* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Earthquakes - armstrong-herrington
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
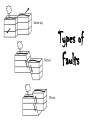
Earthquakes Lesson 1 Let’s Get Quakin’ 1. What is an earthquake? 2. What instrument records earthquakes? 3. What makes up the outer crust of the earth? How many are there? ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ 4. What do we call the place where plates meet? 5. Name the following boundaries. 6. Which fault would be an example of the San Andreas Fault? 7. Which fault would be where new land is being created? 8. Which fault shows where mountains are pushed up? 9. Name the following faults. Earthquakes San Francisco Earthquake 1910 • Sudden shaking of the ground. • Generate seismic waves which can be recorded on a sensitive instrument called a seismograph. The Seismograph • Perhaps the earliest seismograph was invented in China in A.D. 136 by a man named Choko. Earth’s Plates • Broken into 12 rigid plates which are 60200 km thick and float on top of a more fluid zone (magma) • Like how icebergs float on top of the ocean. • Earthquakes occur along plate boundaries (faults) • The Pacific plate is moving to the northwest at a rate of about 4 inches per year. Faults Types of Boundaries Divergent Convergent Transform • Along the boundary separating any two plates, the relative motion between the plates can be classified into one of 3 categories Types of Faults Types of Waves •Type of seismic wave that compresses and expands the ground. • Type of seismic wave that moves the ground up and down or side to side.