* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download saving and investing slide show
Investment management wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative easing wikipedia , lookup
Interbank lending market wikipedia , lookup
Money market fund wikipedia , lookup
Private money investing wikipedia , lookup
Securities fraud wikipedia , lookup
Hedge (finance) wikipedia , lookup
Investment fund wikipedia , lookup
Stock exchange wikipedia , lookup
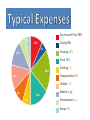
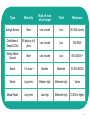
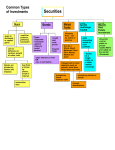
INVESTMENTS The greater the risk – the greater the return Stocks Bonds Savings Accounts Collectibles Mutual Funds Futures Real Estate PYF? • PLAN YOUR FUTURE (pay yourself first) • What are our goals? – Short and long term – WHERE DO YOU SEE YOURSELF 5 YEARS FROM TODAY? – WHERE DO YOU SEE YOURSELF 10 YEARS FROM TODAY? • • • • • Needs vs. Wants? Investigate your options – risk vs. reward Time is on your side … start today! Prepare a budget Stick with the plan and you will succeed! Pay Yourself First 10% 5% 5% 10% Charity 5% 5% Housing 20% 12% Food 15% 20% Clothing 7% Transportation 9% 12% Utilities 12% 9% 15% 7% Medical Entertainment Extras 3 Saving involves an opportunity cost. If you choose to spend $20 on a movie and popcorn, you won’t be able to put $20 in your college fund. On the other hand, if you save $20, you give up a night with your friends. Having a savings goal means making choices. 4 A Great Saving Formula The larger the money pile + the higher the interest rate + the more time you have to save = more in savings! Increase the amount, interest, or time and you may earn even more. 5 Every investment has risks and rewards, which a smart investor must evaluate and weigh. 6 SAVINGS AND INVESTMENTS Security vs. Risk 3 VARIABLES TO CONSIDER • Amount • save the most possible each month • Interest Rate • higher rate = higher growth • Time • longer your money is invested = faster it will grow • start with first paycheck BANK ACCOUNTS Bank or Credit Union SAVINGS ACCOUNT (pro: use money anytime con: low interest rate) • Save money in an account • Lowest interest rate offered (lucky to get 1% per year) • Less risk – will not lose insured by FDIC (Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation) up to $250,000.00 per account • Withdraw funds at anytime CERTIFICATE OF DEPOSIT (pro: greater return con: cannot touch money) • Savings account requires minimum balance and commitment to not use money for a period of time (months, years, • Fixed interest rate and time frame (lucky to get 3% for 5 years) • Cannot use money when need/want, without penalty SAVINGS CHART Save Each Week Interest (annual) Savings in 10 Years $ 7 5% $4,731 $14 5% $9,463 Interest Savings in 10 Years Savings in 20 Years $19.20 5% $12,977 $34,337 $19.20 6% $13,705 $38,632 $19.20 7% $14,484 $43,599 $19.20 8% $15,320 $49,353 $19.20 9% $16,218 $56,029 Note: Savings calculation totals are approximate. 9 COMPOUND INTEREST • Earning interest on the interest Simple interest $100 x 6% interest = $6.00 = $106.00 Compound Interest $106 x 6% interest = $6.36 = $112.36 TIME: The shorter the window of time, the smaller the return Short-Term Options • • • Savings account Certificates of deposit Money market account Long-Term Options • • • • Bonds Stocks Mutual funds 401(k) retirement account 11 HOW LONG WILL IT TAKE TO GROW MY MONEY? • RULE OF 72 Use this calculation to figure out the rate or the number of years needed to double your money – Divide Interest Rate by 72 • 72/6 = 12 years to double your money at that rate – Divide Number of Years by 72 • 72/12 = 6 percent to double your money at that rate Type Maturity Risk of loss of principal Yield Minimum Savings Account None Low: insured Low $0/–$25 (varies) Certificates of Deposit (CDs) 90 days up to 5 years Low: insured Low $50–$500 Money Market Account None Low: insured Low $50–$2,500 + Bonds 1–5 years + Medium Moderate $1,000–$5,000 Stocks Long term Medium–high Moderate–high Varies Mutual Funds Long term Low–high Moderate–high $1,000 or higher 13 Stock/Shares of Stock • • • • • • • • • • • • Represent ownership in company/corporation = shareholder Publicly traded on NYSE or NASDAQ Price changes several times daily (value) Long term investment (20 years) High risk, not insured – could lose investment Buy low, sell high … Must sell ownership to see profit (profit = income= taxes) Sometimes Dividends are paid based on profit of company (Earnings to shareholder – pay tax) Paid on a per share basis (example $1.00 per share) An Annual Report is published each year The SEC (Securities and Exchange Commission) oversees/regulates the sale of stock If you see the stock price fall …. What would you do? (sell or buy) DOW JONES INDUSTRIAL AVERAGE • Index of 30 major US companies • Represent variety of industries in the US • Used to measure how all stocks are performing • See next slide for actual companies chosen for the Down Jones Industrial Average for last year DOW JONES INDUSTRIAL AVERAGE – Sept. 2013 BONDS • Represent an IOU from company or government • For your purchase today, a promise is made of a greater amount to be paid to you in the future (future date varies – 5, 10, 20 years) • Does not represent ownership • Not insured but less likely to lose your investment than with stocks STOCK: COMMON & PREFERRED Common Stock • Ownership share in a corporation. Each share of common stock permits 1 vote to elect members of the Board of Directors of the corporation. Fluctuating dividend paid after Preferred stockholders are paid. Last in line to collect on assets if the corporation goes bankrupt. Preferred Stock • An ownership share in a corporation with a fixed dividend that is paid before any dividends are paid to common stockholders. No voting rights. Blue Chip vs. Penny Stocks Blue Chip Stocks (a/k/a Glamour Stocks) • High quality, high priced stock • Large, strong, financially-stable • Industry-leader with dominant product/service • Long record of steady earnings • IBM, CAT, MMM, JNJ, DIS, GM Penny Stocks • Less than $5 a share • Highly volatile, very risky • New companies • High possible gains, very short time Buying on Margin & Selling Short • Buying on Margin (borrowing money) Buying stock by paying only a percentage of the purchase price (typically 50%) and borrowing the balance from a broker. • Selling Short (borrowing stock) A stock transaction that allows an investor to make money on a stock expected to fall in value. This transaction involves immediate sale of shares not owned by the seller, who expects to buy them back later at a lower price. Bull vs. Bear Market Bull Market (optimistic) • Economy is great – People are working and spending money – Stock prices are going up (can cause overvaluation) Bear Market (pessimistic) • Economy is bad – Recession is looming (people are not working and not spending money) – Stock prices are falling • Good time for short selling MUTUAL FUND (most popular) • Professionally managed by a Fund Manager • People invest in the fund based on it’s purpose – growth or income • The fund consists of a variety of stocks, bonds, real estate, precious metals, etc. • A prospectus – published report explaining fund goal and types of securities purchased to make up the fund. • Represents partial ownership in fund’s collective holdings. Dividends paid can be re-directed into the company or cashed for personal projects. – Everyone in the fund shares the wealth or lose together (more shares = more profit/loss) COLLECTIBLES • Baseball cards, antiques, stamps, coins, jewelry, figurines, toys • “One man’s garbage is another man’s treasure” • Anything that appreciates in value over time • Must be a buyer in order to sell REAL ESTATE • Flipping (short term) – Buying a house, fixing it up, and selling for more than you paid – Some real estate properties will always appreciate in value – LOCATION, LOCATION, LOCATION – Some real estate properties are a real gamble – no guarantee you can sell at a profit – Must pay property taxes to town and monthly mortgage (type of loan) to bank/credit union issuing the mortgage FUTURES • Commodities Exchange (similar to NYSE) • Obligation to buy/sell a specific commodity on specific date and amount – Corn – Wheat – oil – gold – bonds PORTFOLIO • a/k/a your collection of investments • Include a mixture of types of investments • DIVERSITY – balance risks with rewards – Purchase stocks and mutual funds with bonds and savings accounts (Jim Cramer video clip: Diversify) • REMEMBER the greater the risk the better the return (or percentage earned) – Why?