* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ecosystems - Kylies
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
River ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
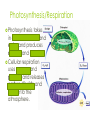
Ecosystems Cloze Ecosystems Abiotic factors are non-living. Biotic factors are living. Sunlight is the primary source of energy in ecosystems. 10% of energy is transferred up through trophic levels. The rest of the energy is used up in maintaining the organism and heat. Herbivores are primary consumers. Ecosystems Consumers on the next level up are called secondary consumers and are omnivores and small carnivores. Tertiary consumers are medium or large carnivores. Quaternary consumers are large carnivores. Larger species populations are found at lower trophic levels. This is as result of the small level of energy that is transferred up from each level. Species Interactions Predation has a predator and its prey. One species benefits and one species is harmed. Competition is where species compete for available resources including food and shelter. Mutualism is an interaction where both species benefit. Parasitism is where one species benefits and the other is harmed but not killed. Commensalism is when one species benefits and the other species is neither harmed nor benefits. Photosynthesis/Respiration Photosynthesis takes in carbon dioxide and water and produces oxygen and glucose. Cellular respiration uses oxygen and glucose and releases carbon dioxide and water into the atmosphere.