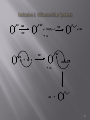* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ethers and Epoxides
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
1,3-Dipolar cycloaddition wikipedia , lookup
Stille reaction wikipedia , lookup
Discodermolide wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
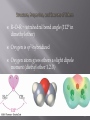
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
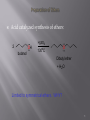
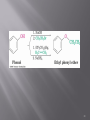
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Elias James Corey wikipedia , lookup
Nucleophilic acyl substitution wikipedia , lookup
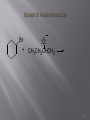
1 An ether has two organic groups (alkyl, aryl, or vinyl) bonded to the same oxygen atom, R–O–R Diethyl ether is used industrially as a solvent Tetrahydrofuran (THF) is a solvent that is a cyclic ether Epoxides contain a C-O-C unit which make-up a three membered ring Thiols (R–S–H) and sulfides (R–S–R) are sulfur (for oxygen) analogs of alcohols and ethers 2 3 Ethers are named two ways: As alkoxy derivatives of alkanes Derived by listing the two alkyl groups in the general structure of ROR’ in alphabetical order as separate words and adding the word ether When both alkyl groups are the same, the prefix di- precedes the name of the alkyl group (Ethers can be described as symmetrical or unsymmetrical) 4 CH3CH2 O CH2CH3 Diethyl ether Ethoxyethane CH3CH2 O CH3 Ethyl methyl ether Methoxyethane CH3CH2 O CH2CH2CH2Cl 3-Chloropropyl ethyl ether 1-Chloro-3-ethoxypropane 5 Epoxides (oxiranes) “epoxy” always preceeds the name of the alkane O O 1,2-Epoxycyclohexane 2-Methyl-2,3-epoxybutane 6 OCH3 1 O 6 O 2 O 7 3 O Br 4 O Cl 8 O Br 5 Br OCH3 7 1. Isopropyl methyl ether 2. 4-t-butoxy-1-cyclohexene 3. Phenyl propyl ether 4. O- nitro anisole 8 R–O–R ~ tetrahedral bond angle (112° in dimethyl ether) Oxygen is sp3-hybridized Oxygen atom gives ethers a slight dipole moment (diethyl ether 1.2 D) 9 CH3CH2OCH2CH3 Diethyl ether bp =35oC solubility in water: 7.5 g/100mL CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3 Pentane bp =36oC solubility in water: insoluble CH3CH2CH2CH2OH 1-Butanol bp =117oC solubility in water: 9 g/100mL 10 Acid catalyzed synthesis of ethers: 2 OH butanol H2SO4 O 130oC Dibutyl ether + H2O Limited to symmetrical ethers. WHY? 11 HCl 2 OH O + 130 C H OH H O H3 O+ + Cl- H O H O+ H---Cl H + H3O+ + H O+ - Cl O 12 Williamson ether synthesis •Metal alkoxides react with primary alkyl halides by an SN2 pathway to yield ethers. •Secondary and tertiary substrates react following an E2 mechanism 13 OH O – Na+ NaH O THF + CH3CH2----I + H2 + NaI THF O H O– Na+ THF + Na+ H- CH3CH2----I + H2 O NaI + 14 O CH3CH2O + CH3CH2Br + Br SN2 E2 ? ? 15 How would you prepare the following compounds using a Williamson synthesis? Methyl propyl ether Anisole (methyl phenyl ether) 16 Br O + CH3CH2CHCH3 17 React alkene with an alcohol and mercuric acetate or trifluoroacetate Demercuration with NaBH4 yields an ether Overall Markovnikov addition of alcohol to alkene 18 19 20 Ethers are generally unreactive Strong acid will cleave an ether at elevated temperature HI, HBr produce an alkyl halide from less hindered component by SN2 (tertiary ethers undergo SN1) 21 22 Note that the halide attacks the protonated ether at the less highly substituted site. 23 24 Specific to allyl aryl ethers, ArOCH2CH=CH2 Heating to 200–250°C leads to an o-allylphenol Result is alkylation of the phenol in an ortho position 25 Concerted pericyclic 6-electron, 6-membered ring transition state Mechanism consistent with 14C labeling 26 27 Cyclic ethers behave like acyclic ethers, except if ring is 3-membered Dioxane and tetrahydrofuran are used as solvents 28 Three membered ring ether is called an oxirane (root “ir” from “tri” for 3-membered; prefix “ox” for oxygen; “ane” for saturated) Also called epoxides Ethylene oxide (oxirane; 1,2-epoxyethane) is industrially important as an intermediate Prepared by reaction of ethylene with oxygen at 300 °C and silver oxide catalyst 29 30 Treat an alkene with a peroxyacid 31 peroxyacetic acid H C6H5 H O O + H5C6 H (E)-1,2-diphenylethene O H CH3 C6H5 O H5C6 OH + O H trans-1,2-diphenyloxirane CH3 acetic acid 32 Addition of HO-X to an alkene gives a halohydrin Treatment of a halohydrin with base gives an epoxide Intramolecular Williamson ether synthesis 33 34 Water adds to epoxides with dilute acid at room temperature Product is a 1,2-diol (on adjacent C’s: vicinal) Mechanism: acid protonates oxygen and water adds to opposite side (anti-addition) 35 36 1,2-ethanediol from acid catalyzed hydration of ethylene Widely used as automobile antifreeze (lowers freezing point of water solutions) 37 Anhydrous HF, HBr, HCl, or HI combines with an epoxide Gives trans product 38 39 40 Strain of the three-membered ring is relieved on ring-opening Hydroxide cleaves epoxides at elevated temperatures to give trans 1,2-diols Complete the reaction O CH2 OH- H2O, 100oC Methylenecyclohexane oxide 41 O - CH2 OH O– CH 2OH H O H OH CH 2OH + - OH 100 C 42 43 Adds –CH2CH2OH to the Grignard reagent’s hydrocarbon chain Acyclic and other larger ring ethers do not react 44 Thiols (RSH), are sulfur analogs of alcohols Named with the suffix -thiol SH group is called “mercapto group” 45 1 SH 2 SH Br 3 SH 46 1. Cyclopentanethiol 2. 3-methyl-4-heptanethiol 3. 4-ethyl-4-isopropyl-2-methyl-3-hexanethiol 47 Sulfides (RSR), are sulfur analogs of ethers Named by rules used for ethers, with sulfide in place of ether for simple compounds and alkylthio in place of alkoxy 48 1 2 3 4 S S ethyl phenyl sulfide sec-butyl isopropyl sulfide 49 From alkyl halides by displacement with a sulfur nucleophile such as SH The alkylthiol product can undergo further reaction with the alkyl halide to give a symmetrical sulfide, giving a poorer yield of the thiol 50 Thiolates (RS) are formed by the reaction of a thiol with a base Thiolates react with primary or secondary alkyl halide to give sulfides (RSR’) Thiolates are excellent nucleophiles and react with many electrophiles 51