* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download EARTHQUAKES !!!
Ionospheric dynamo region wikipedia , lookup
Seismic inversion wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Shear wave splitting wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Earthquake engineering wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Surface wave inversion wikipedia , lookup
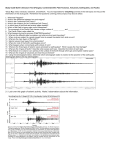
EARTHQUAKES !!! 1) Earthquakes (EQ) are a shaking of the ground 2) Caused MAINLY by the breaking of rock due to moving tectonic plates. 3) EQ occur Mainly on plate boundaries & volcanoes 3) EQ CAN occur anywhere at any time. 4) EQ occur at least 1 per minute somewhere in the world. Approximately 20 Earthquakes have occurred while you have written this. • http://nationalatlas.gov/mapmaker EQ around the world RISK map… • http://nationalatlas.gov/mapmaker • http://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/state s/virginia/hazards.php http://earthquake.usgs.gov/eqcent er/recenteqsanim/world.php • Recent EQ Fault lines 4) Faults are breaks or cracks in the Crust 5) Formed by forces/stress in the rocks as the plates move. 6) Types of Forces, Faults, & Plate Boundaries • Type 1 A. Caused by COMPRESSION (squeezing) B. Causes REVERSE or THRUST FAULTS (the hanging wall moves up!) 6) Types of Forces, Faults, & Plate Boundaries C. Forms at CONVERGENT BOUNDARIES (plates that move together) D. Landforms: Plateaus – high flat areas. (ex: Colorado Plateau) Mountains. (ex: Appalachians, Blue Ridge, etc…) 6) Types of Forces, Faults, & Plate Boundaries • Type 2 A. Caused by Tension (pulling) B. Causes Normal FAULTS (the hanging wall moves down, but the footwall moves up!) 6) Types of Forces, Faults, & Plate Boundaries C. Forms at DIVERGENT BOUNDARIES (plates that move apart) D. Landforms: Rift valleys. (ex: The GREAT RIFT VALLEY in Africa) <the Horn of Africa is literally tearing away from Africa> 7&9) Types of Forces, Faults, & Plate Boundaries • Type 1 A. Caused by Shearing (ripping sideways) B. Causes STRIKE-SLIP FAULTS (both walls moves sideways!) 6 cont’d) Types of Forces, Faults, & Plate Boundaries C. Forms at TRANSFORM BOUNDARIES (plates that move sideways or laterally) D. Landforms: Mostly just Earthquakes & visible fault lines. (ex: San Andreas Fault in CA) 7) There are 2 sides of a fault line • Footwall (or Footblock) Hanging wall (or Hang block) Fault lines 9) FOCUS – the Origin of the EQ (underground!) 10) EPICENTER – the Origin of the EQ (above ground…like ‘X’ marks the spot on a map) 11) Fault- labeled picture SEISMIC WAVES 12) Damages of Earthquake TSUNAMI – caused by EQ on Ocean floor. Water is pushed up & moves fast towards shore. Tsunami-Sri Lanka 12) Damages of Earthquake • LIQUEFACTION- EQ shakes wet ground, causing buildings to sink. 13) Strength of Earthquakemeasured by damage done. 3 SCALES TO Measured : 1) RICHTER SCALE- measures EQ strength. 2) MERCALLI SCALE measures EQ damage 3) MOMENT MAGNITUDE **The highest numbers in the scale mean the worst Earthquakes!! Measured by: 1) Tiltmeter- vertical movements by water changes Measured by: 2) CreepmeterHorizontal movements by wire Measured by: 3) Laser guidance- horizontal movements by Laser Measured by: 4) GPS- satellites measure ground changes Measured by: 5) SeismographGround shakes, records strength. 1) MERCALLI Scale– measures total damage • http://www.dnr.sc.gov/geology/images/Equak e%20intens2-pg.pdf 2) RICHTER – magnitude (strength) & the earthquake (EQ) waves. Good for ONLY nearby EQ 3) MOMENT MAGNITUDE SCALE – measures TOTAL energy. Good for ALL EQ. • 4) Highest # on ANY scale is the WORST EQ. Strength of EQ 13) Determined by amount of damage 14 &15) Epicenter of EQ found by using the intersection of at least 3 seismograph locations. Seismograph & Seismogram 16) Seismograph – machine that records the arrival of all 3 seismic waves & strength 17) Seismogram – the written sketch of the EQ 19) Seismograms: 3 basic types • No EQ recorded • Low-Intensity EQ • High-Intensity EQ 20) Seismic Wave – Vibrations caused by the breaking of rock. SEISMIC WAVES 21) 3 types of Seismic Waves a. Type 1: PRIMARY WAVE • • • • a.k.a. ‘P-Wave’ The first wave to arrive The fastest wave Moves as a ‘COMPRESSION’ WAVE • Travels through the entire Earth. 3 types of Seismic Waves b. Type 2: Secondary Wave • a.k.a. ‘S-Wave’ • The second wave to arrive • Speed = ½ of the Pwave • Moves as a ‘ROLLING’ WAVE • Travels through all of Earth EXCEPT LIQUID IRON**** 3 types of Seismic Waves c. Type 3: Surface Waves • a.k.a. L-Wave (‘Love’ • • • • • Waves) Last wave to arrive Slowest of all waves Most damaging (all of energy is at surface) Motion is chaotic (Rolling, backwards & side-side) Moves only at surface. SPEED of P-waves & S-waves P wave speed S wave Speed 400 mph 200 mph 600 mph 300 mph 1200 mph 600 mph 300 mph 150 mph 22) No EQ P-Wave S-Wave L-Wave 23) Why Study Seismic waves? To learn the composition of the Inner Earth Mohorovicic Discontinuity!! 24) Located between CRUST and UPPER MANTLE. 25) It is a boundary where SEISMIC WAVES SPEED UP. 26) The Shadow Zone!! – a region of Earth without EQ • Reasons: Seismic waves SLOW DOWN & BEND as they travel through Earth. • The S- Wave does not travel through the outer core(liquid iron). • This produces a region without EQ. Hence, the SHADOW ZONE! 27) Shadow Zone image 28) Virginia receives EQ MAINLY due to the SETTLING OF BEDROCK. This doesn’t usually cause bad damage 30) CONVERGENT boundary 29) Features & Plate 31) COMPRESSION forces boundaries 32) REVERSE Faults PLATEAU 33) ex: COLORADO PLATEAU 34) CONVERGENT Boundary 29) Features & Plate 35) COMPRESSION Forces boundaries 36) REVERSE faults FOLDED MOUNTAINS 37) ex: APPALACHIANS 38) DIVERGENT Boundary 29) Features & Plate 39) TENSION Forces boundaries 40) NORMAL faults FAULT BLOCK MOUNTAINS 41) ex: GREAT BASIN, OTHERS 42) CONVERGENT Boundary 29) Features & Plate 43) COMPRESSION Forces boundaries 44) REVERSE faults UP WARPED MOUNTAINS 45) ex: ROCKIES 46) VOLCANOES AT CONVERGENT, DIVERGENT 29) Features & Boundary and Plate HOT SPOTS boundaries 47) COMPRESSION /TENSION Forces VOLCANIC 48) REVERSE /NORMAL faults MOUNTAINS 49) ex: MT. ST. HELENS, MAUNA KEA (HAWAII), ICELAND, ETC… Features & Plate boundaries 50) Transform boundaries form NO mountains 51) Most mountains made by CONVERGENT boundaries and COMPRESSION forces 52) Volcanoes forma at CONVERGENT boundary, DIVERGENT BOUNDARIES, AND HOT SPOTS (WEAK PLACES IN CRUST WHERE LAVA COMES OUT. OCCUR ANYWHERE.) PREDICTION- Can’t predict because 1) 2) 3) 4) Energy not always released Equipment doesn’t always work Low understanding Other reasons… Safety Design of buildings based on • 1) ABSORPTION OF ENERGY • 2) REINFORCEMENT • 3) FIRE PREVENTION