* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Energy Flow in an Ecosystem
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
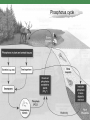
Unit 8: Ecology ECOLOGY BIODIVERSITY Climate zones determine communities Figure 5-2 Terrestrial biomes Figure 5-9 Nonliving and Living Components of Ecosystems Populations & Communities Ecological niche An organism’s role in its community Includes what it needs to survive – – – – – Nutrients Light Space (habitat) Oxygen or carbon dioxide Inorganic compounds How it interacts with other species Species interactions When two organisms interact together in one of several ways. Can be intraspecific or interspecific One interaction is competition What is the graph telling us about the effect of competition on species A and B? Predation is another (interspecific) interaction Predators adaptations Locate, sneak up on & subdue prey Prey adaptations elude & defend horns, speed, coloration spines, thorns, toxins More Interspecific interactions Symbiotic interactions parasitism (-/+) mutualism (+/+) lichens (algae & fungus) commensalism (+/0) barnacles attached to whale Symbiosis mutualism commensalism +/+ +/0 +/-/predation +/- parasitism and competition Two Necessities for Survival: Energy Flow and Matter Recycling Producers: Basic Source of All Food Most producers capture sunlight to produce carbohydrates by photosynthesis: This process of turning inorganic materials into organic materials using energy from the sun is called primary production. Respiration: Getting Energy for Survival Organisms break down carbohydrates and other organic compounds in their cells to obtain the energy for internal reactions. This is done through aerobic respiration or anaerobic respiration. Consumers: Eating and Recycling to Survive Consumers get their food by eating or breaking down all or parts of other organisms or their remains. Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores Decomposers and Detritivores Energy Flow Energy flows through an ecosystem Route of energy flow is determined by an ecosystem’s trophic structure. Trophic interactions move energy through an ecosystem Simple example: Food Webs Trophic levels are interconnected within a more complicated food web. Energy Flow in an Ecosystem: Losing Useful Energy in Food Chains and Webs MATTER CYCLING IN ECOSYSTEMS Nutrient Cycles: Global Recycling recycle nutrients through the earth’s air, land, water, and living organisms. nutrients are the elements and compounds that organisms need to live, grow, and reproduce. Carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, oxygen biogeochemical cycles move these substances through air, water, soil, rock and living organisms. Nutrient cycling All organisms are made up of organic molecules Carbohydrates Proteins Lipids Nucleic acids Essential nutrients are those that are required to make the organic molecules C, H, N, O, P, S Organic matter cycles within ecosystems Both autotrophs and decomposers play vital roles Carbon Cycle: The Nitrogen Cycle: Bacteria in Action Phosphorus cycle