* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ocular disease
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Antibiotics wikipedia , lookup
Carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae wikipedia , lookup
Ebola virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Cross-species transmission wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Anaerobic infection wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Dirofilaria immitis wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Tuberculosis wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Antiviral drug wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
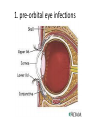
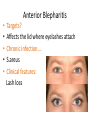
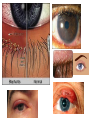
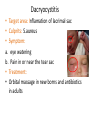
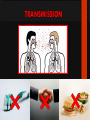
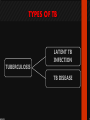
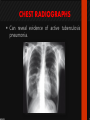
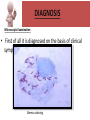
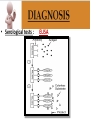
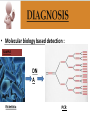
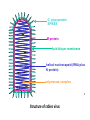
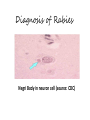
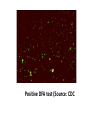
Ocular diseases How important are your EYES??? And how worse the conditions can get? In what ways “no tears baby shampoo” can help you? 1. pre-orbital eye infections Anterior Blepharitis • • • • • Targets? Affects the lid where eyelashes attach Chronic infection…. S.areus Clinical features: Lash loss Posterior Blepharitis • Targets? Affects the inner portion of the eyelid • Clinical features: • Infection can cause and ‘internal Stye’ DIAGNOSIS • A slit-lamp examination can diagnose blepharitis in the clinic. • Treatment • Careful daily cleansing of the eyelid edges helps remove the skin oils that cause bacteria to grow too much • use of baby shampoo or special cleansers. Antibiotic ointments may also be helpful. Canaliculitis • Target area: canaliculi • Clinical features: a. Formation of gritty casts that obstruct the lacrimal duct leading to eye watering b. Nasal lid swelling c. Chronic conjunctivitis • Treatment: • Antibiotics canaculotomy Dacryocystitis • Target area: Inflamation of lacrimal sac • Culprits: S.aureus • Symptom: a. eye watering b. Pain in or near the tear sac • Treatment: • Orbital massage in new borns and antibiotics in adults Questions….. Thank you Syeda Kashmala Zahra Inflammation of the conjunctiva and inner surface of eyelids. Most common ocular inflammation. Can be a local infection or part of systemic infection. Allergic Bacterial (most common) Viral (most common)-Adenovirus Chemical Transmission of Etiologic Agent Person-to-person contact. Infected objects and water. Prevention Maintain good hygiene and wash hands often. Change pillowcases frequently. Replace eye cosmetics regularly. Do not share eye cosmetics, towels or handkerchiefs. Handle and clean contact lenses properly. Keep hands away from the eye. Signs and Symptoms Viral (Pink Eye) • Shows a fine, diffuse pinkness of the conjunctiva. Bacterial Pus production Diagnosis Laboratory investigations are not performed for most virus caused infections. Conjunctival scraping and swabs are taken for Gram stain and culture ( on blood, chocolate and Sabouraud agar) Immunofluorescent staining PCR for viral diagnostics. Treatment Depends on cause. Allergic conjunctivitis may respond to allergy treatment. Cool compresses and artificial tears may sooth it. Persistent allergic conjunctivitis may also require topical steroid drops. Antibiotic medication like eyedrops and ointments. Warm compresses. And He gave you hearing, sight, and hearts that you might give thanks (to Allah} (An-Nahl 78) THANK YOU INFECTIONS IN SPECIAL PATIENTS POPULATION WHAT ARE SPECIAL PATIENTS? Special patients are the people who have their defense mechanisms of the body impaired by any means which leads to repeated infections of varying severity in them BACTERIAL INFECTIONS MYCOBACTERIUM TUBERCULOSIS Discovered by ROBERT KOCH in 1992 Causative agent of Tuberculosis (TB) TRANSMISSION TYPES OF TB LATENT TB INFECTION TUBERCULOSIS TB DISEASE SYMPTOMS SHORTNESS OF BREATH WEIGHT LOSS COUGH FEVER CHEST PAIN LOSS OF APPETITE DIAGNOSIS Tuberculin skin test Acid fast staining Chest radiographs CHEST RADIOGRAPHS Can reveal evidence of active tuberculosis pneumonia. TREATMENT The vaccine is a live vaccine, derived from a strain of Mycobacterium bovis. It was first administered to humans in 1921. THANK YOU RICKETTSIAL INFECTIONS OROOJ SURRIYA INTRODUCTION • Almost all zoonotic rickettsial infections • Causative agent : Rickettsia are TRANSMISSION • The arthropods used as vectors feed on blood or tissue fluid of vertebrate host. DIAGNOSIS Microscopic Examination • First of all it is diagnosed on the basis of clinical symptoms Giemsa staining • Serological tests : ELISA • Molecular biology based detection : SAMPLE DN A Rickettisia PCR Zoonosis Ameema Tariq Definition • Zooneses are diseases of vertebrate animals that can be transmitted to man: either directly or indirectly through an insect vector. • When an insect vector is involved, the disease is also known as an arboviral disease. • Examples of viral zoonoses that can be transmitted to man directly include rabies, hantaviruses, lassa and ebola fevers. Reverse Zoonosis • If the transmission is from humans to non-human animals then the process is termed as reverse zoonosis or anthroponosis. Zoonoses • Does NOT include – Fish and reptile toxins – Allergies to vertebrates – Experimentally transmitted diseases Zoonoses: Animal Species BIRDS REPTILES, AMPHIBIANS FISH WILD ANIMALS Psittacosis West Nile Cryptococcus REPTILES, FISH, & AMPHIBIANS salmonella mycobacterium WILD ANIMALS hantavirus Plague Tularemia Routes of Transmission INDIRECT DIRECT Foodborne Droplet or Aerosol Water-borne Oral Fomite Contact Vector-borne Environmental ORTHOZOONOSES –May be perpetuated in nature by a single vertebrate species –E.g. rabies,anthrax METAZOONOSES –Require both vertebrates and invertebrates to complete transmission –All arboviral infections –Some bacterial diseases –Some parasitic diseases Metazoonoses • • • • Invertebrate Host: Mosquitoes Vertebrate Host: Birds Incidental Hosts: HUMANS, horses, amphibians, other mammals METAZOONOSES Zoonoses: Etiologic Classification Viral Bacterial Parasitic Mycotic Rabies Virus Rabies virus particles RHABDOVIRUSES G glycoprotein SPIKES M protein lipid bilayer membrane helical nucleocapsid (RNA plus N protein) polymerase complex 26 Structure of rabies virus Diagnosis of Rabies Negri Body in neuron cell (source: CDC) Positive DFA test (Source: CDC Knowledge sharing 60