* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download GEO142_mid_term_II_s..
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
Seismic communication wikipedia , lookup
Shear wave splitting wikipedia , lookup
Seismic inversion wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Reflection seismology wikipedia , lookup
Surface wave inversion wikipedia , lookup
Earthquake engineering wikipedia , lookup
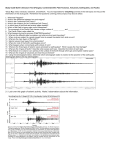
The Geology of Pacific Northwest Volcanoes, Mountains and Earthquakes Mid Term II: Study Guide Science and Material Properties: What are the steps in the scientific method? Could you give an example of the scientific method? Could you tell what step you are in given some information? What is a force? What is stress? What is strain? What are the three types of stress and strain? What is elastic? What is plastic? Plate Tectonics (part 2): What is the elastic rebound theory? Where was it devised? Using what observations (do you remember which earthquake)? What is liquefaction? How do we know about the earth’s interior? Have we been there to make direct observations? What is the average composition of oceanic crust? What about continental crust? Which type of crust is thicker? Which type of crust is denser? How is a tsunami generated? Could you calculate a plate motion rate? What information do you need? If you made a measurement on a map, what are the steps you would take to convert that measurement from a “map distance” to a “real world distance?” Faults: What is a fracture? What is a fault? What is an earthquake? What are the different kinds of faults? What kind of stress and strain is associated with each of these different faults? Which fault would one expect to be associated with which tectonic plate boundary? What is the strike and what is the dip of a fault? What kinds of faults are dip‐slip faults? What makes a fault a strike‐slip fault? What is the difference between a right lateral and a left lateral strike‐slip fault? What is a blind fault? What is an anticline? How is it different than a syncline? What are examples of the different kinds of tectonic plate boundaries? What are the four largest earthquakes ever recorded (what year, what location)? Seismology: What are the four types of seismic waves? What are the two main classifications that these four types of waves fit into? If you saw an animation or an illustration showing the motion, could you identify the seismic wave? Which is the fastest seismic wave? Which is the second fastest? If you saw a drawing of seismic waves reflecting and refracting through the earth, could you label the seismic wave as it is recorded at the seismograph (e.g. SS, PPP, PKP, SKS, etc.)? What is the reason why there is a shadow zone (considering S waves)? How does a seismograph work? Could you determine the location of an earthquake given some seismic records? What is a travel time curve and could you use it? Which seismic wave cannot travel through fluids?