* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Natural Selection - Northwest ISD Moodle
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Dual inheritance theory wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Group selection wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
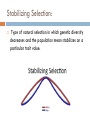
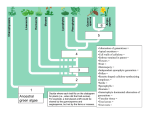
Warm-up questions: • How could genetic mutations be advantageous to a population? Adaptations for survival • Which type of trait is most likely to be expressed by offspring? (dominant or recessive) Dominant NATURAL SELECTION “Survival of the Fittest” Natural Selection: The process in which organisms better adapted to their environment tend to survive and produce more offspring. First fully described by Charles Darwin. Survival of the Fittest: The continued existence of organisms that are best adapted to their environment, with the extinction of those that are not. Term used to describe natural selection. Mutations and Survival If mutations are beneficial to living in the environment, it is more likely to survive and pass on this mutated trait. Genetic diversity helps a population be more varied and the likelihood of survival to be increased. Genetic Trait VS Acquired Trait Genetic trait: a trait that is passed down from parents through genetics. Acquired trait: trait that has been adapted in order to serve a, immediate need. Directional Selection: When natural selection favors one extreme of a trait. Over time, the favored extreme will become more common and the other extreme will be less common or lost. Stabilizing Selection: Type of natural selection in which genetic diversity decreases and the population mean stabilizes on a particular trait value. Disruptive Selection: The make up of this type of population would show phenotypes of both extremes, but have very few individuals in the middle. The rarest of the three types of natural selection. Practice PBA You will now fill out the graphs on your game packet and write a practice PBA. Practice Prompt: Is it more important to have a large amount of genetic diversity within the starting population, or to have many of the same traits throughout? Your PBA must used evidence from your graphs and will be in the “Claim, Evidence, and Reasoning” format.