* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download I can describe an atom and its components I can relate energy levels
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
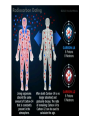
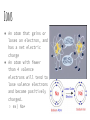
Matter, part 2 ● I can describe an atom and its components ● I can relate energy levels of atoms to the chemical properties of elements ● I can define the concept of isotopes Isotopes ● Atoms of the same element that have different mass numbers ○ All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons ○ The number of neutrons can vary ○ ex)Chlorine atoms have 17 protons but can have 18 or 20 neutrons. ■ There are chlorine atoms with mass #s of 35 and 37. (17+18=35, 17+20=37) Isotopes ● Atomic mass- the average of the mass numbers of the isotopes of an element. ○ Most elements are mixtures of isotopes ○ ex) Atomic mass of chlorine is 35.453, the average of the mass numbers of naturally occurring isotopes of chlorine-35 and chlorine-37 Radioactive Isotopes ● Some isotopes are unstable and tend to break down ○ The isotope emits energy in the form of radiation ● The spontaneous process through which unstable nuclei emit radiation is called radioactive decay. Radioactive Isotopes ● In radioactive decay, a nucleus can... ○ lose protons and neutrons ○ change a proton to a neutron ○ change a neutron to a proton ● Because the # of protons identifies an element, decay changes the identity of the element Electron Energy Levels ● The exact position of an electron cannot be determined ○ Electrons occupy areas called energy levels ● The volume of an atom is mostly empty space ● The size of an atom depends on the number and arrangement of its electrons Electron Energy Levels ● The first energy level can hold 2 electrons ● The second energy level can hold 8 electrons ● The third energy level can hold 18 electrons ● The fourth energy level can hold 32 electrons. Valence Electrons ● Electrons in the outermost energy level ○ Determine the chemical behavior of the different elements ● Elements with the same number of valence electrons have similar properties. ○ ex) A sodium ion (atomic # 11) and a potassium ion (atomic # 19) each have one valence electron. ○ Both are highly reactive metals, and easily combine with other elements Valence Electrons Ions ● An atom that gains or loses an electron, and has a net electric charge ● An atom with fewer than 4 valence electrons will tend to lose valence electrons and become positively charged. ○ ex) Na+ Ions ● An atom with more than 4 valence electrons tends to gain electrons and form a negatively charged ion. ○ ex) Cl- Abundance of Elements ● The 2 most abundant elements in the universe are hydrogen and helium ● All other elements account for less than 1% of all atoms in the universe. ● 98.5% of Earth’s crust is made of only 8 elements.