2:06 linked in ppt] o Chemical Weathering Feldspar into Clay [28 sec] o Mechanical and Chemical Weathering: Breaking or Baking? [2:50 linked in ppt] o Erosion Lab [8:17] video shows several labs on erosion that can be done as a demonstration, in stations or groups, or shown in place of doing the lab if time and resources are limited o Study Jams: Weathering and Erosion o Bill Nye the Science Guy: Erosion [32:33] o Weathering and Erosion Song [3:02] Online Resources o Animation of Chemical Weathering [linked in ppt] o Animation of sediments being eroded by Classzone [linked in ppt] o Animation of erosion by a waterfall [linked in ppt] o Animation of the formation of an arch [linked in ppt] o Images of Erosion from Classzone o Images of how Glaciers erode rock [linked in ppt] o Images of Wave Erosion [linked in ppt] o Animation of Weathering, Erosion, and Deposition – click on the arrows on the left for each animation o Sediments being deposited by Classzone [linked in ppt] o Animation of the formation of a sand dune [linked in ppt] 2/21/2016 13 TCSS 6th Science Geology Unit Essential Question and Standard(s) Standard: S6E5h. Describe soil as consisting of weathered rocks and decomposed organic material. 7. How is soil formed? Textbook page 188-194 Vocabulary Essential* Soil Weathered rocks Decomposed Organic material Supplemental** Humus Horizon Fertile *Essential Vocabulary listed in the Standards Resources [Back to Top] Soil ppt Soil Notes Soil Summarizer Activities o What is in our Soil? Activity [from state frameworks] o Cup of Soil Recipe – have students make a recipe for soil Videos o The Living Soil [9:24] Online Resource o Discovery Channel: The Dirt on Soil Assessment S6E5h. GOFAR Constructed Response Soil **Supplemental Vocabulary listed in the state frameworks and/or other state document TCSS 2/21/2016 14 TCSS 6th Science Geology Unit Essential Question and Standard(s) Standard(s): S6E5i. Explain the effects of human activity on the erosion of the earth’s surface. S6E5j. Describe methods for conserving natural resources such as water, soil, and air. 8. How does human activity affect the Earth’s surface? Textbook page 196-200 Vocabulary Essential* Air Soil Water Erosion Conserving/Conservation Supplemental** Pollutants Wetlands Reduce Pesticides Reuse Fertilizers Recycle Overgrazing Runoff Terracing Contour plowing Wind break Strip planting Mulching No-till farming Emissions Crop rotation Acid rain Cover crop Ozone layer Greenhouse gases Greenhouse effect CFC’s (chlorofluorocarbons) Resources [Back to Top] *Essential Vocabulary listed in the Standards **Supplemental Vocabulary listed in the state frameworks and/or other state document TCSS Human Impact ppt Human Impact Graphic Organizer Demonstrations o Runoff – pour water over a smooth surface to demonstrate how it flows quickly then demonstrate again with a rough surface to slow down the runoff o Soil Cover Experiment – image of a possible experiment on soil cover and water quality Soil Erosion Formative Assessment Reduce, Reuse, Recycle Chart – allow students to complete this individually or in pairs Effects of Stream Pollution, in a Jar Human Impact Summarizer Videos o Water Pollution [3:19] o Water Conservation Tips [3:18] o Nature is Speaking [1:28] linked in ppt o Explore More: Water Quality [29:11] o Fifteen to River: Explaining Storm Water Runoff [1:49] o Nature is Speaking: I am Soil [1:25] o The Greenhouse Effect [1:55] linked in ppt o Global Warming Song [4:01] linked in ppt o Air Pollution Causes, Effects, and Solutions [9:24] linked in ppt o Reduce, Reuse, Recycle [1:37] o Bill Nye The Science Guy Pollution Solutions [23:02] Online Resources o http://www3.epa.gov/recyclecity/house.htm [linked in ppt] Click on various parts of the house to see how it can be reduced, reused, or recycled | Biology Corner Recycle City Worksheet Sample GOFAR Question: Erosion of topsoil is a problem in many places. In some crop fields the plant material is left in the soil after harvest. Explain why having plant material in fields helps to prevent erosion. Exemplar 2/21/2016 Assessment 15