* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 8th Grade Science Test 3 – Earth Science Study Guide
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
History of paleontology in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
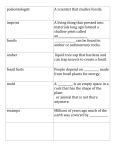
Name: ______________________________ Date:___________ Period: _____ Bin# ___ 8th Grade Science Test 3 – Earth Science Study Guide – Answer Key Ongoing science skills and techniques review: 1. What tool would you use to find the mass of an object? – Triple Beam balance 2. What tool would you use to find the volume of an object? – Graduated Cylinder 3. What tool would you use to find the length of an object? - Ruler 4. What does a line graph show? - They show how something changes over time or the relationship between two quantities 5. What does the Y – Axis represent? X- Axis? - Dependent Responding Variable, Manipulated Independent Variable 6. How many meters are in 16.3 km? - 1,630m 7. Why do we use dimensional analysis? - It helps us convert from unit of measurement to another. 8. How many significant figures are in 6.305? - 4 9. How many significant figures are in 000.7850? - 4 LT 1. Explain what fossils are and how most fossils form 10. Most rocks that form from fragmental rock particles are classified as Sedimentary rocks. 11. What type of rock are Stromatolites found in? – Sedimentary Rocks LT 2. Identify and describe different types of fossils 12. Describe preserved remains. – Preserved remains were once living organisms that became trapped in tar, amber and ice and preserved over time.. 13. Describe what a petrified fossil is. – A petrified fossil is when sediment covers the remains of an organism and eventually hardened minerals are left behind 14. Describe what a trace fossil is. – A trace fossil is evidence of a once living organism ie footprints 15. What is the difference between a mold and a cast fossil? – a mold is a hollow area in sediment in the shape of the ancient organism and a cast is a copy of the shape of the organism. LT 3. Describe several ways that scientist determine the relative age of fossils 16. What is relative age? - the age of rock compared to other rocks 17. How do scientists use relative age to date rocks? – Scientists use the law of superposition to date rocks. LT 4. Describe how geologists use index fossils to date rocks. 18. What are index fossils? Give an example of an index fossil. – A fossil that is widely distributed and represents a type of organism that existed for a brief amount of time. An example of an index fossil would be a Trilobite The diagrams show the index fossils found in rock layers in at least two different locations. Use the diagram to answer questions 19 – 22. Name: ______________________________ Date:___________ Period: _____ Bin# ___ 19. According to the law of superposition, the oldest rock layers at site 1 and 2 are layers A and W 20. The youngest rock layer at each location is layers G and Z 21. What are the index fossils for the layers B and W? Shell, Ammonite and Fish 22. Layer F at site 1 and Layer Y at site 2 both contain the fossils for dinosaurs and plants. What can these index fossils tell us about the period in which they were formed? The area was inhabited by dinosaurs and plants LT 5. Explain the law of superposition. 23. Explain the law of superposition – The law of superposition states that the oldest layer of rock is located at the bottom and the youngest layer of rock is located at the top. LT 6. Describe the process of radioactive decay 24. Describe the process of radioactive decay. - As a radioactive element within the rock decays, it changes into another element. Therefore, the composition of the rock changes slowly over time. The amount of the radioactive element goes down, but the amount of the new element goes up. 25. What is the half-life of an element? The half-life of a radioactive element is the time it takes for half of the radioactive atoms to decay. 26. What are the two types of radioactive dating? Potassium-Argon Dating and Carbon-14 Dating LT 7. Explain how the absolute age of a rock can be determined using radioactive dating. 27. Which radioactive element is used to determine the absolute age of late Permian (260million years ago) period animal? Potassium Argon Radioactive Decay of Potassium-40 Time gone by (in billions of years) Name: ______________________________ Date:___________ Period: _____ Bin# ___ 28. When the rock first forms, what is the percent of potassium-40 compared with the percent of argon-40? 100% Potassium-40 and 0% Argon-40 29. What is the half-life of potassium-40? 1.3 billion years 30. What are the percentages of the two elements at 1.3 billion years? 50% Potassium-40 and 50% Argon-40 31. After the first 1.3 billion years, does the rock contain more potassium40 or argon-40? Neither, it is even 32. What are the percentages of the two elements after three half-lives of potassium-40? 25% Potassium-40 and 75% Argon-40 33. Does a geologist have to wait 1.3 billion years before seeing a difference in the amounts of these two elements? Explain. No, the object decays at a constant rate. LT 8. Describe the characteristics of the Earth's interior. 34. Describe the crust. - outermost layer of the Earth 35. Describe the mantle. – a liquid hot material between the crust and the outer core 36. Describe the inner core. – a dense ball of solid metal 37. Explain how heat is transferred. – a layer of molten metal that surrounds the inner core. LT 9. Identify what causes convection currents. 38. What causes convection currents in the Earth? - The heating and cooling of a fluid, Changes in a fluid’s density, and The force of gravity 39. How does the material in the mantel move? – Hot columns of mantle material rise slowly through the asthenosphere. At the top of the asthenosphere, the hot material spreads out and pushes the cooler material out of the way. The cooler material sinks back towards the core and the cycle continues. LT 10. Recall the causes of earthquakes and volcanoes and how they change the surface of the Earth in a short period of time. 40. What causes “hot spot” volcanoes to form? – Magma from deep within the mantle rises and melts through the crust. 41. Where do most volcanoes occur on Earth surface? – Volcanoes occur mostly on convergent boundaries 42. What are geysers? – Hot water and steam become trapped underground causing a fountain of water and steam to erupt from the ground. 43. What is the force that causes magma to erupt at the surface of the Earth? – Dissolved gases under pressure LT 11. Recall how Earth's plates move and change the surface of the Earth over long periods of time. 44. What happens when two plates collide with each other? – A convergent boundary happens 45. What theory do geologists believe is the driving force behind plate tectonics? – Heat from the Earth’s core result in the convection currents which moves the Earth’s plates.